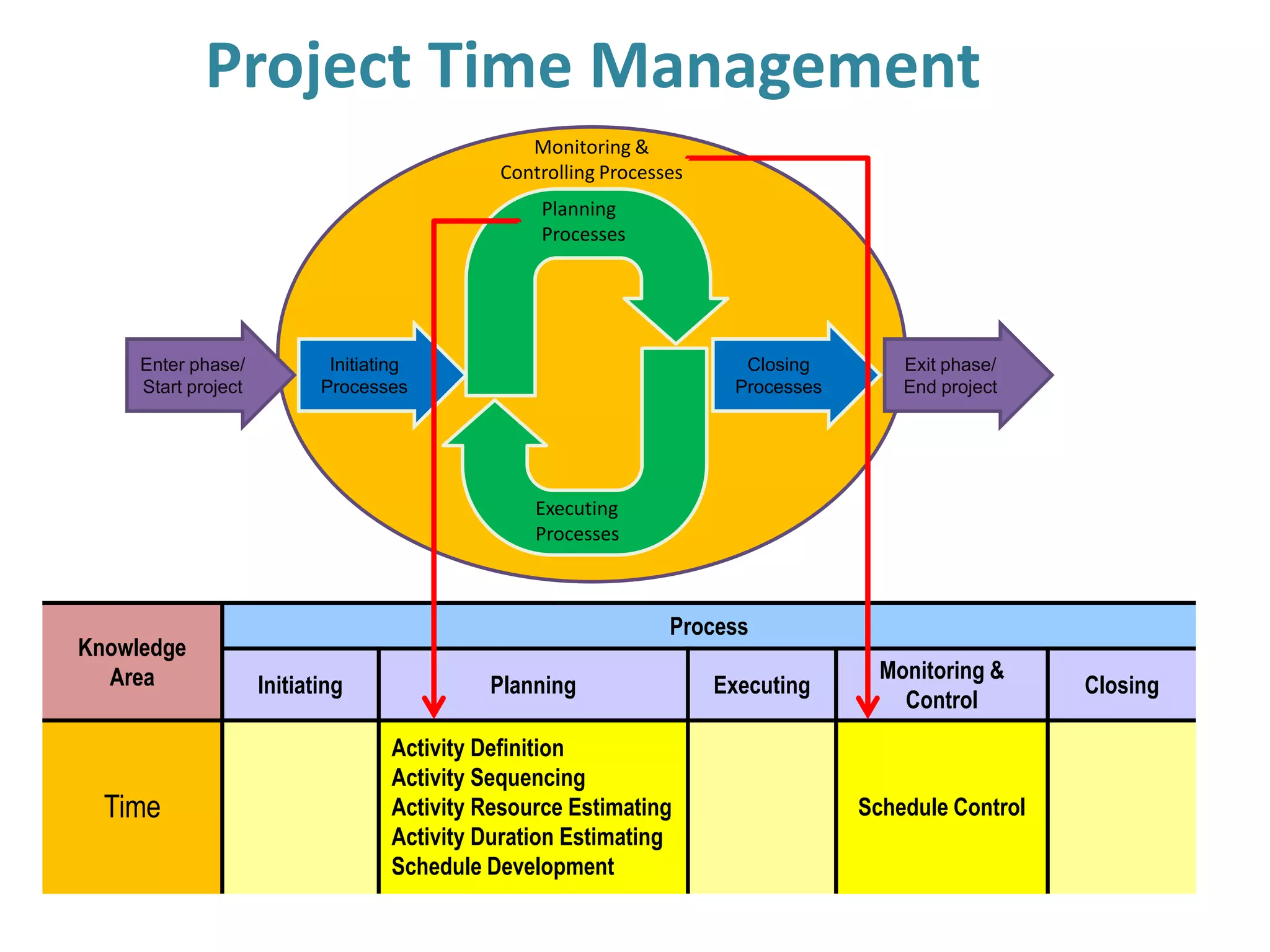
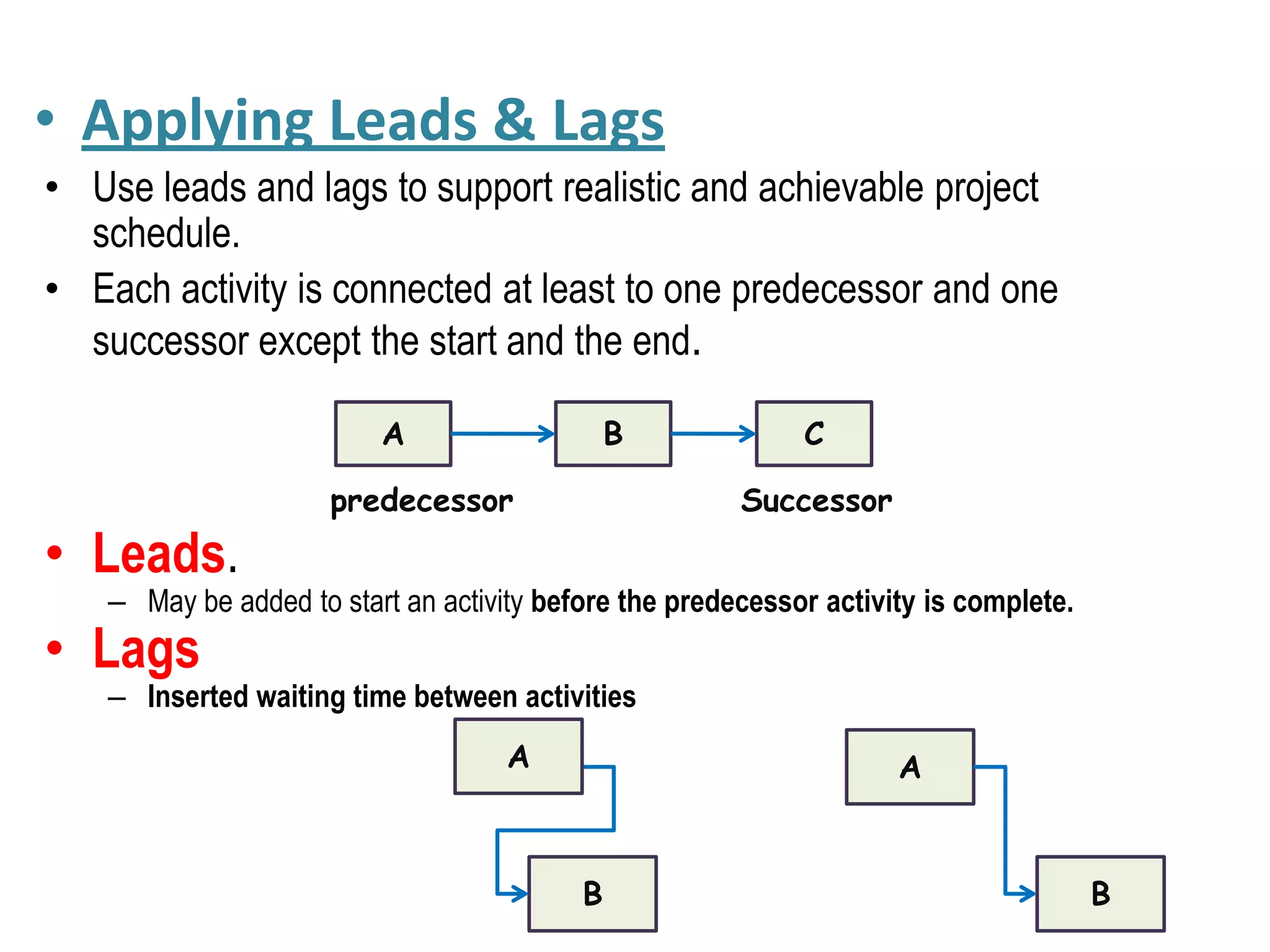
