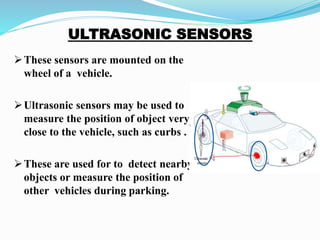
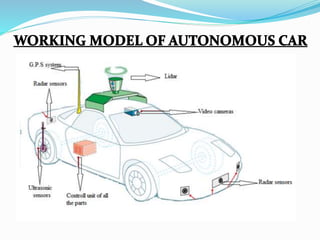
The document discusses autonomous vehicles and their components. It notes that autonomous vehicles can drive themselves without human assistance using sensors like LIDAR, radar, cameras and ultrasonic sensors connected to a central CPU. The document provides a brief history of autonomous vehicles, outlines the hardware components and their functions. It also discusses some of the work done on autonomous vehicles between 2012-2020, and lists potential advantages like reduced accidents and disadvantages like hacking risks.