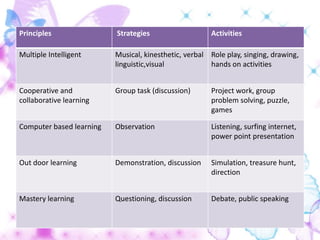
1) The document discusses general principles in teaching language skills, including increasing comprehensibility, interaction, and thinking skills. It provides strategies like using visual aids and a student's native language to increase comprehensibility.
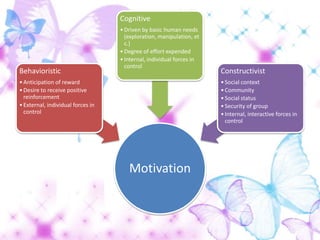
2) Learner attitudes and motivation are also covered, noting the importance of positive attitudes towards the language and intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation comes from within while extrinsic motivation involves external rewards.
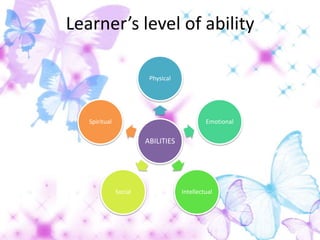
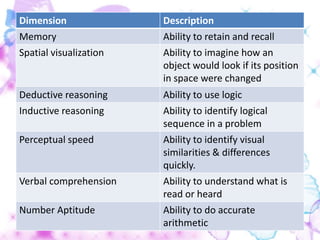
3) The document outlines different types of learner abilities that may impact language learning like physical, emotional, social, and intellectual abilities. Memory, reasoning skills, and comprehension abilities are discussed as examples of intellectual abilities.