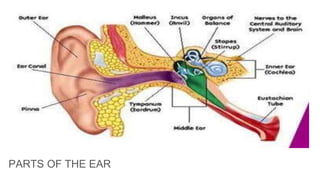
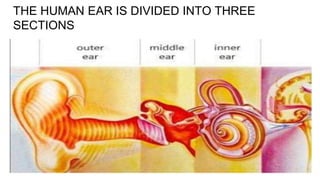
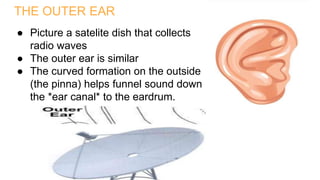
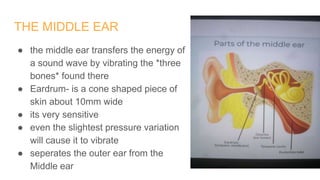
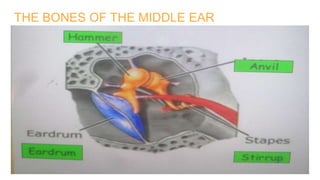
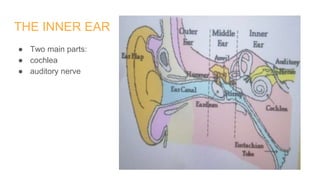
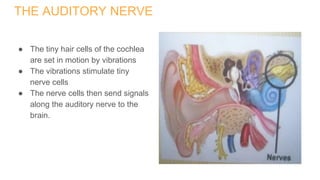
The human ear is divided into three main parts - the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and funnels them through the auditory canal to the eardrum. The middle ear contains three small bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that transfer vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. In the inner ear, the cochlea converts the vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve, allowing us to perceive sound. The ear works by capturing sound waves, transmitting vibrations through the bones to the inner ear, where they are converted into nerve signals and interpreted as sound by the brain.