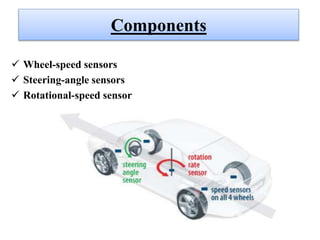
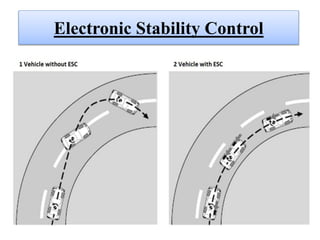
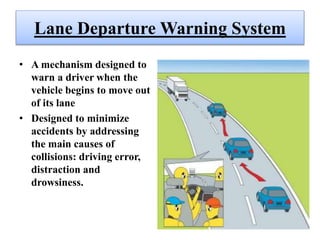
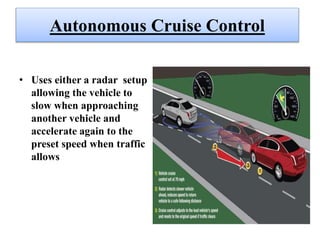
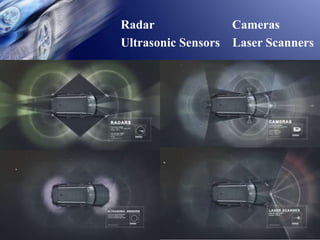
This document discusses self-driving or autonomous vehicles. It provides an introduction to autonomous cars and their ability to sense surroundings using sensors and computer vision. The document outlines some of the technologies used in autonomous vehicles, including radar, lidar, GPS, cameras, ultrasonic sensors and more. It describes how components like ABS, electronic stability control, adaptive high beams, night vision and parking sensors contribute to autonomous functionality. The document discusses advantages such as reduced accidents and improved mobility for disabled/elderly, as well as disadvantages including job loss and hacking risks. It concludes that autonomous vehicles could significantly reduce traffic and avoid accidents by 2020.