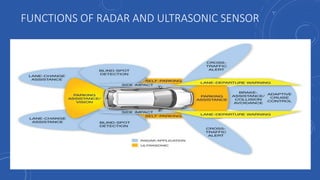
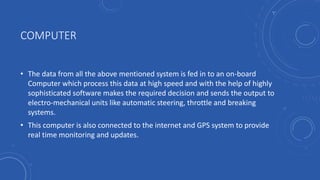
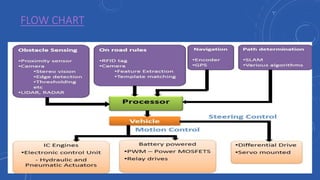
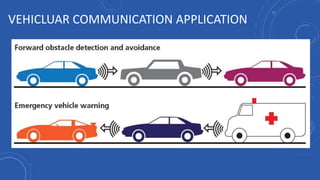
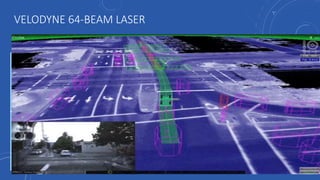
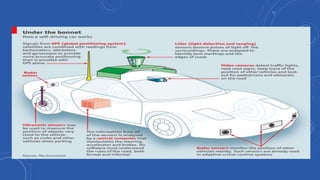
- People would have more free time that is currently spent driving that could be used for work or leisure activities like reading, socializing, or entertainment.
- Transportation services utilizing self-driving cars could become more accessible for those unable to drive such as the elderly or disabled.
- New types of businesses may emerge catering to passengers in self-driving cars such as mobile offices, restaurants, or shops.