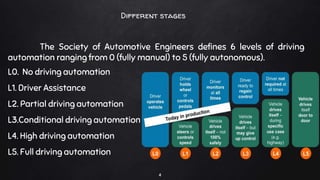
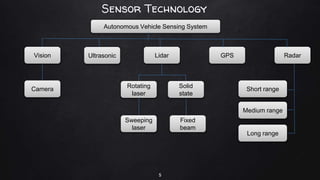
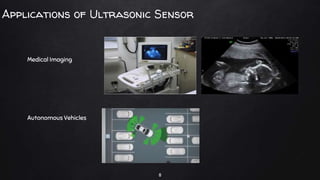
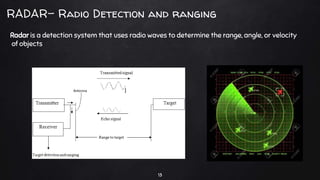
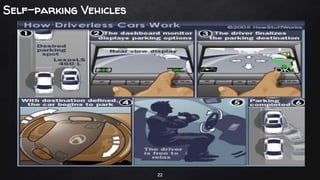
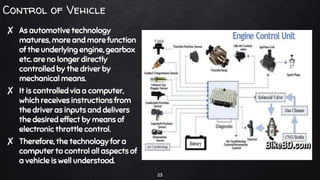
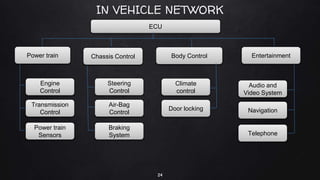
A driverless vehicle, or autonomous car, operates without human intervention, utilizing advanced technology such as adaptive cruise control and emergency braking. There are six levels of automation defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers, with level 0 being fully manual and level 5 fully autonomous. While driverless technology offers advantages like improved traffic flow and reduced accidents, it also poses challenges including high costs, potential job losses in driving professions, and security vulnerabilities.