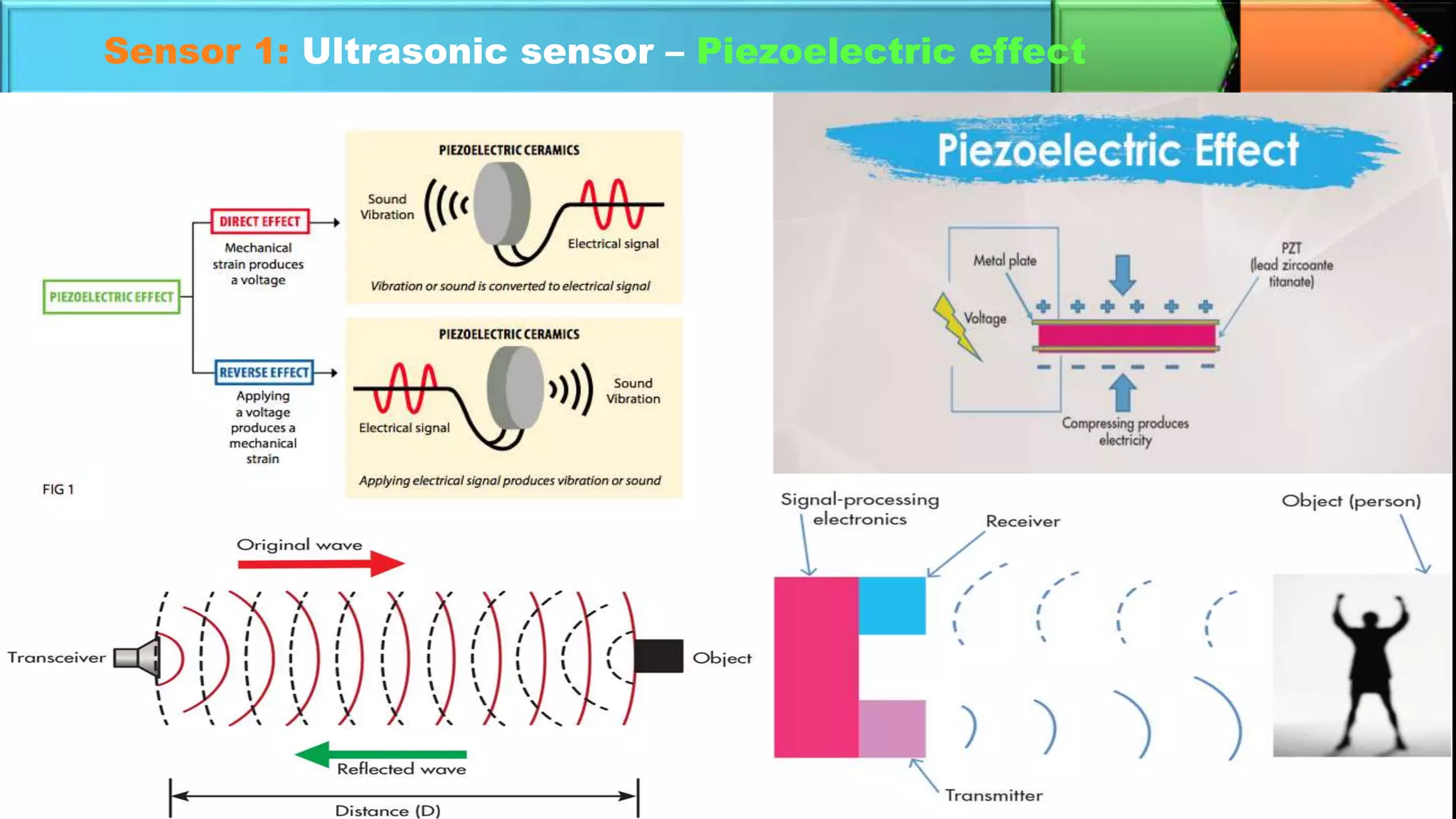
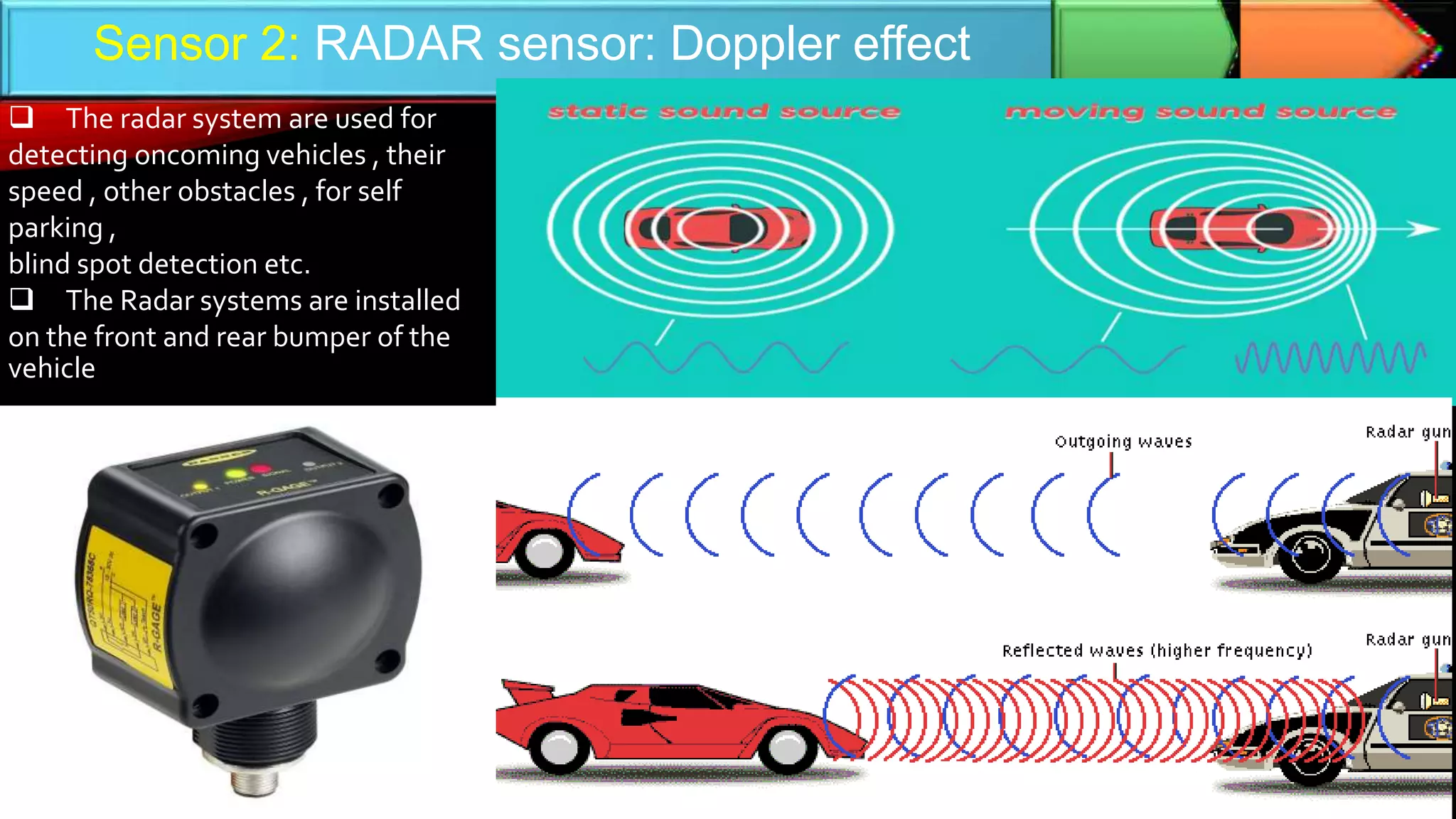
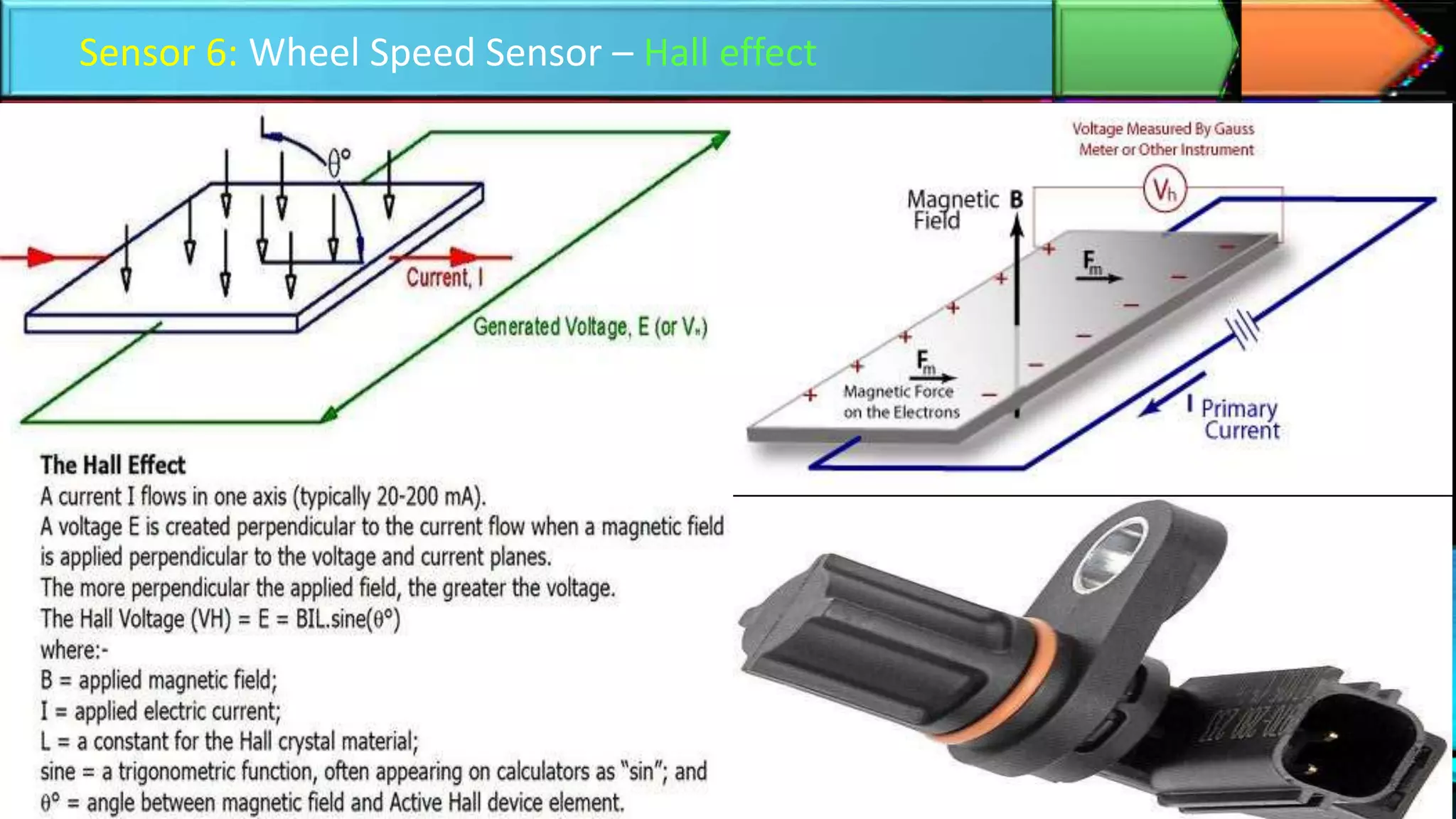
The document discusses autonomous cars, highlighting their definitions, historical development, and the various sensor technologies used for navigation and safety, such as ultrasonic, radar, lidar, and GPS sensors. It outlines the advantages, including improved safety and traffic efficiency, and addresses limitations such as hacking risks and sensor failures. The current status of self-driving cars is illustrated with the example of Waymo's commercial service in Phoenix, and the document concludes with a perspective on future advancements in autonomous vehicle technology by 2040.