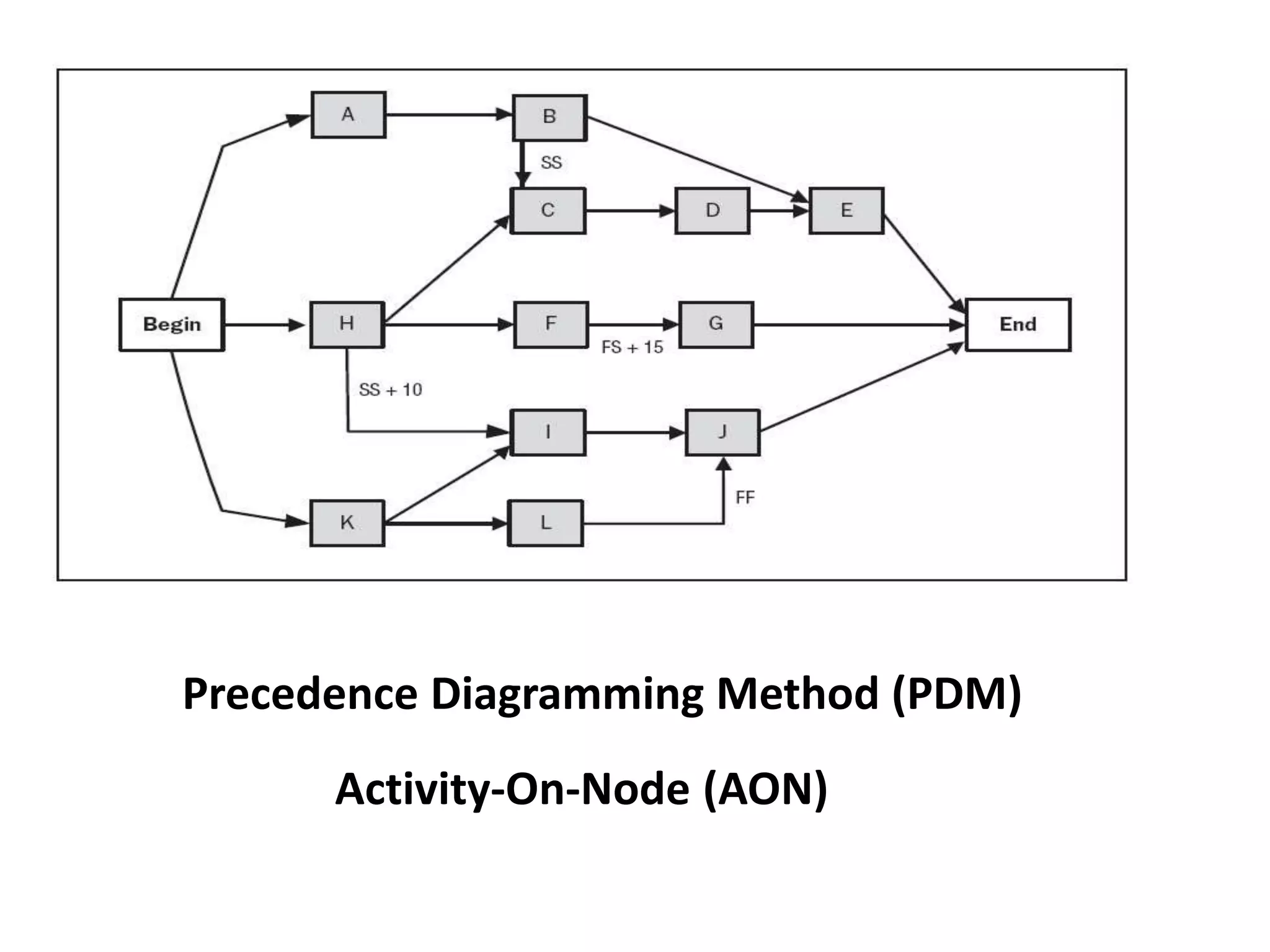
The document discusses project time management processes including:
