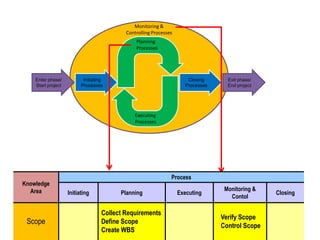
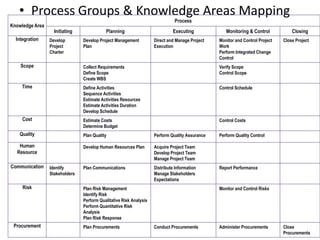
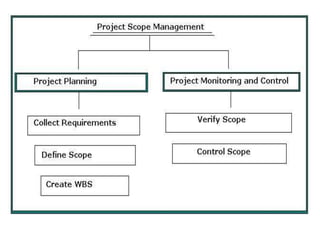
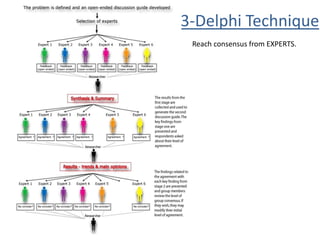
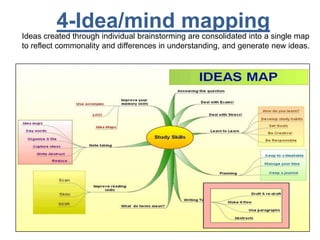
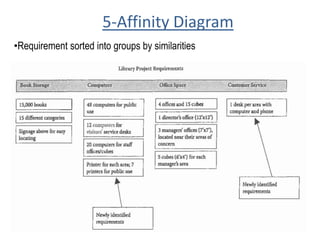
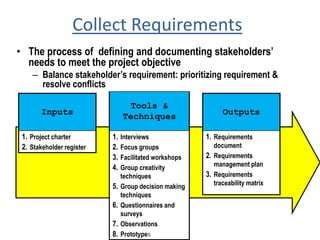
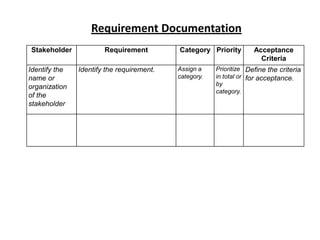
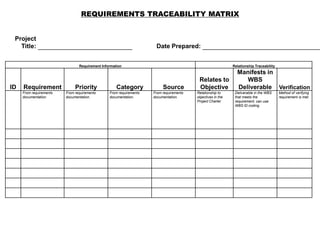
The document discusses project scope management. It provides an overview of the key processes involved, including collecting requirements, defining scope, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS), verifying scope, and controlling scope. It maps these scope processes to the five process groups (initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, closing) and notes that collecting requirements involves defining and documenting stakeholder needs through techniques like interviews, focus groups, workshops, and prototypes. It also discusses defining the product and project scope, as well as developing a requirements management plan to trace requirements throughout the project life cycle.