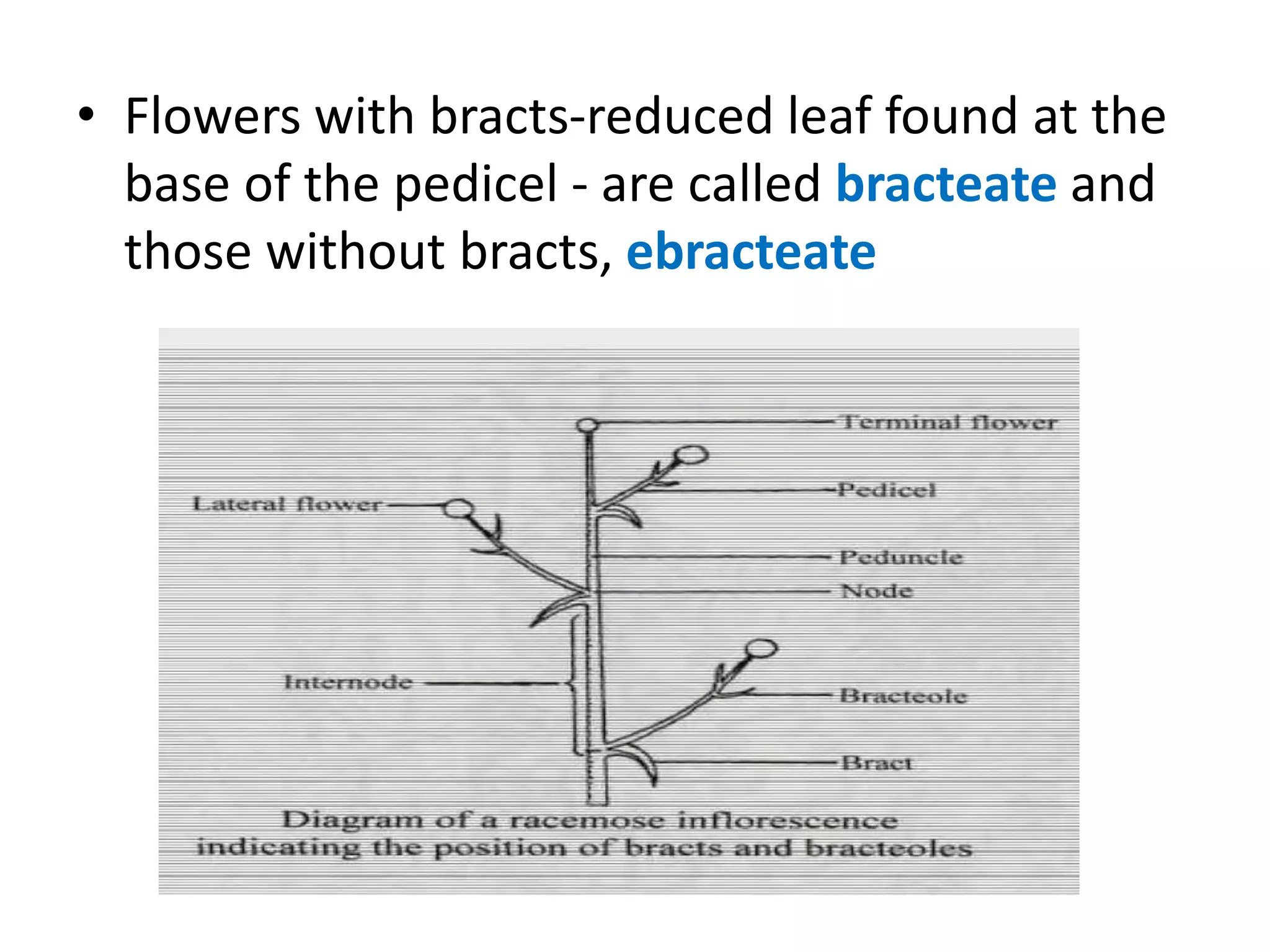