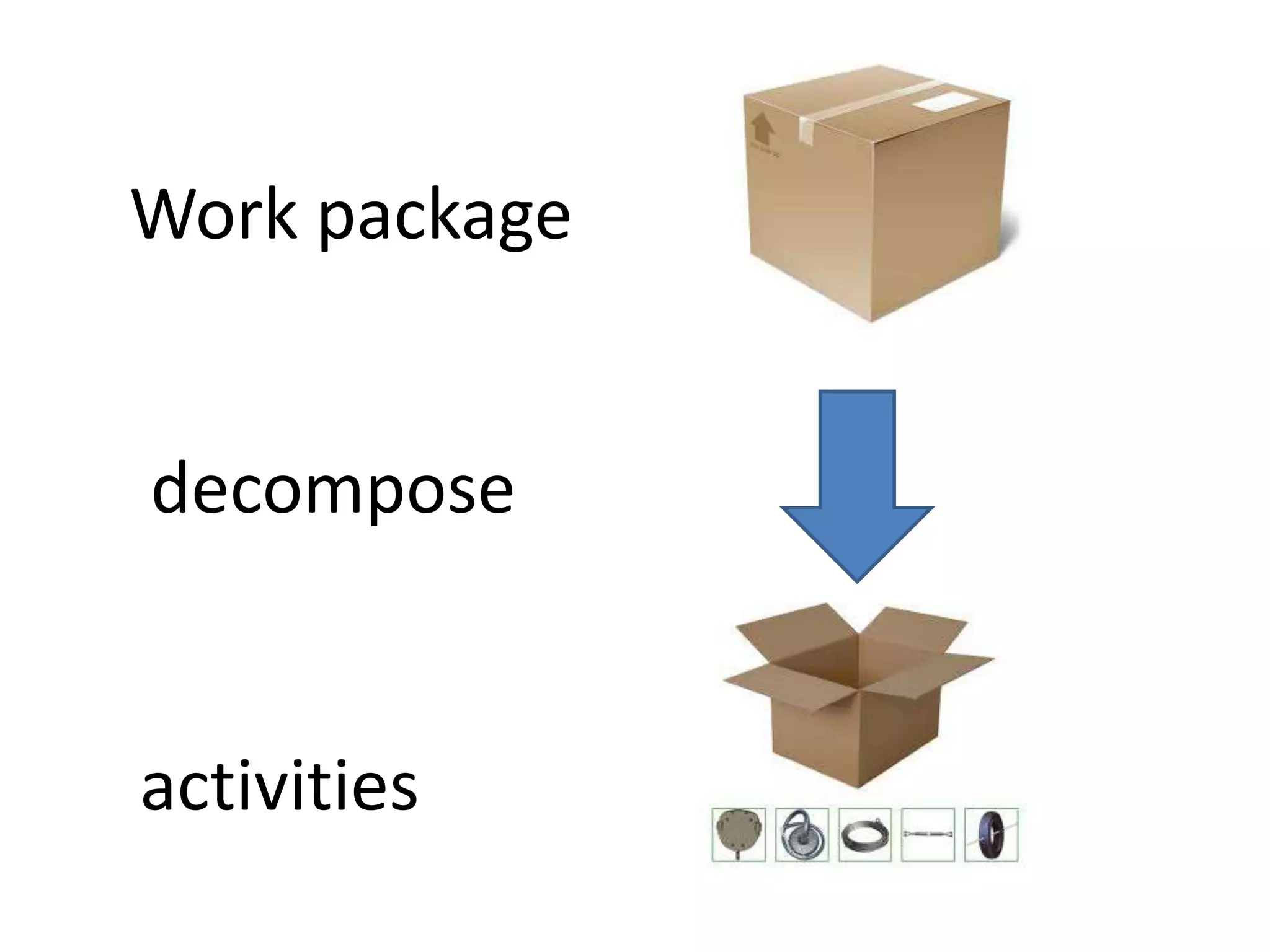
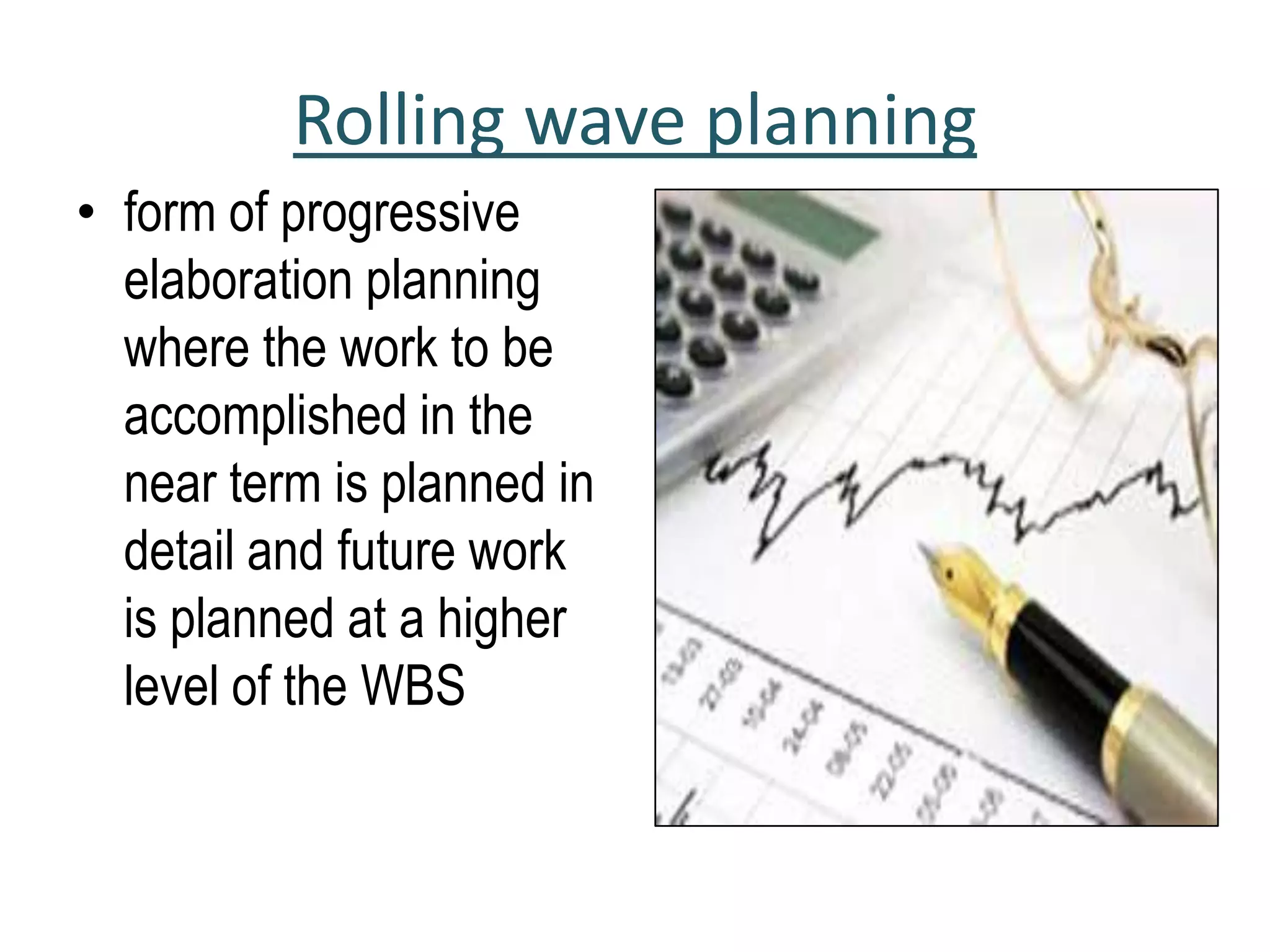
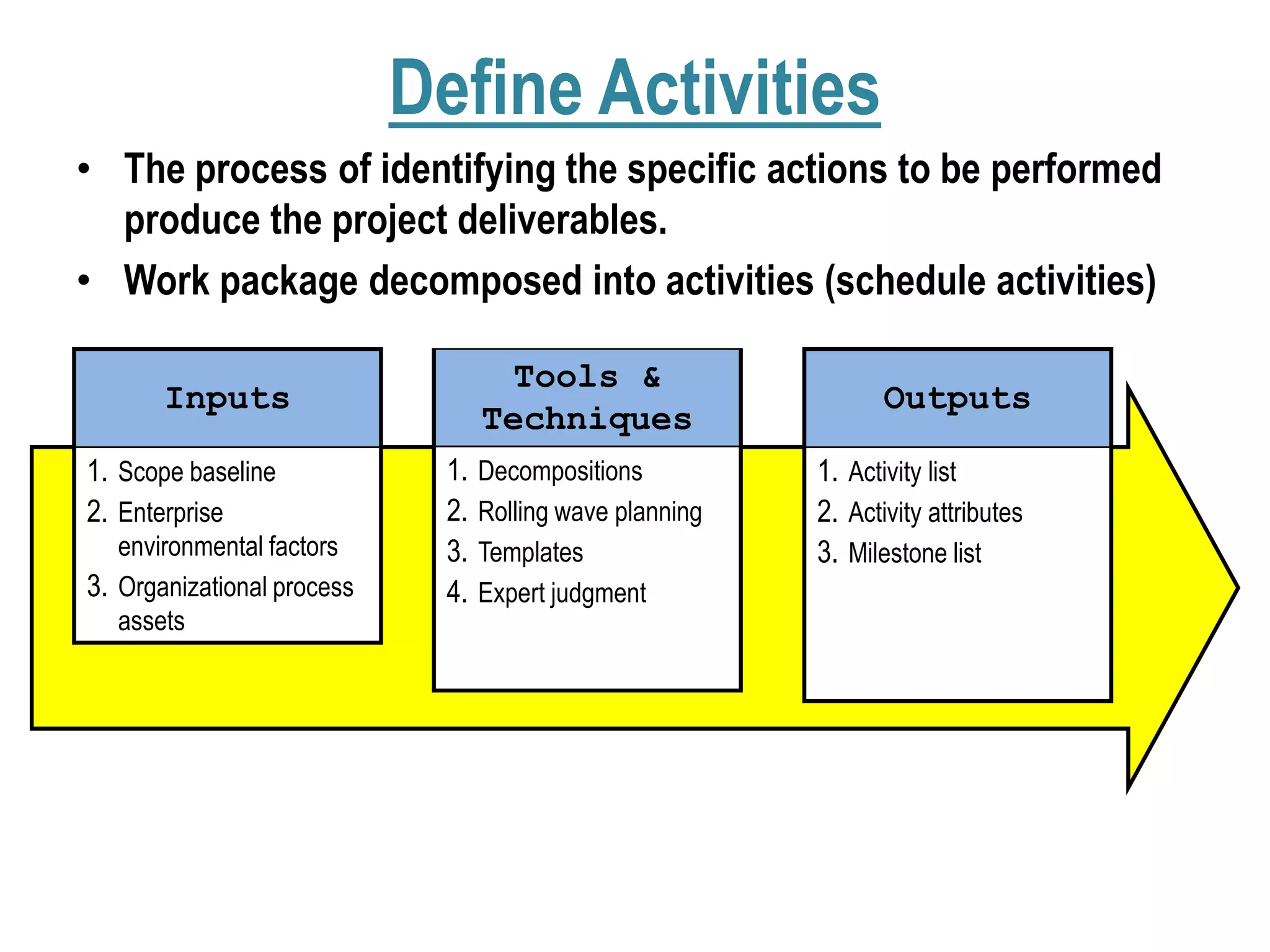
