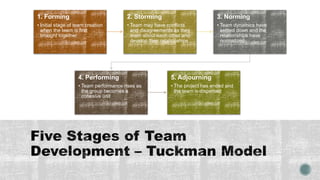
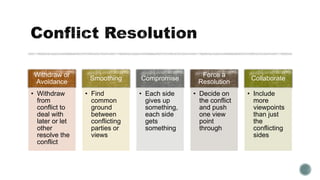
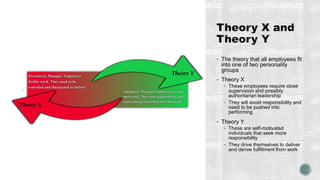
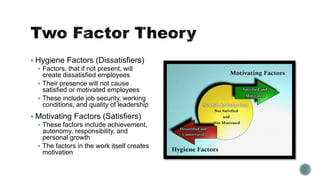
The document outlines the processes involved in project resource management, emphasizing the organization and management of project teams and resources. It details various roles, responsibilities, and the importance of stakeholder involvement, while discussing team dynamics, conflict resolution, and motivational theories. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity of effective planning, monitoring, and controlling resource utilization throughout the project lifecycle.