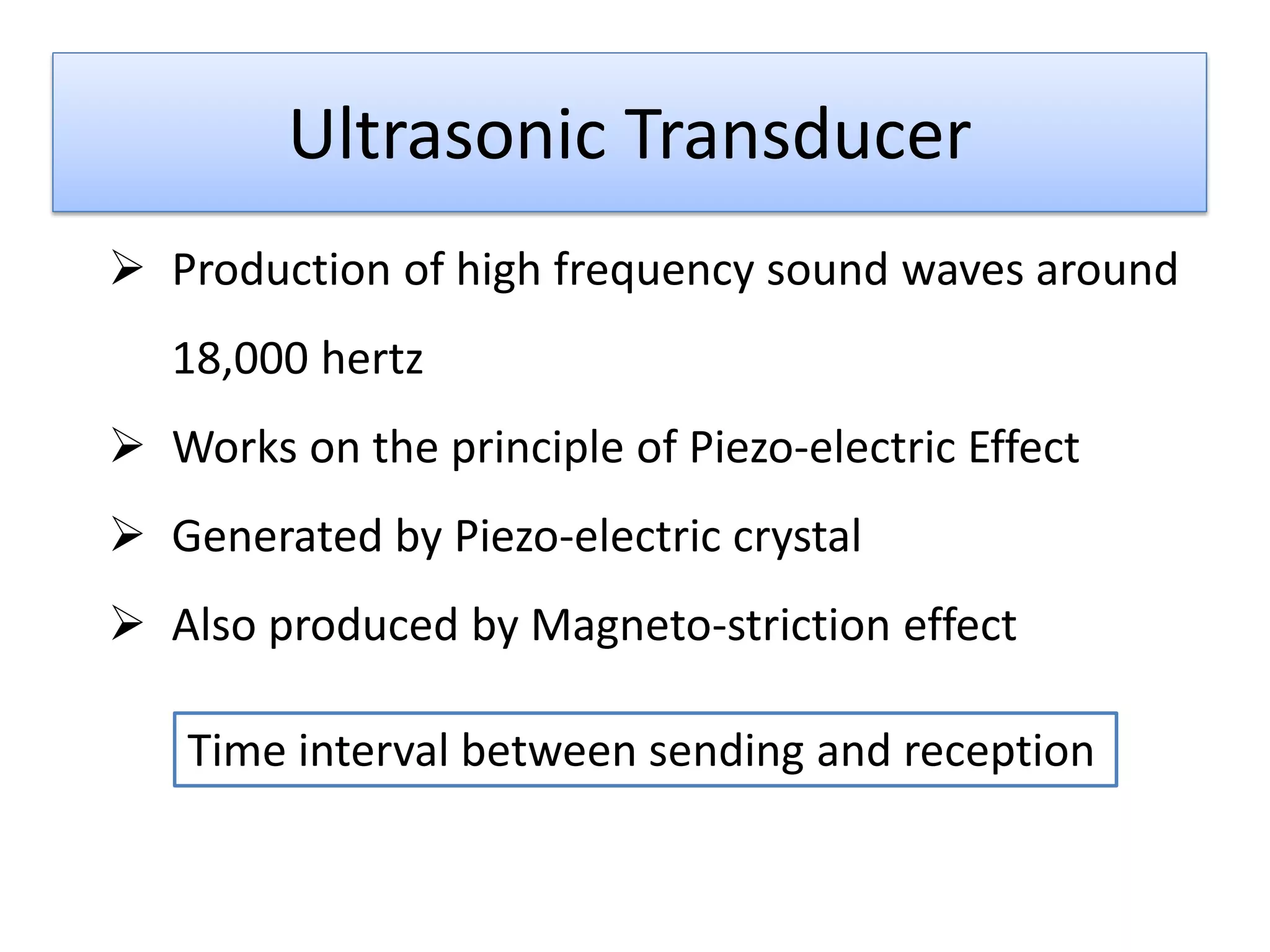
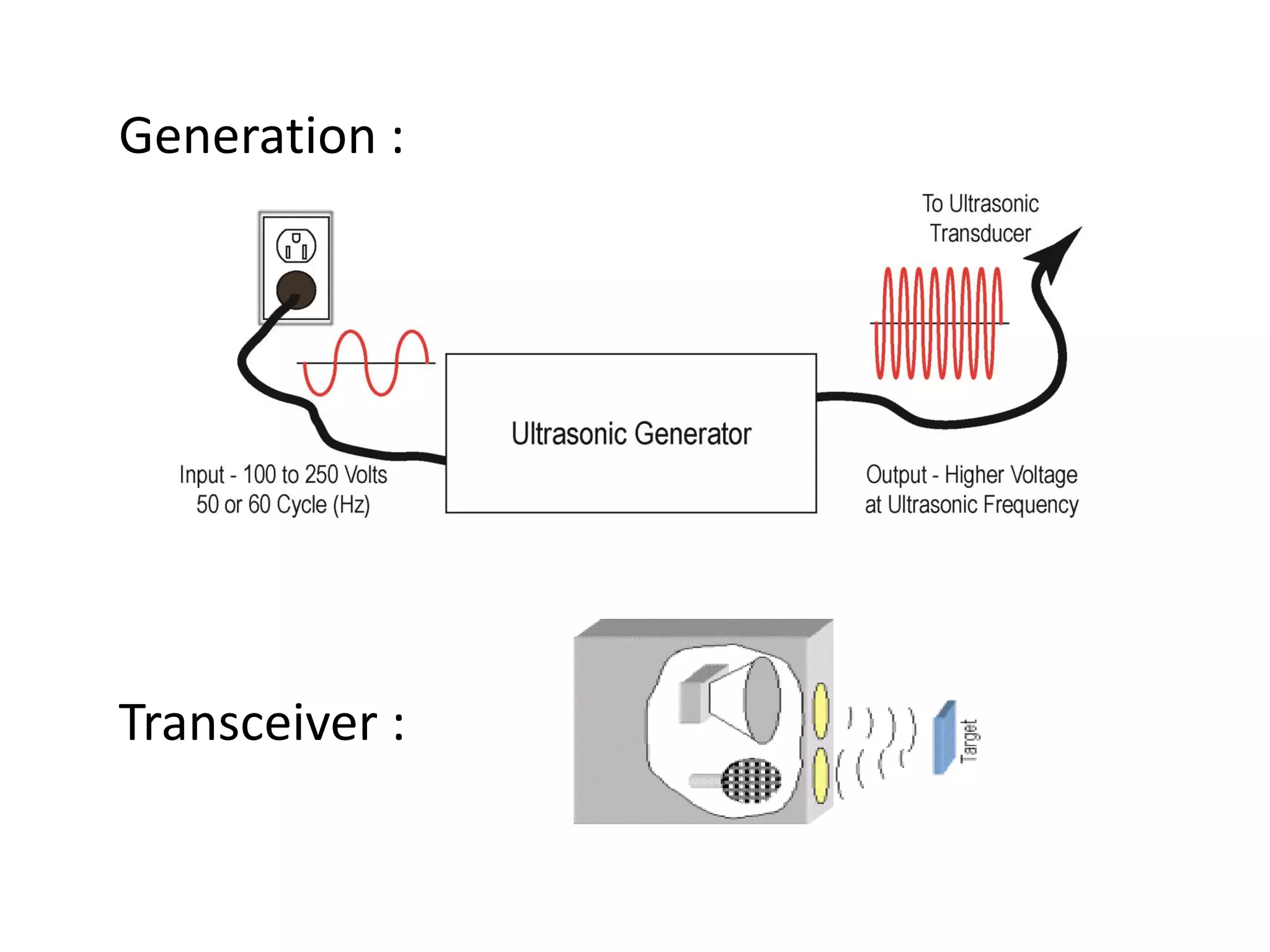