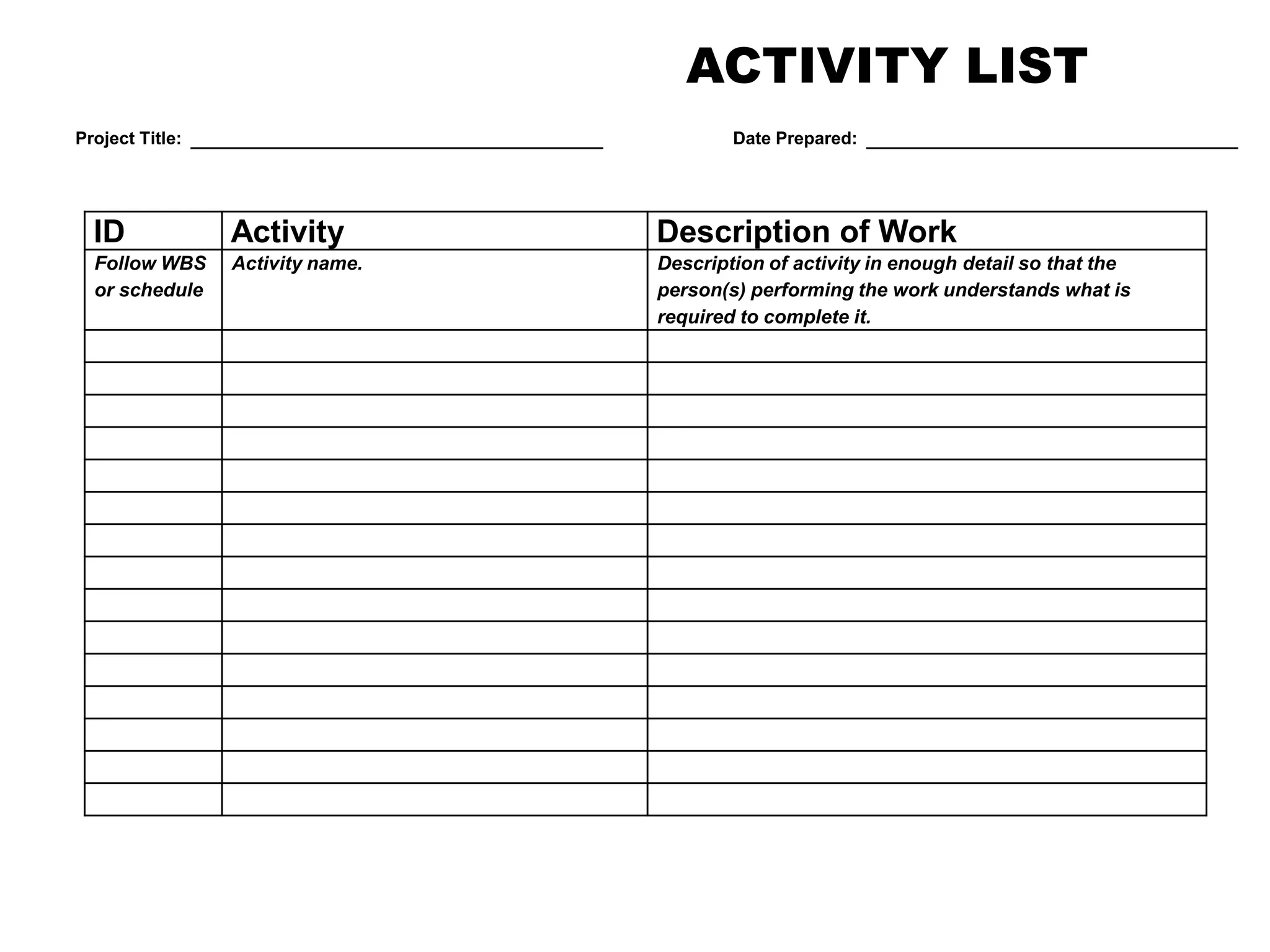
1. Defining activities by decomposing work packages