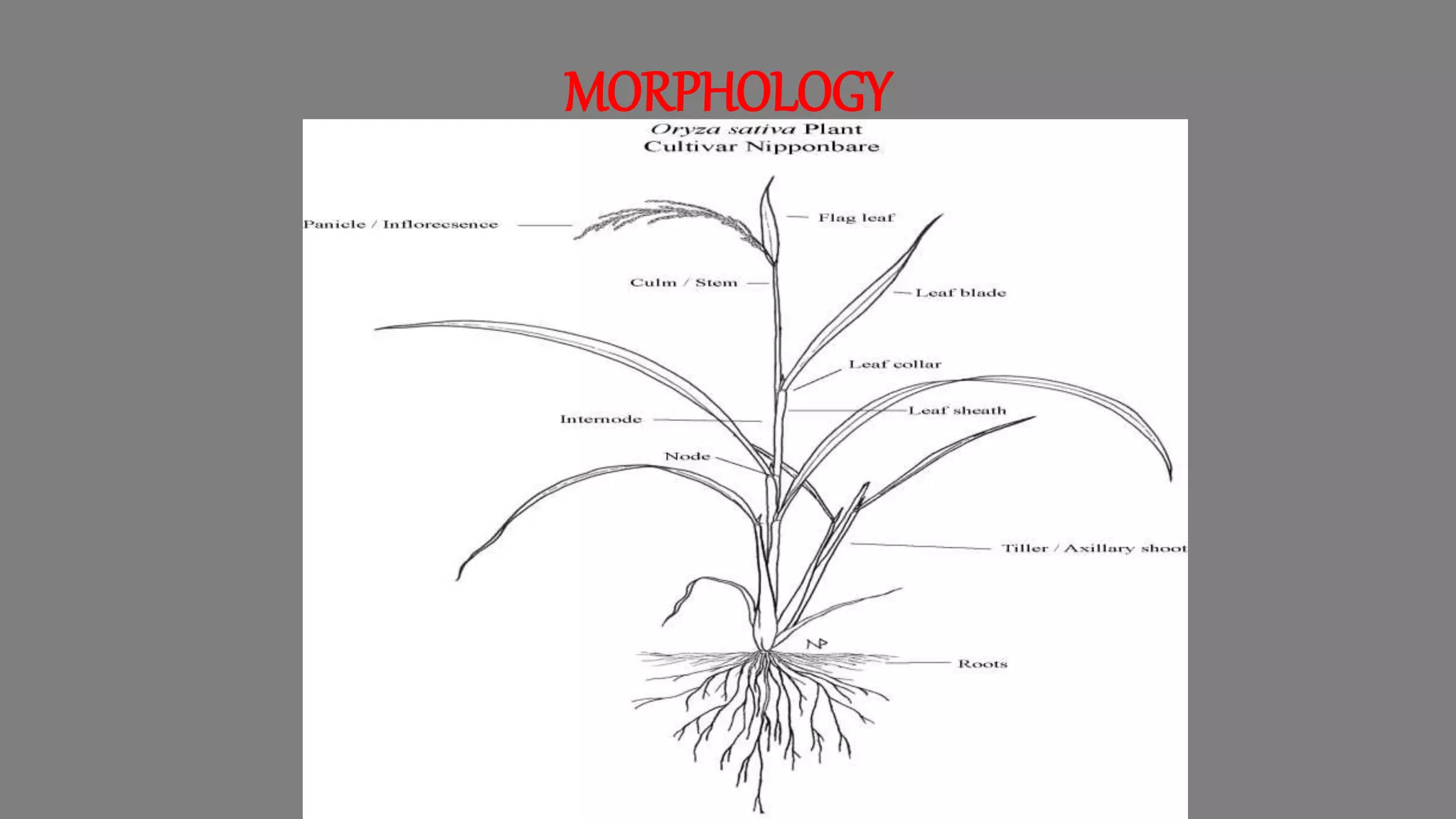
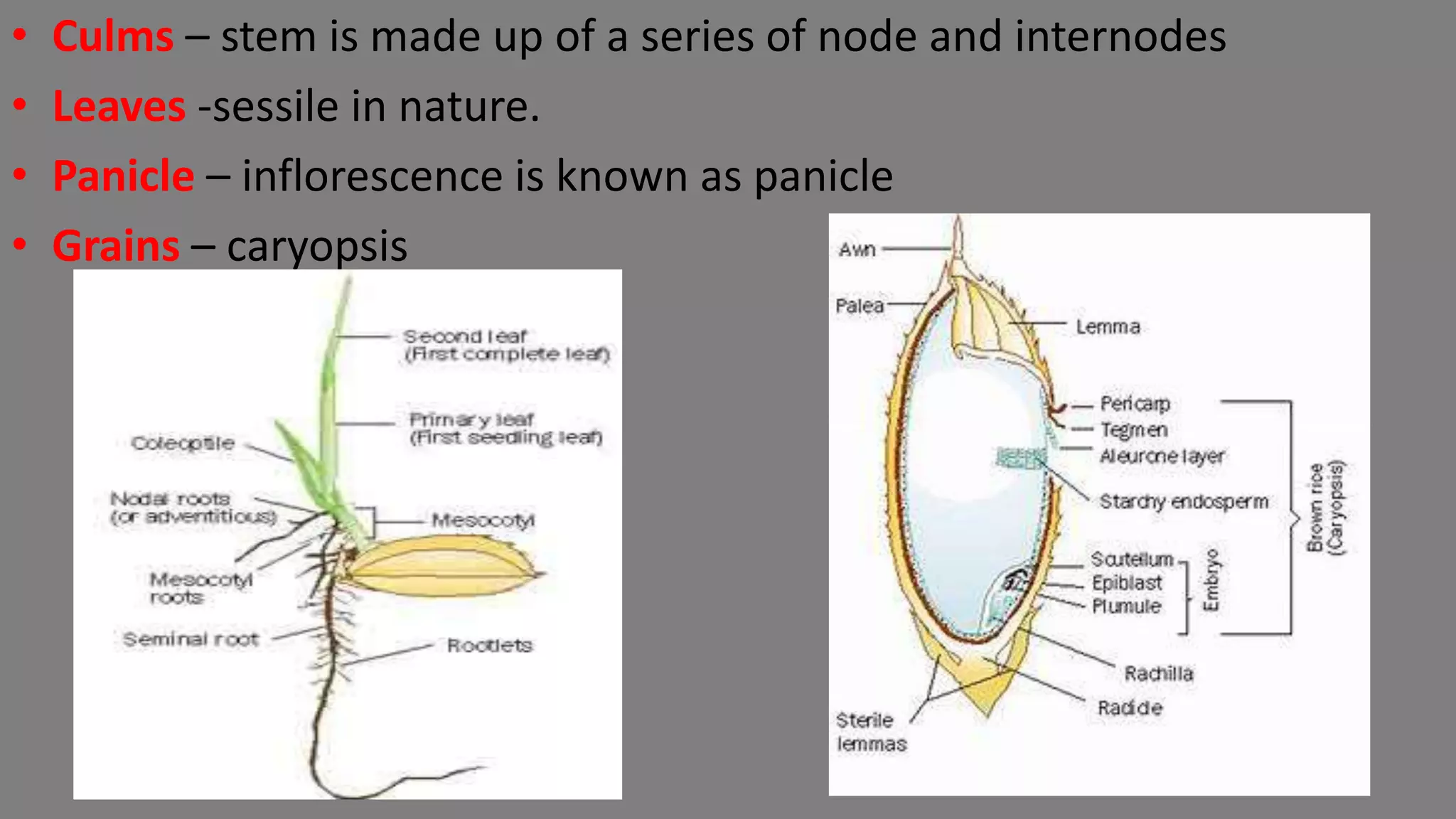
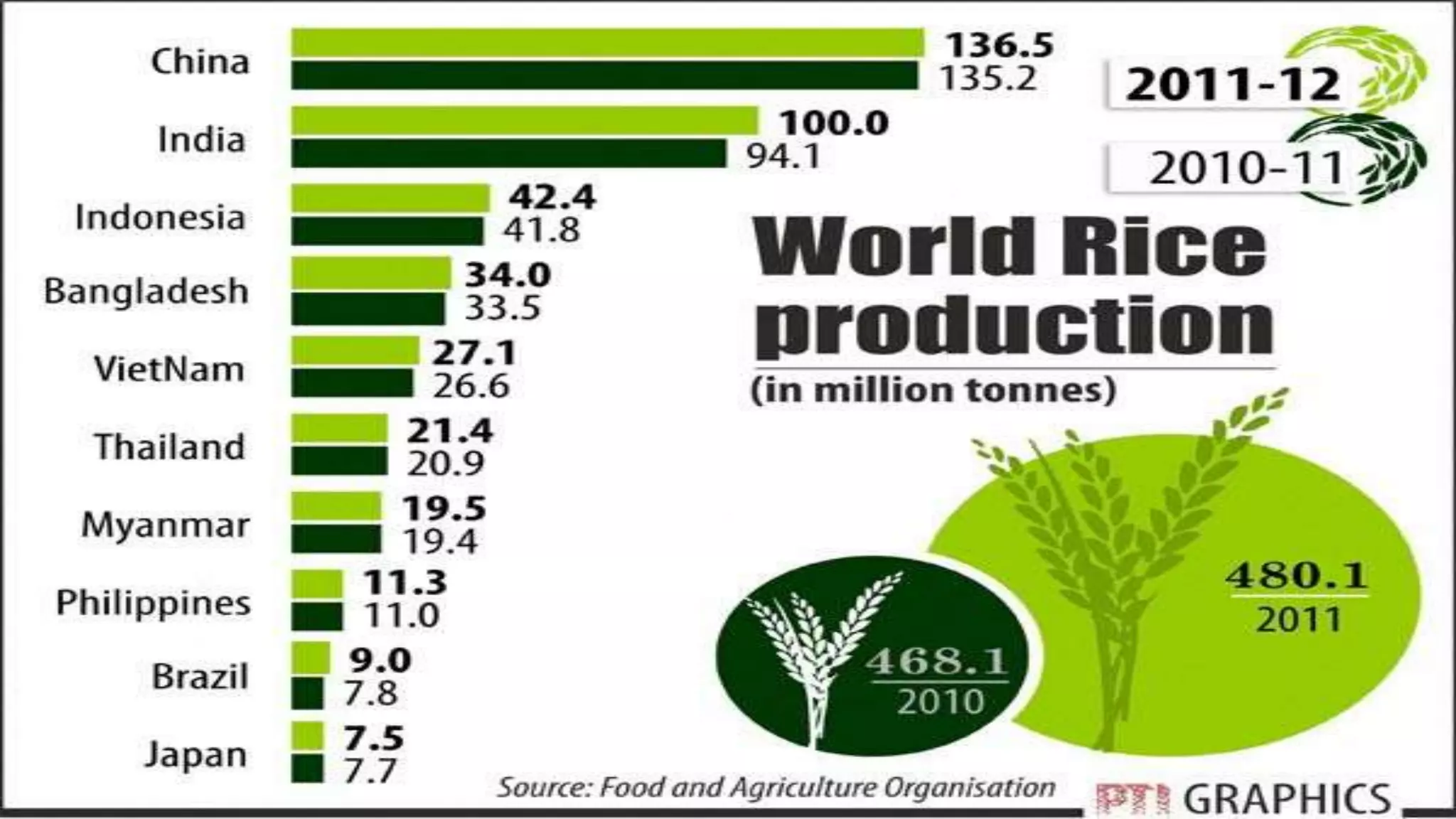
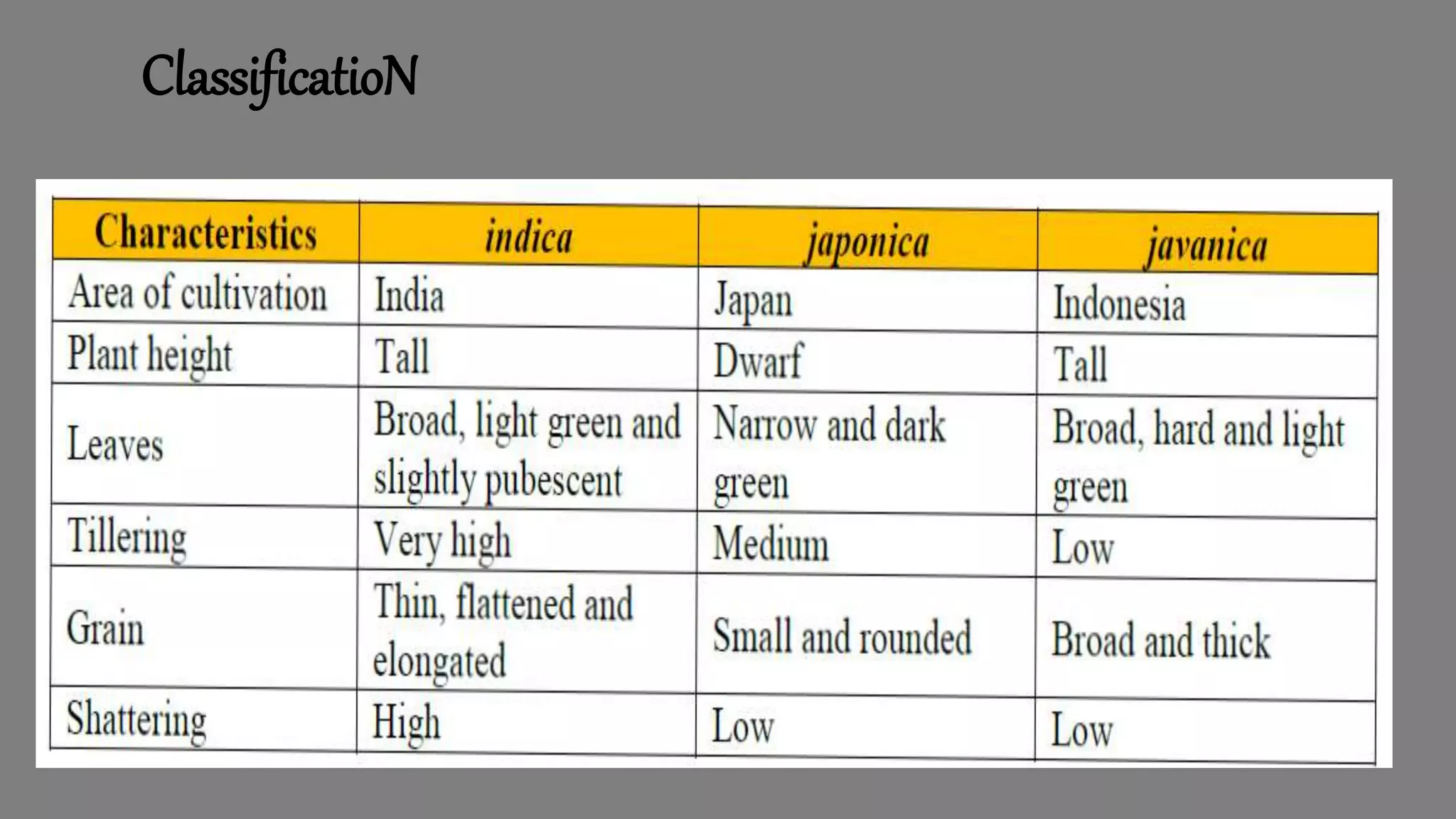
This document provides an overview of rice cultivation including its botanical classification, key growing regions, varieties, cultivation practices, and nutritional importance. It discusses rice morphology, climatic and soil requirements, and summarizes the major production techniques including land preparation, nursery management, transplanting, and harvesting. Key production statistics for India and the world are also presented.