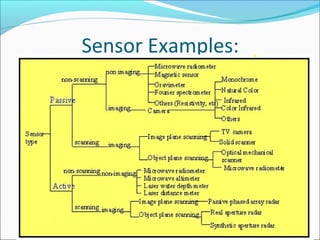
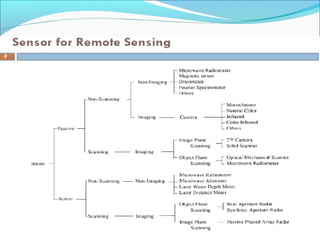
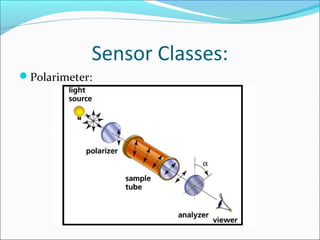
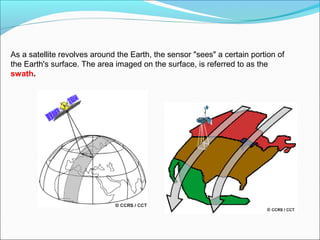
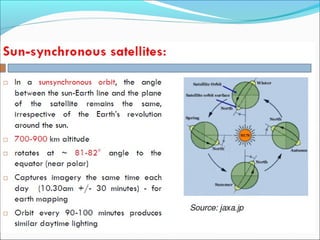
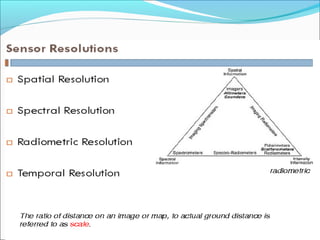
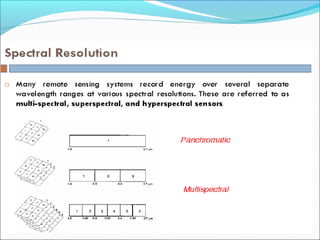
Sensors are devices that measure physical quantities and convert them into signals that can be read by instruments. There are two main types of sensors: active sensors that emit energy and measure reflected radiation, and passive sensors that measure incoming radiation from external sources like the sun. Examples of active sensors include radar and LIDAR, while examples of passive sensors include cameras, spectrometers, and radiometers. Sensors can operate across different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and be used for applications like imaging, scanning, and measuring wind speed and direction.