and identifying specific tasks.
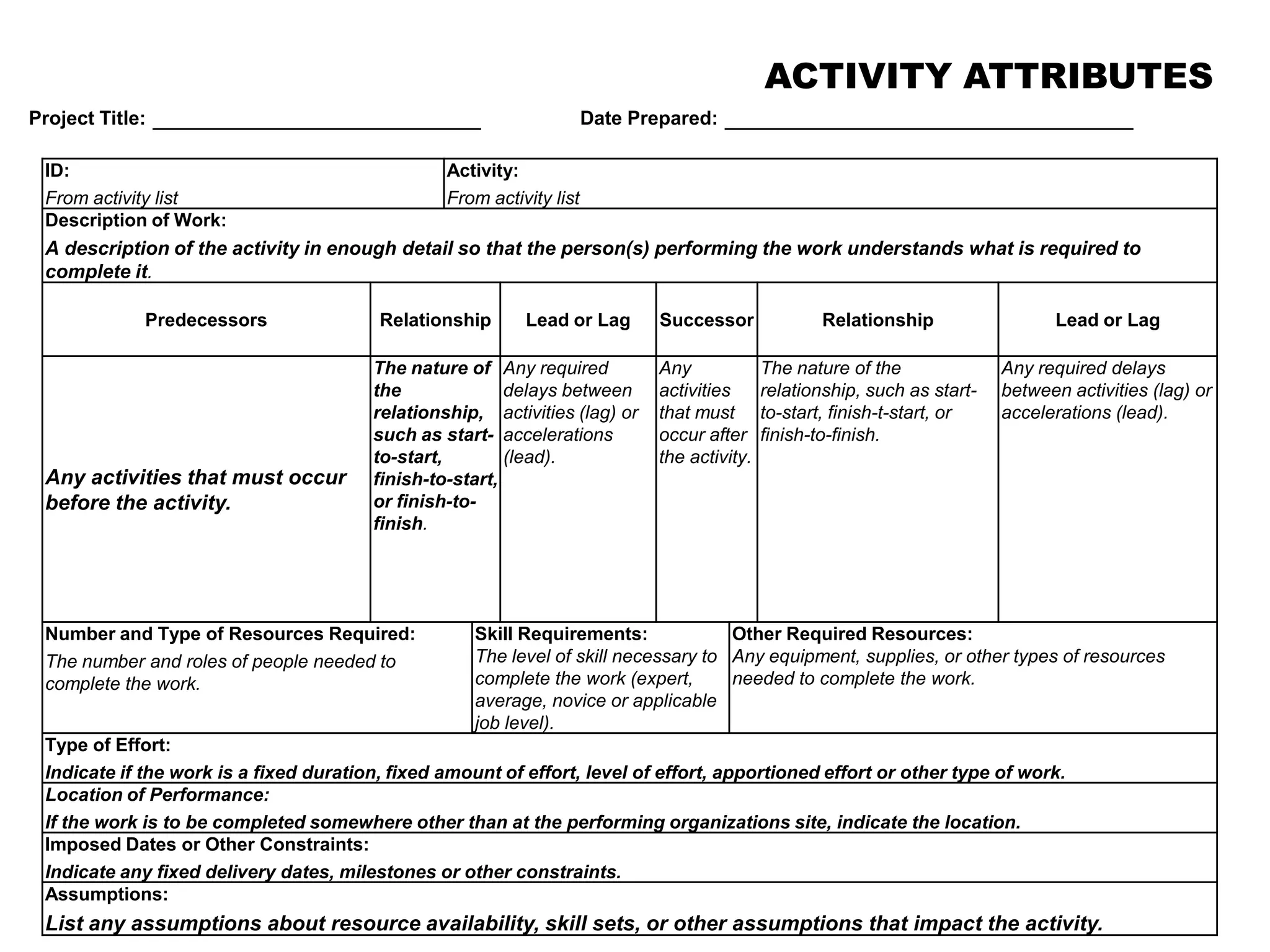
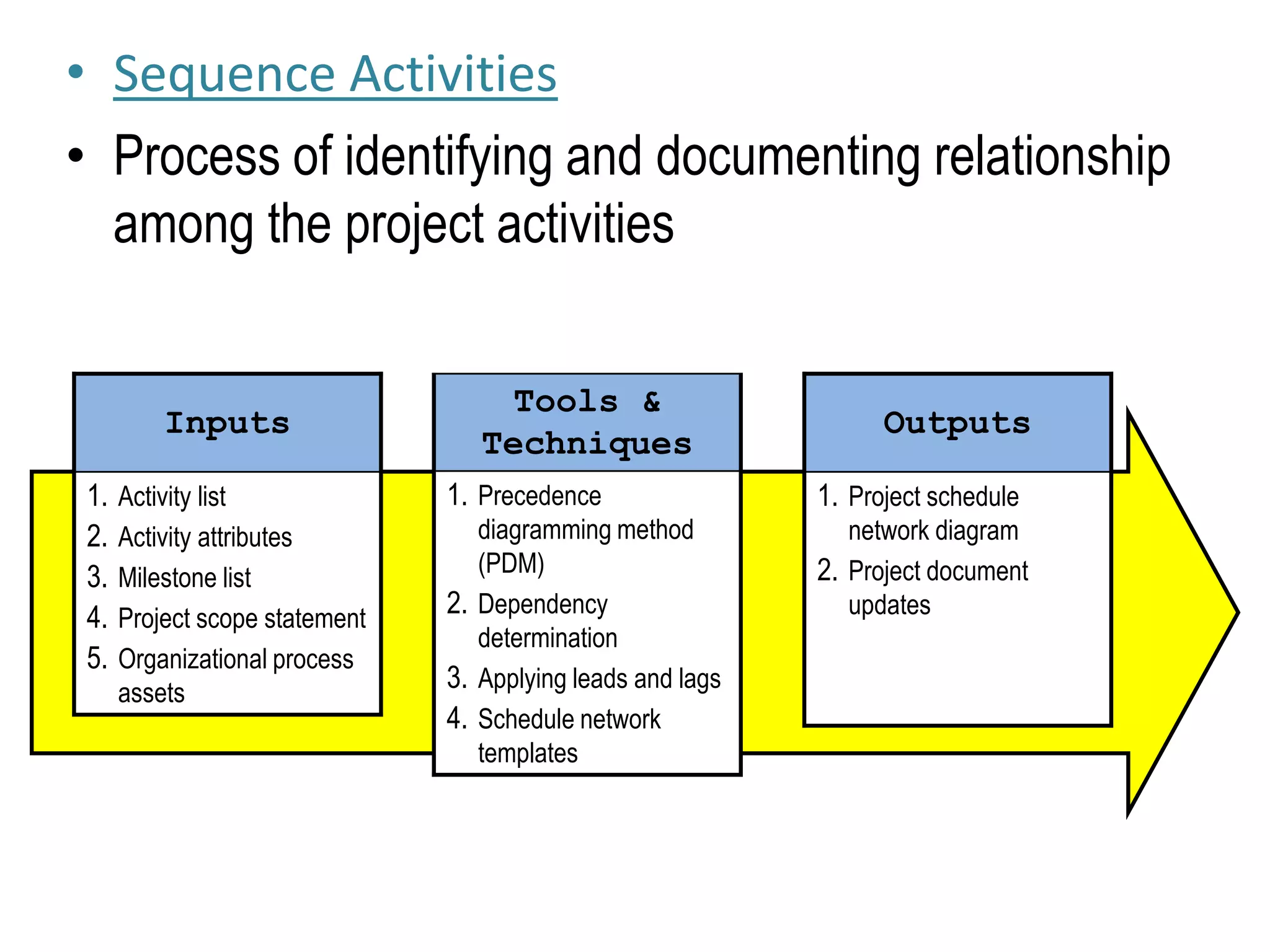