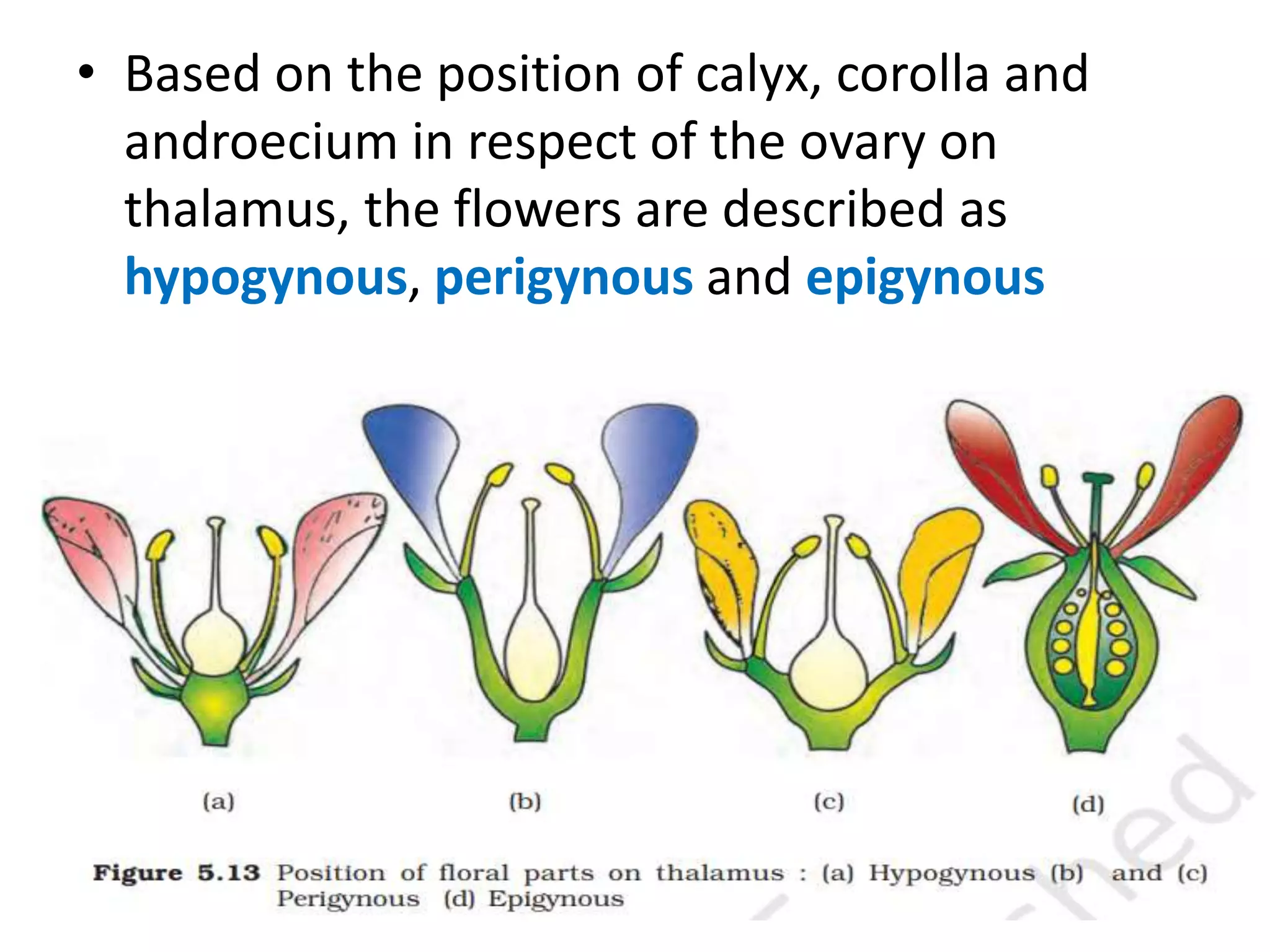
