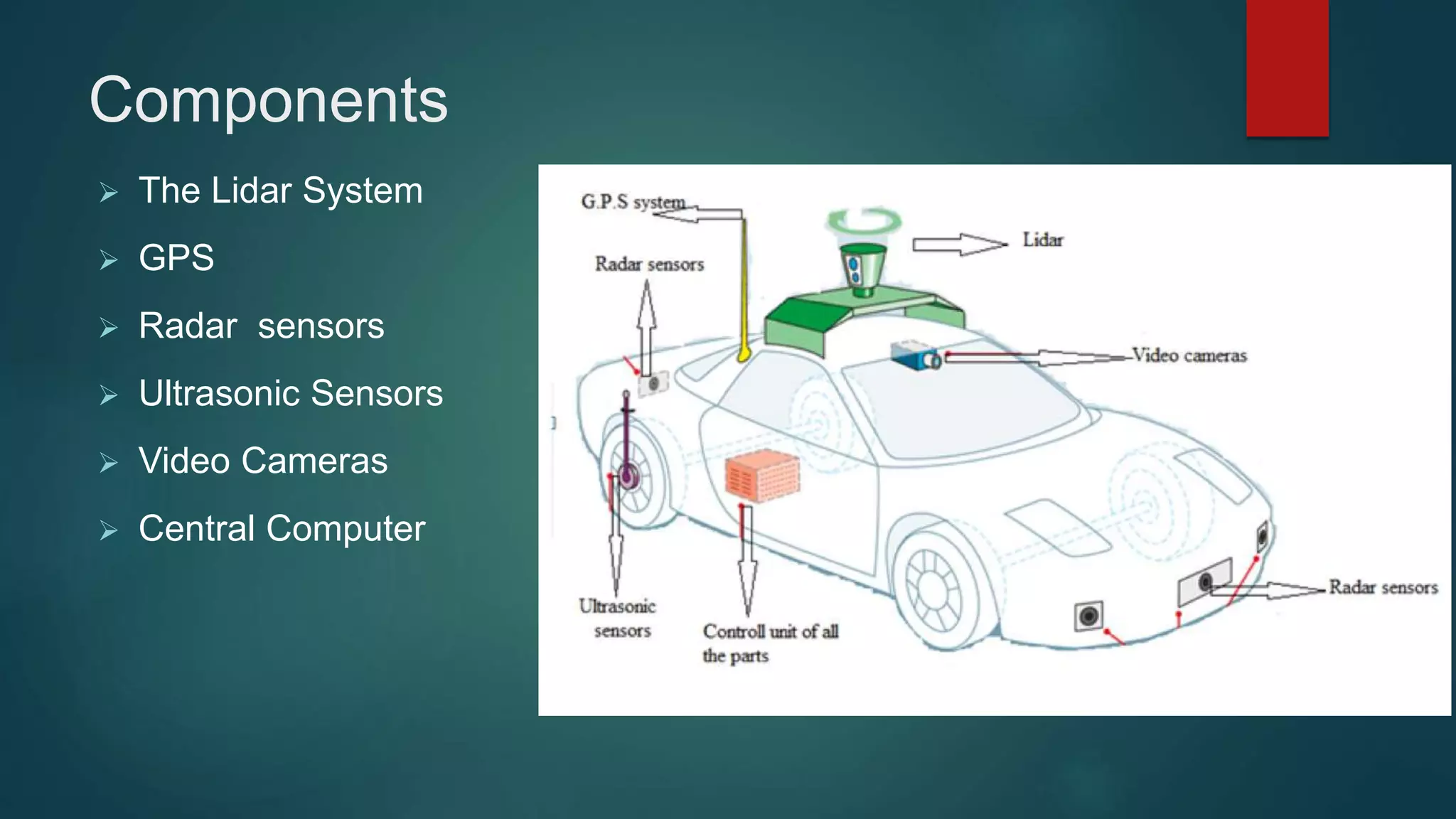
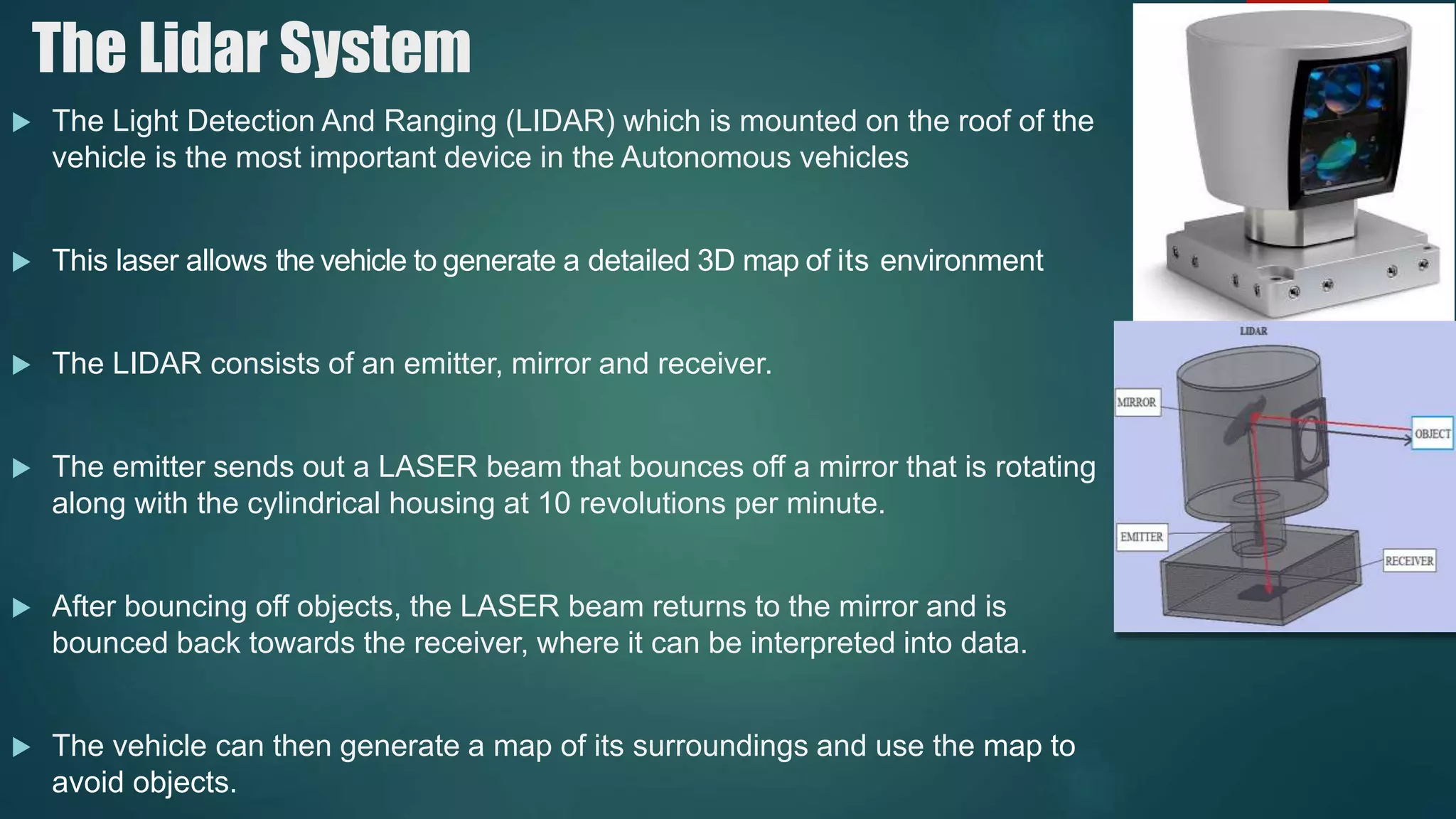
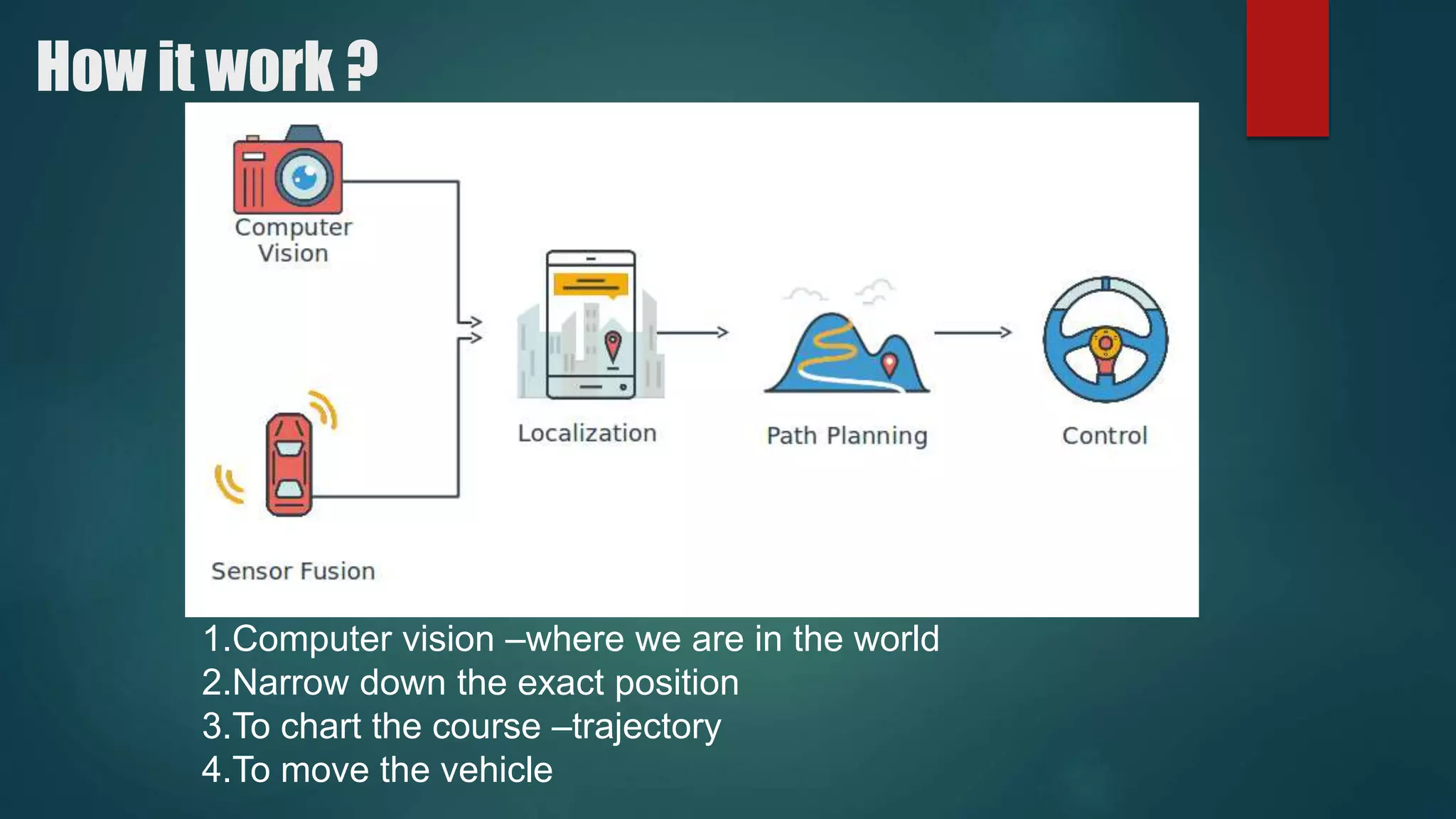
The document discusses autonomous vehicles and their potential benefits and challenges. It defines autonomous vehicles as vehicles that can travel from one point to another without human supervision. It notes that human error causes over 90% of automobile accidents and that autonomous vehicles could help reduce accidents by taking human error out of driving. The document outlines some of the key technologies used in autonomous vehicles, such as LIDAR, GPS, radar, ultrasonic sensors, video cameras, and a central computer. It discusses companies working on autonomous vehicle technologies like Google, Mercedes Benz, and Tesla. It also discusses some of the pros and cons of autonomous vehicles.