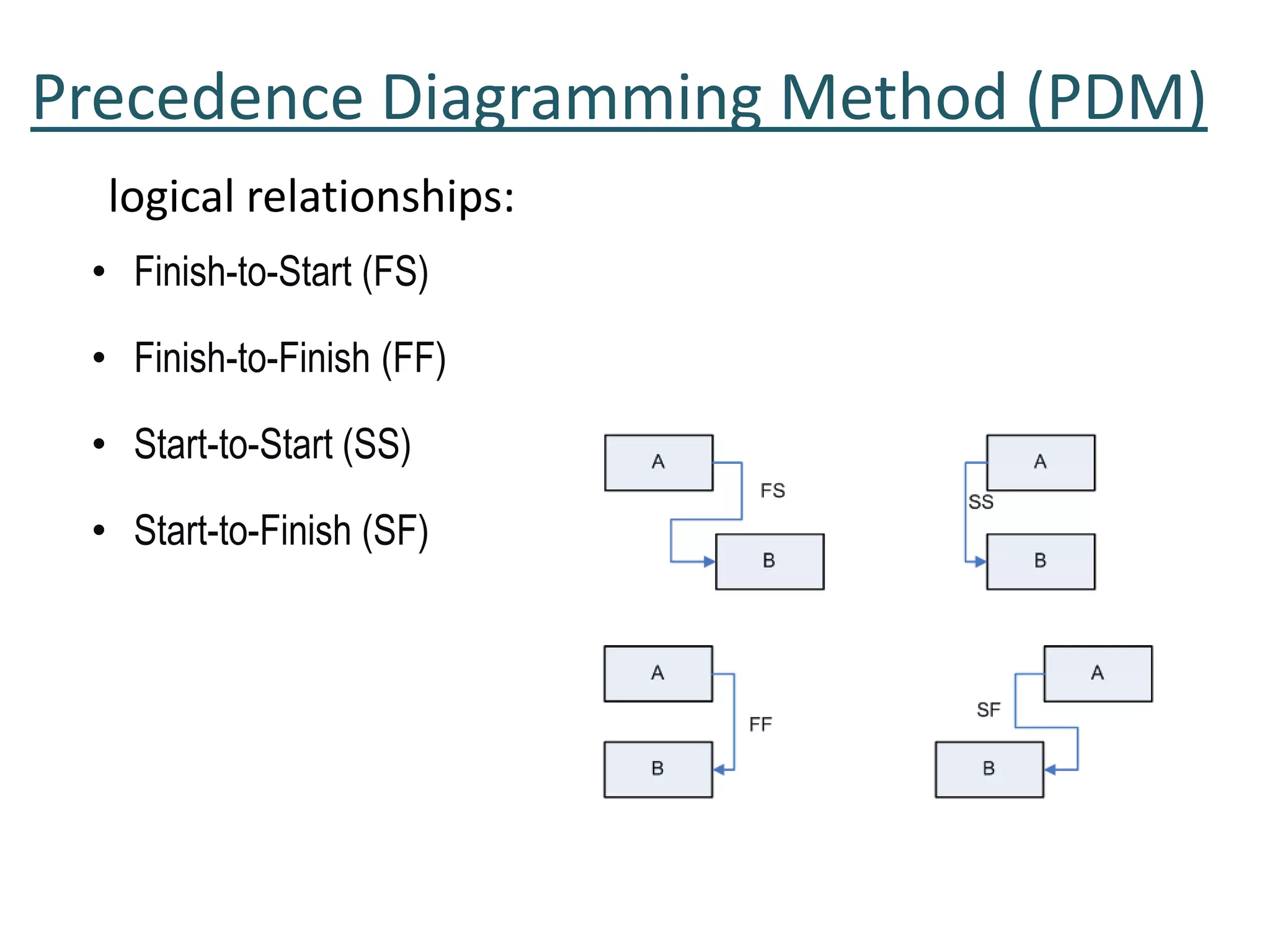
2. Sequencing activities by determining dependencies