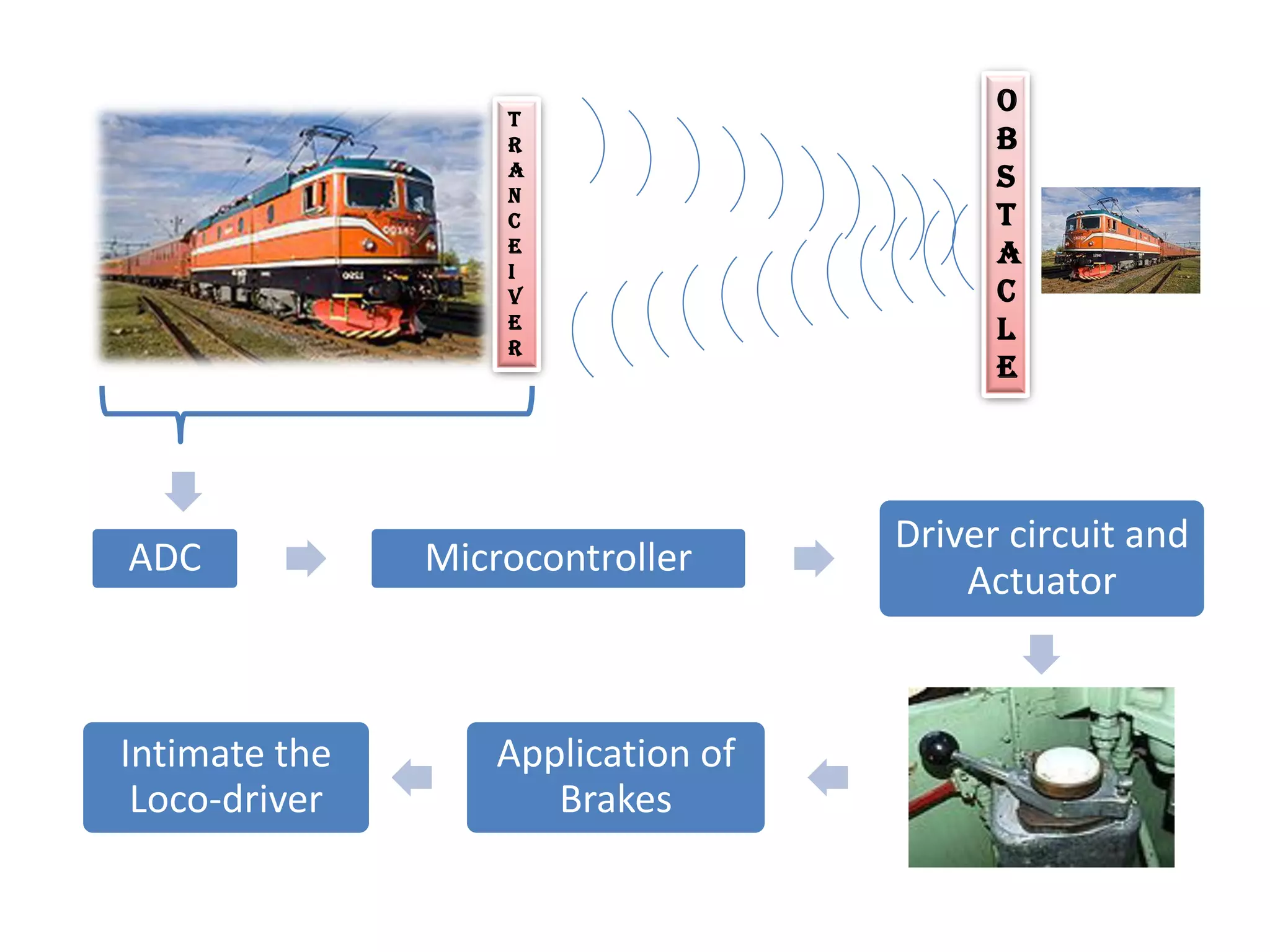
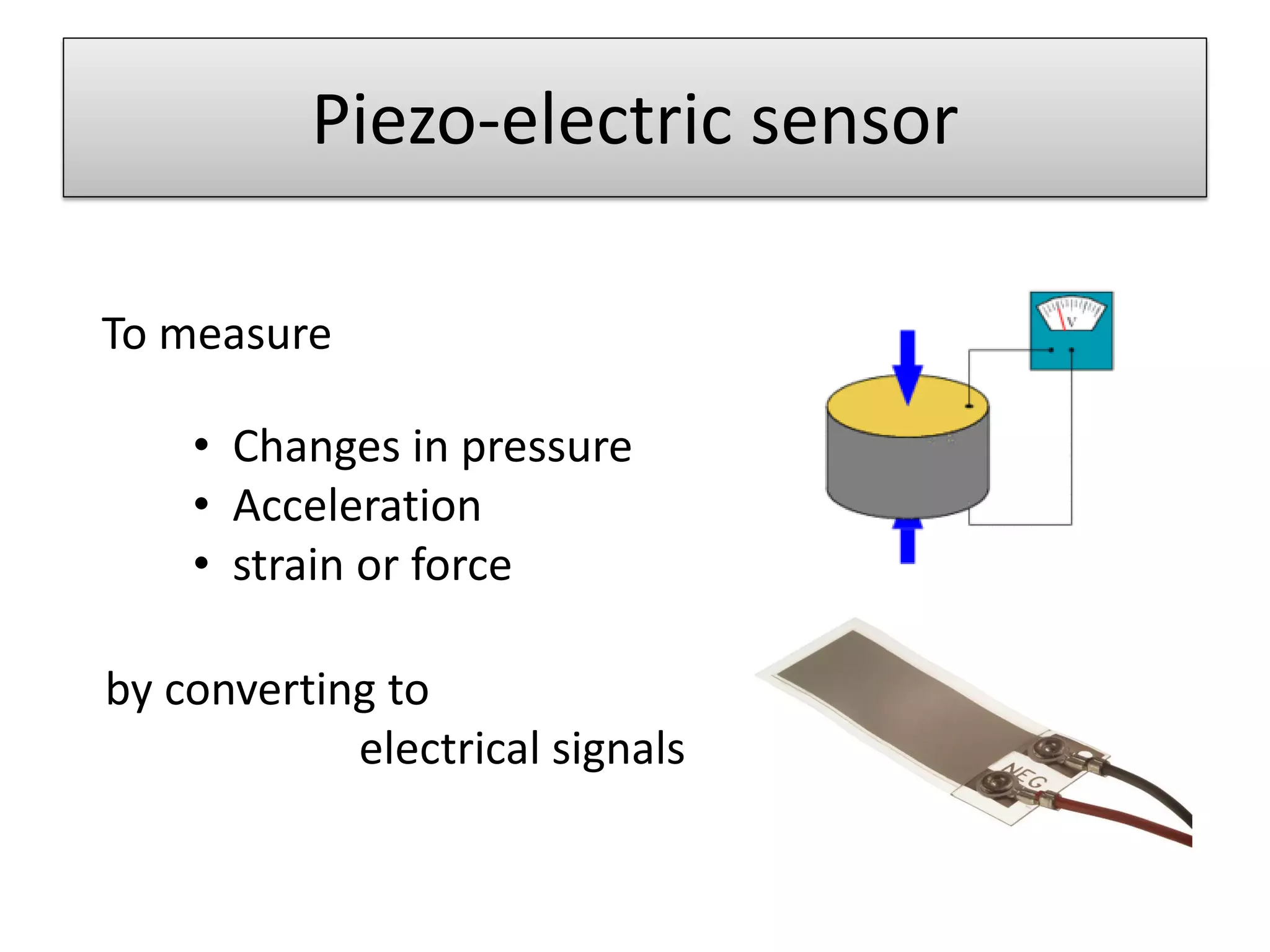
This document proposes three ideas to help avoid train collisions and accidents:
1. An automated braking system for trains that can detect obstacles from long distances and apply the brakes optimally.
2. Real-time train monitoring systems along tracks that provide trains' speed, direction, and location to prevent vehicle collisions at crossings.
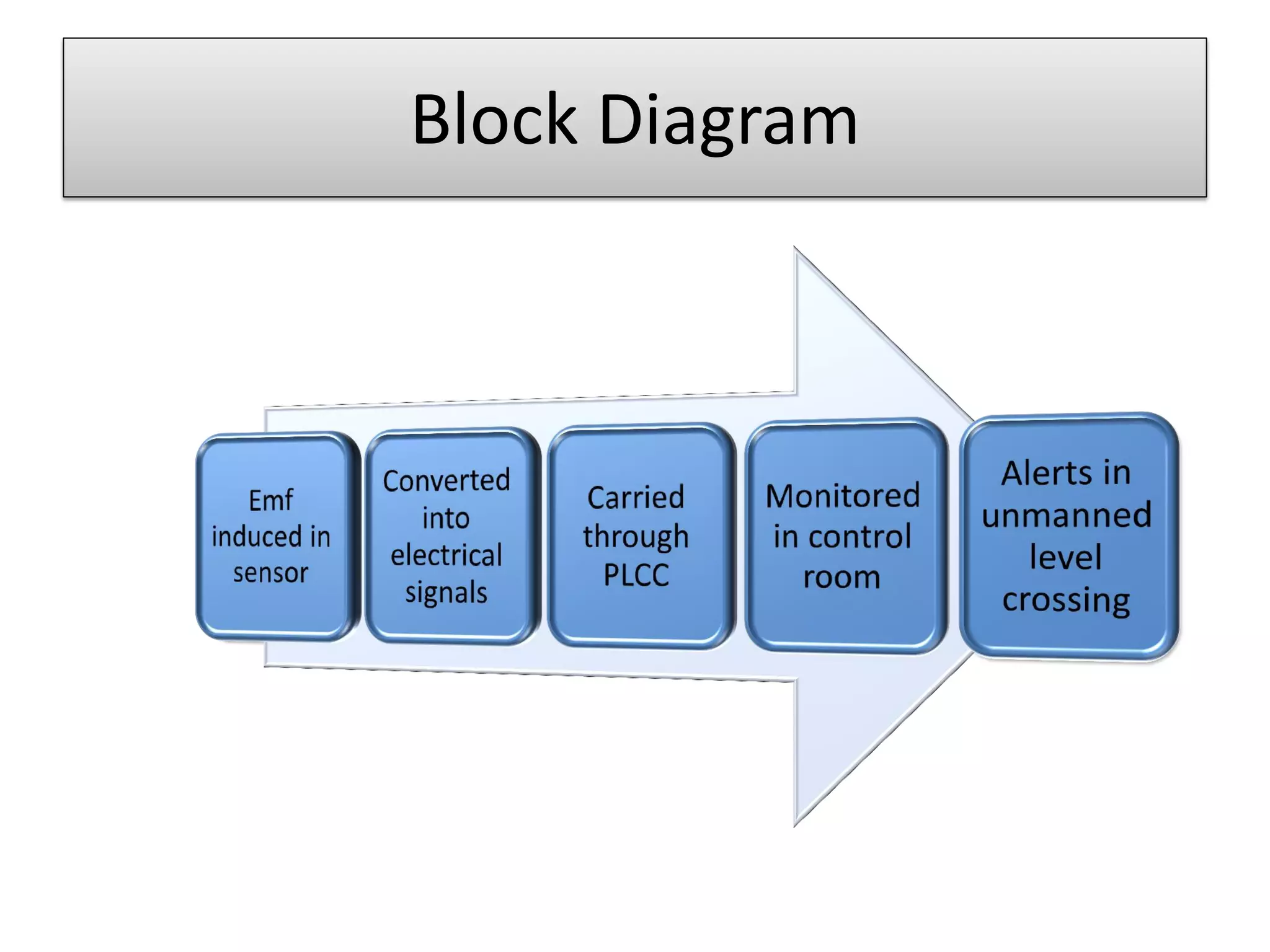
