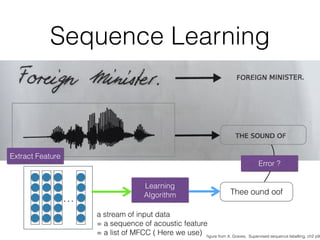
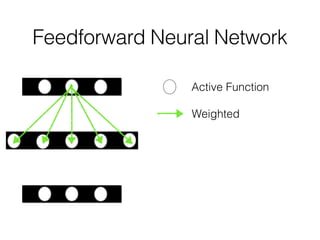
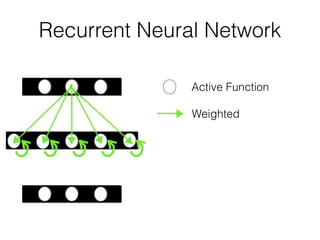
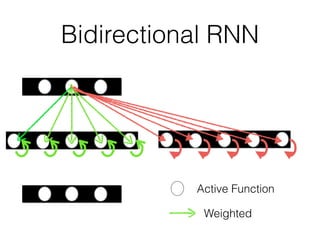
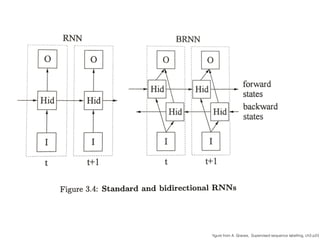
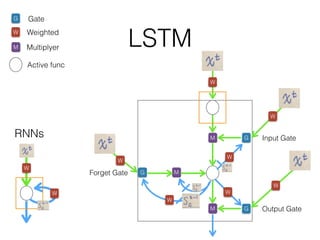
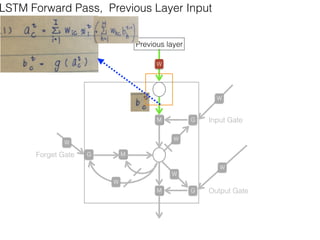
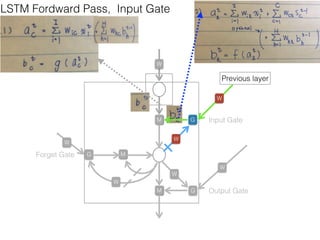
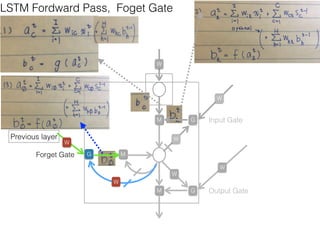
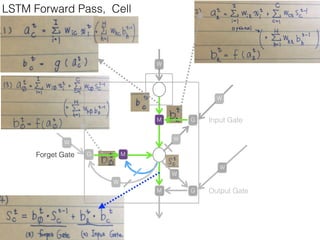
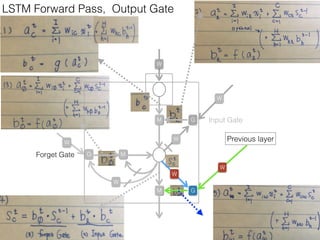
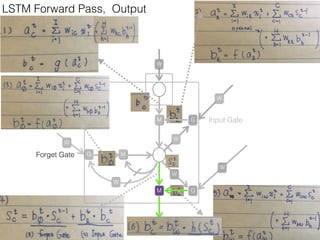
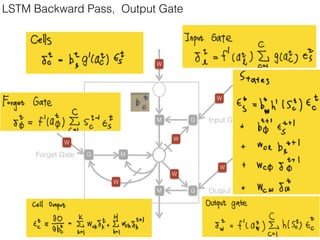
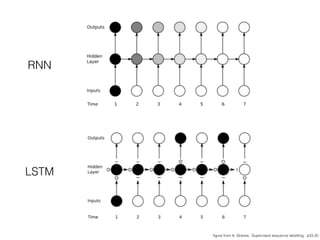
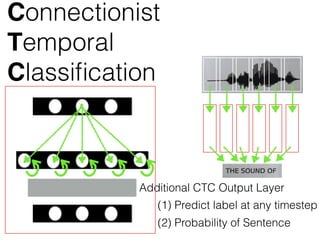
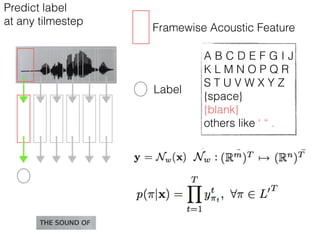
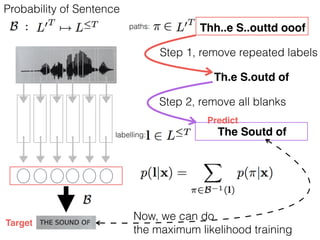
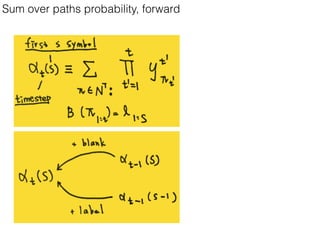
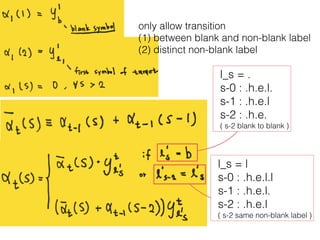
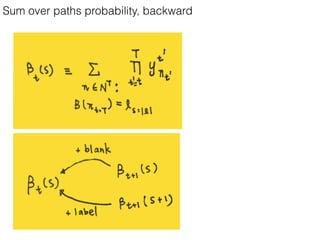