between tasks using precedence diagramming.
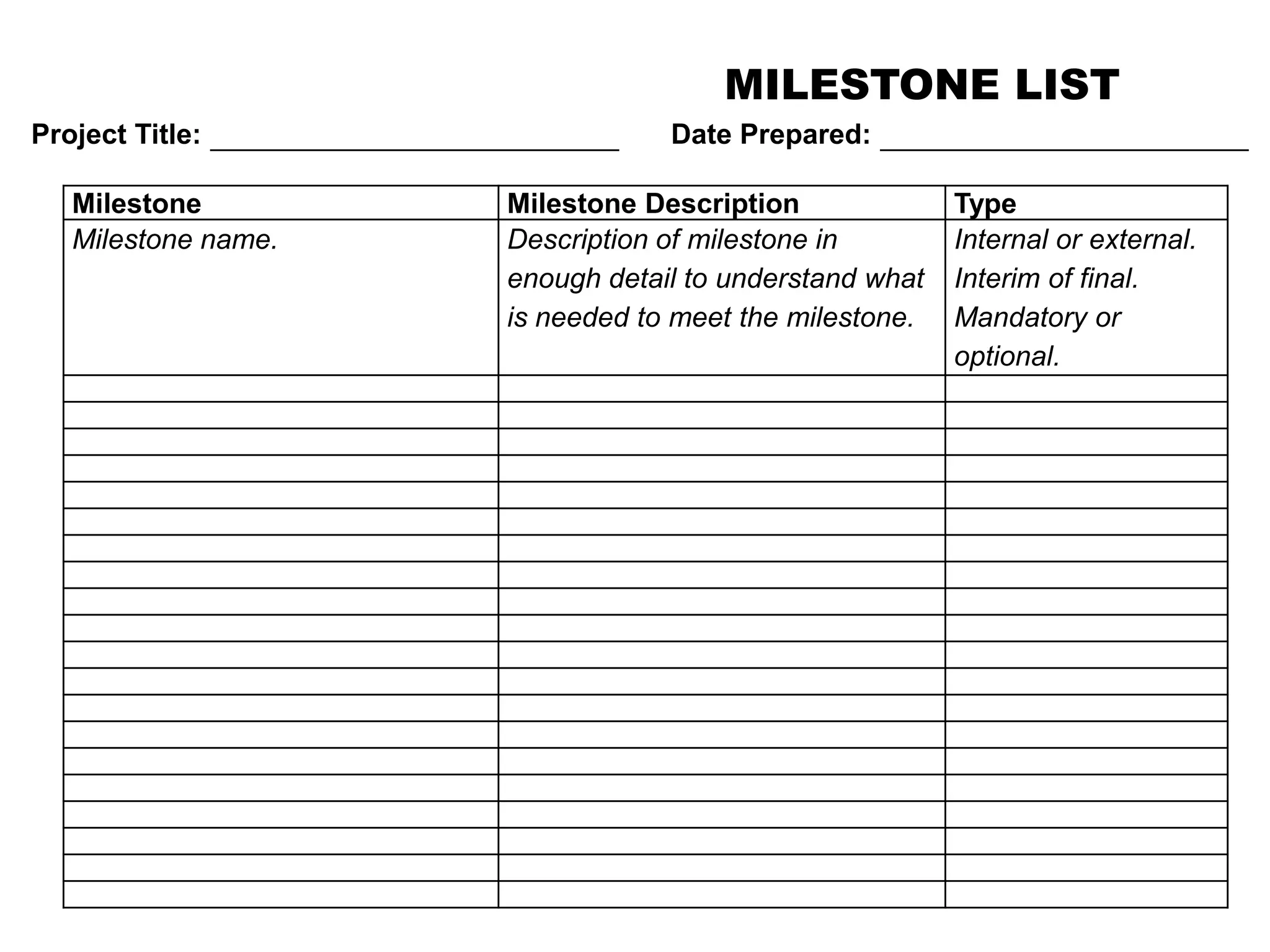
3. Developing schedule attributes like activity lists, relationships, and milestones to build the project schedule network diagram.