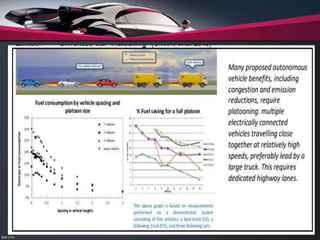
The document presents information on driverless cars, including a brief history of autonomous vehicles from 1969. It discusses how driverless cars use sensors and software to navigate without human input, and considers issues like safety, economic impacts, and how autonomous technology could affect transportation. While driverless cars may reduce accidents and open up new mobility options, challenges include high costs, job disruption, and ensuring computer systems don't cause crashes. The conclusion discusses both benefits of and social barriers to autonomous vehicle adoption.