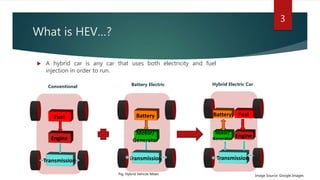
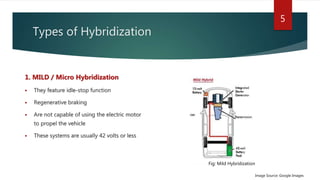
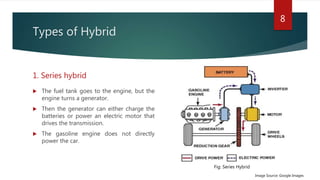
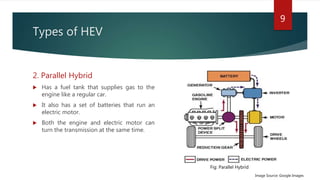
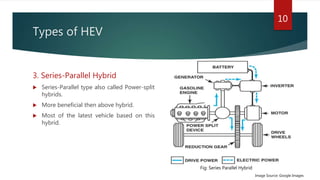
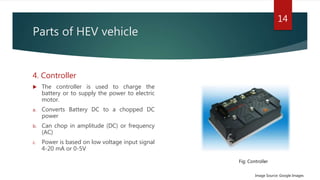
The document provides a comprehensive overview of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), detailing their definition, historical development, types of hybridization, and components. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of HEVs, highlighting their environmental benefits but also noting their higher costs and potential safety risks. The future scope emphasizes ongoing advancements in HEV technology and increased adoption by major automobile manufacturers.