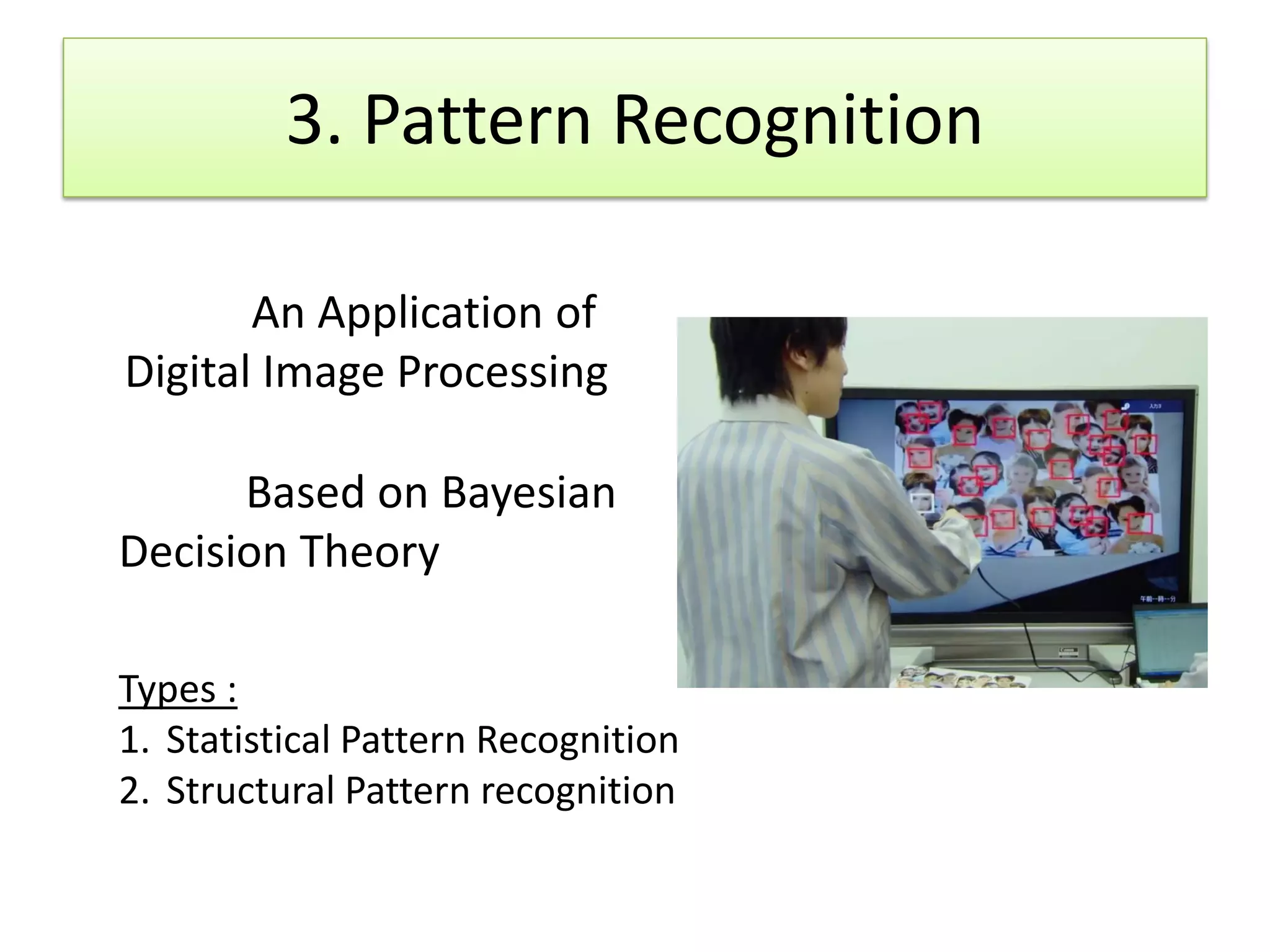
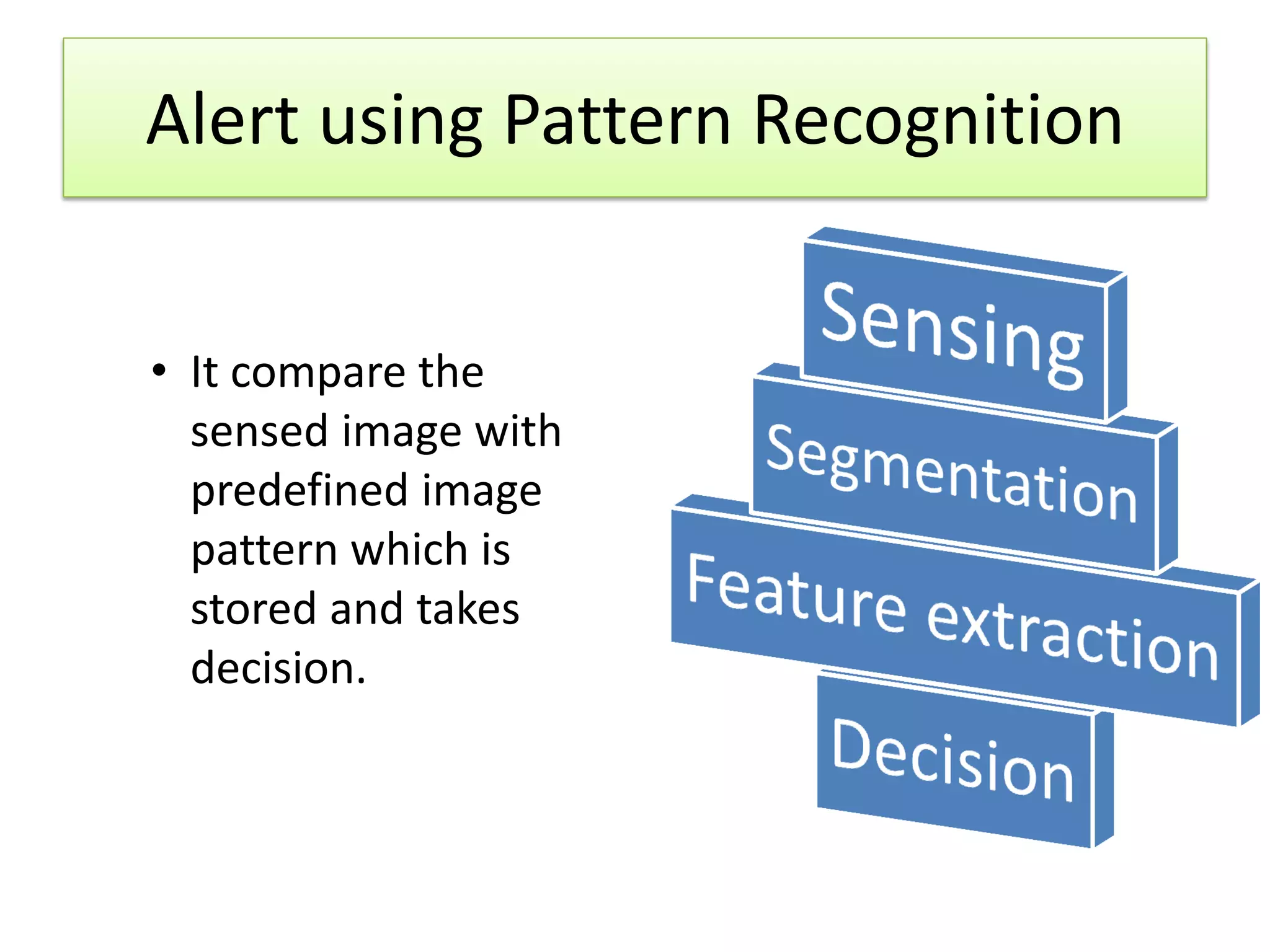
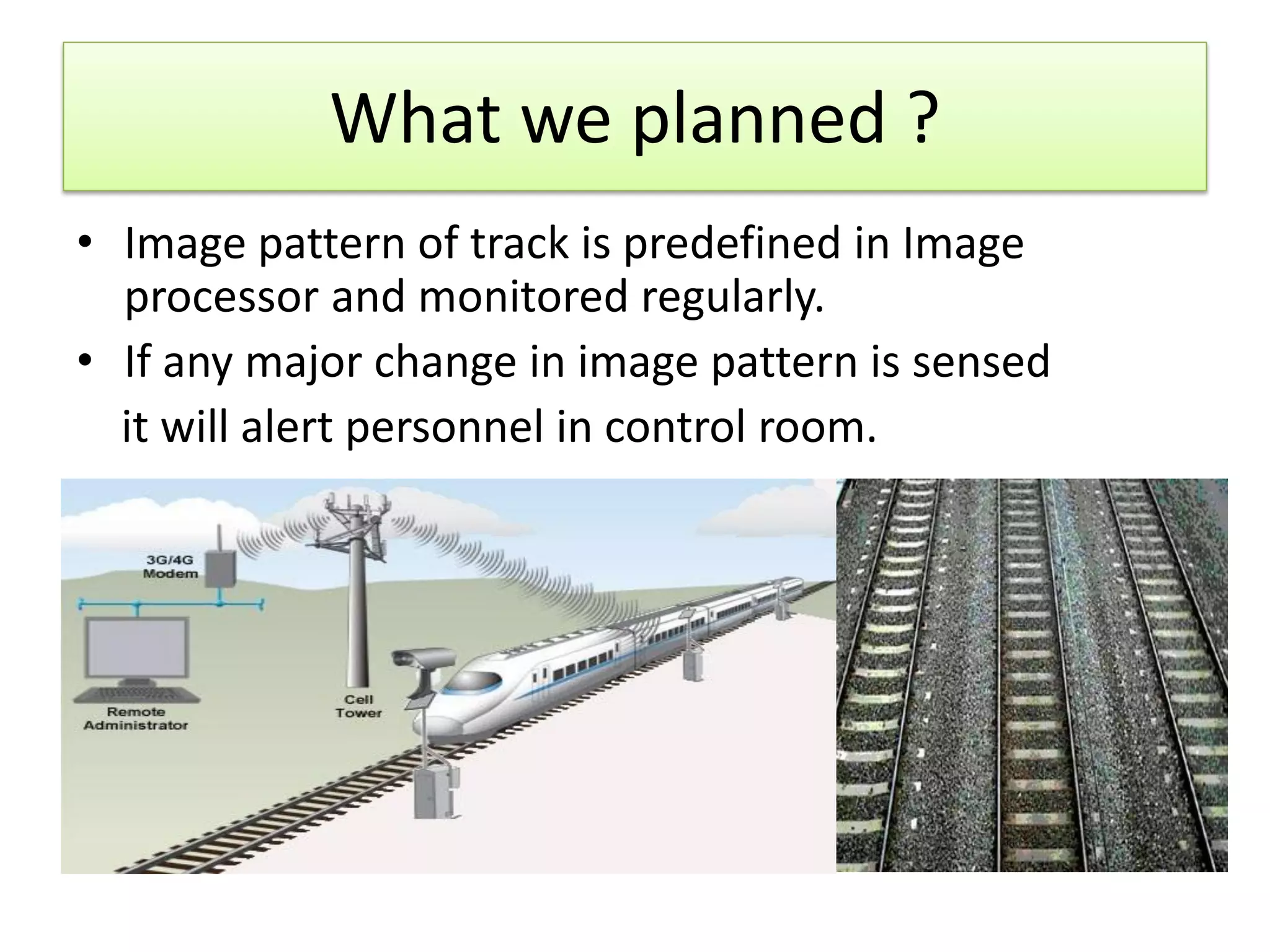
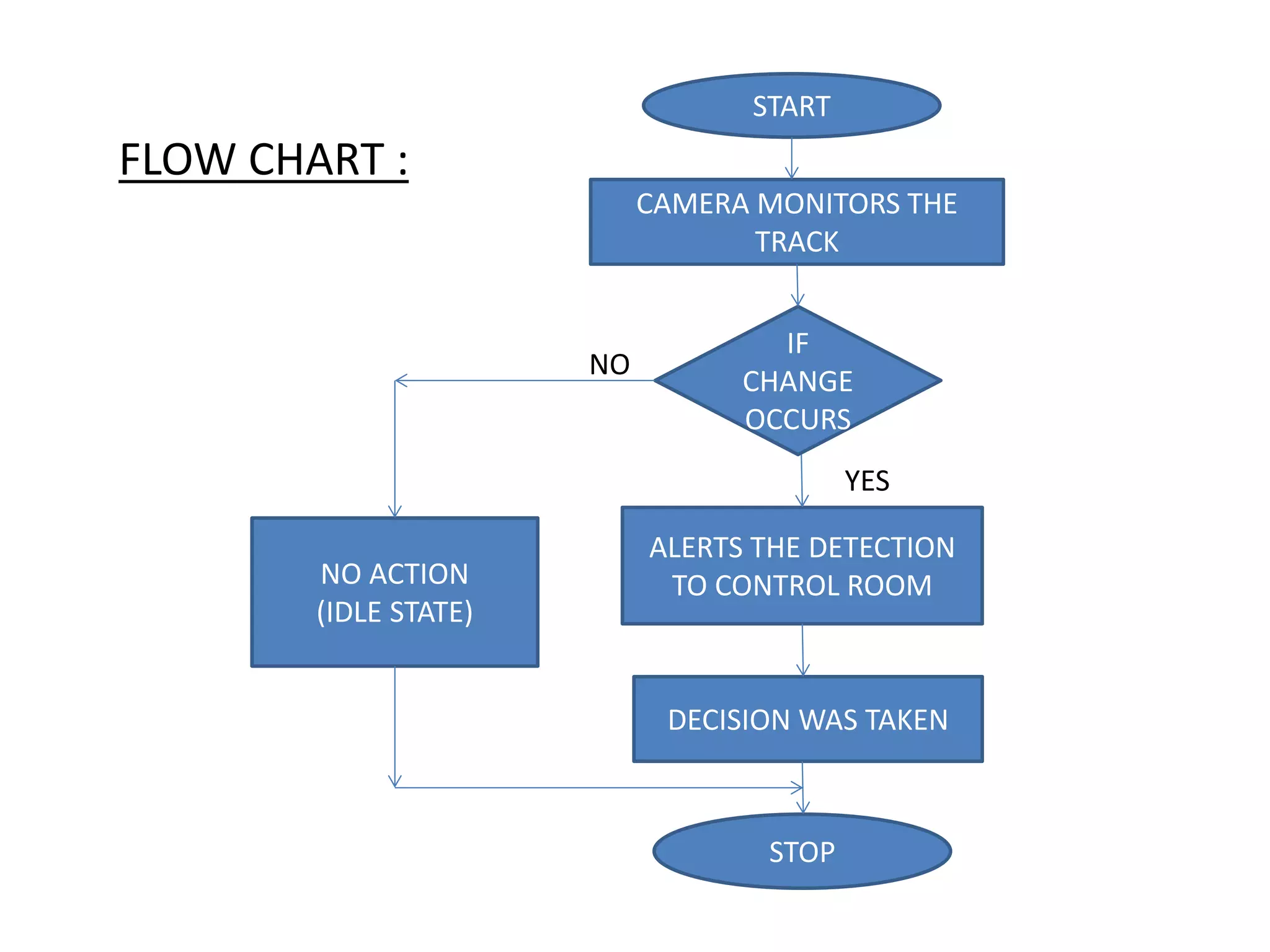
3. An alert system using pattern recognition of images along the tracks to detect changes like animals and notify personnel of potential collisions.
