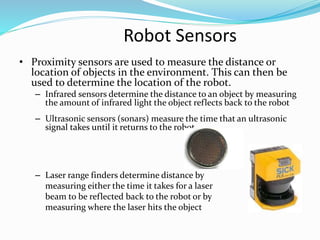
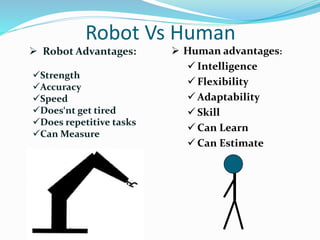
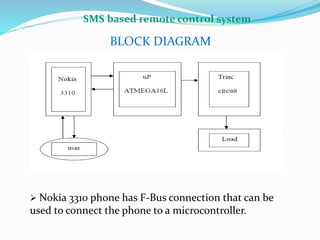
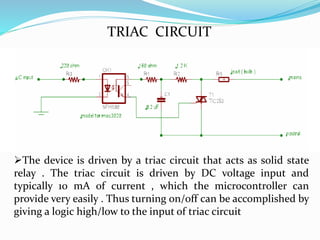
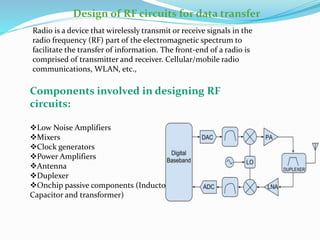
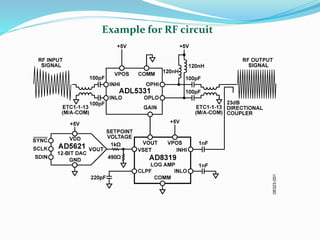
This document discusses a sensor-based motion control system for a mobile car robot. It contains modules for object detection and angle determination using IR sensors, developing SMS protocol communication, and designing RF circuits for wireless data transfer. The document provides background on robot definitions, types of robotics, and how sensor feedback is used for robot control. It describes proximity, infrared, ultrasonic, and computer vision sensors that robots use to perceive their environment. The mobile car robot project uses an IR sensor to detect objects and determine the robot's path, SMS communication for remote control, and an RF circuit for wireless data transmission.