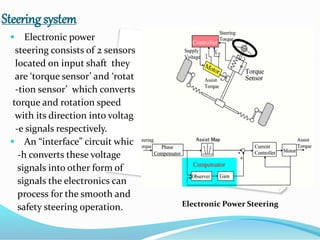
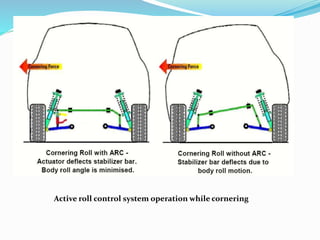
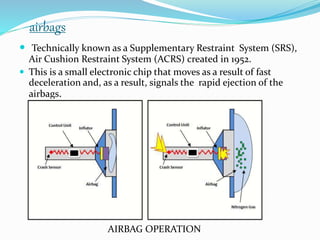
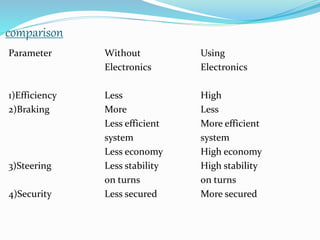
This document provides an overview of automotive electronics or autotronics. It discusses the history of electronics in vehicles from engine control units in the 1970s to modern innovations like GPS and wireless connectivity. The main systems involved in autotronics that improve vehicle performance are the braking, steering, suspension, transmission, and engine systems. Adaptive cruise control and airbags are two safety features that rely on electronic sensors and controls. Implementing electronics in vehicles provides advantages like improved efficiency, reliability, safety, and reduced emissions compared to mechanical systems alone.