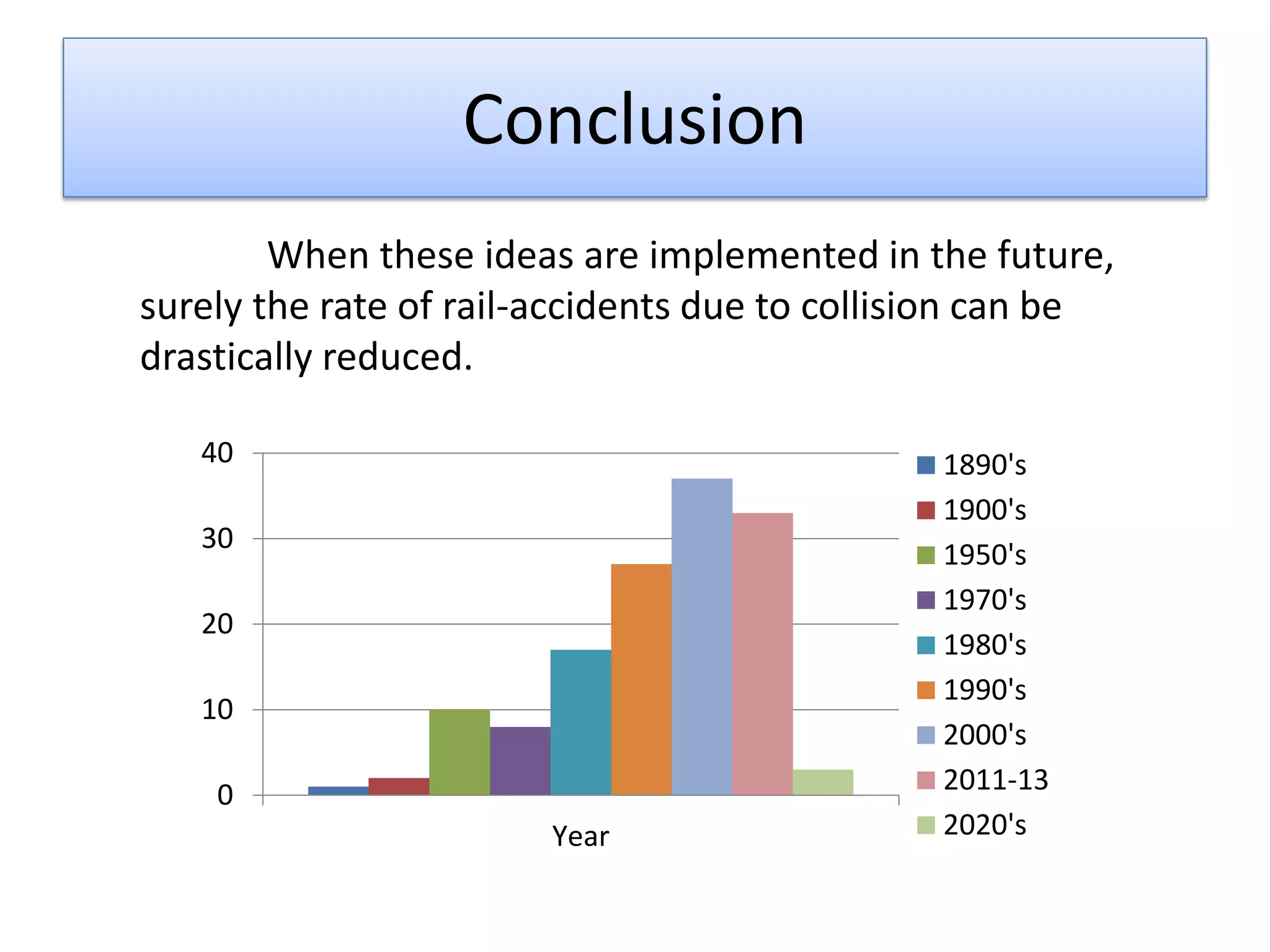
Implementing these ideas could greatly reduce rail accidents from collisions in the future.