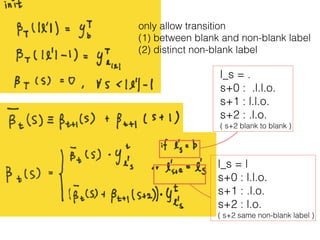
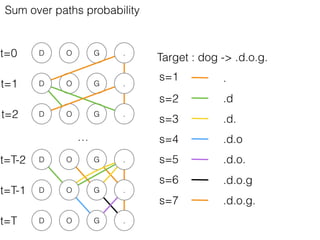
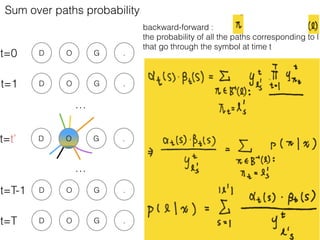
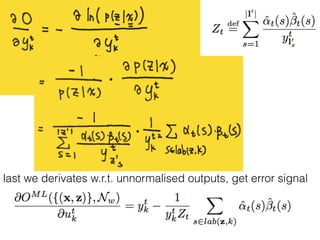
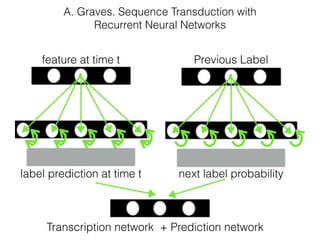
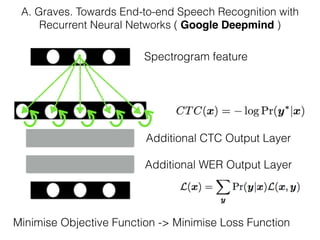
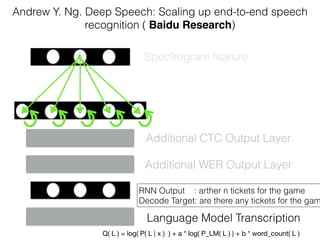
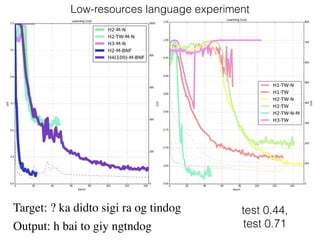
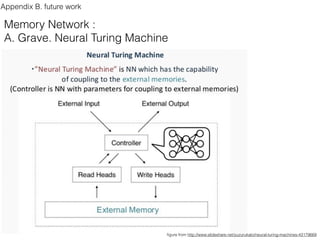
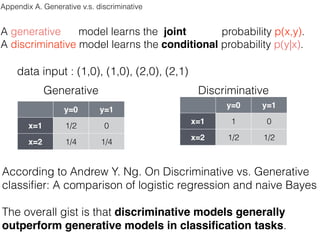
This document discusses sequence learning from acoustic models to end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. It covers feedforward neural networks, recurrent neural networks including LSTM, connectionist temporal classification, and building an end-to-end ASR system. Experimental results on a low-resource language are also presented. Key papers on the topics are referenced.