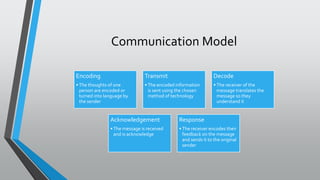
The document outlines the communications management knowledge area in project management, highlighting processes like planning, managing, and monitoring communications to ensure effectiveness at each project stage. It discusses various communication types, methods, and models while emphasizing the importance of stakeholder engagement and the execution of a communications management plan. Additionally, it describes interactive, push, and pull communication methods, as well as the roles of written and oral communication.