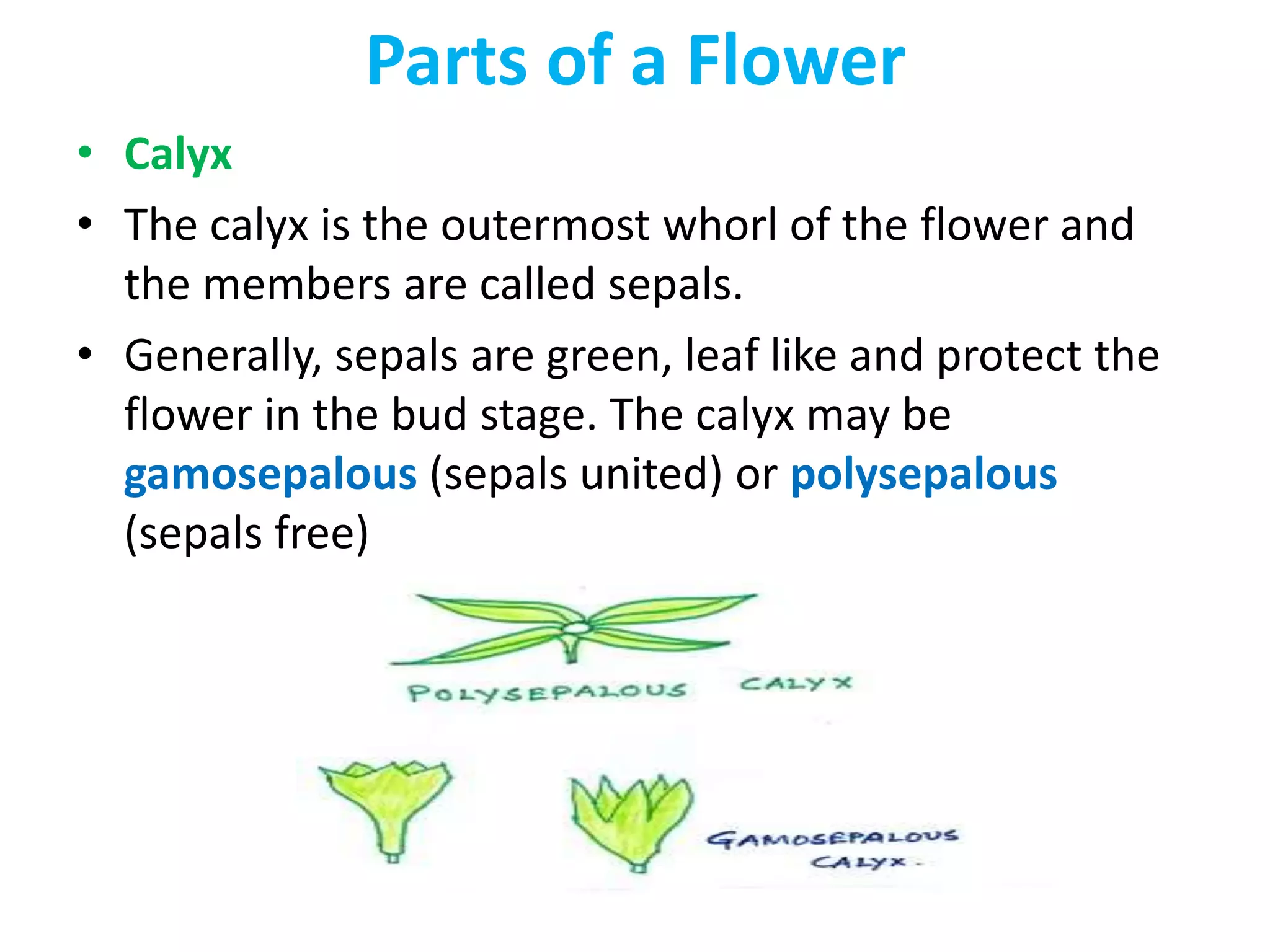
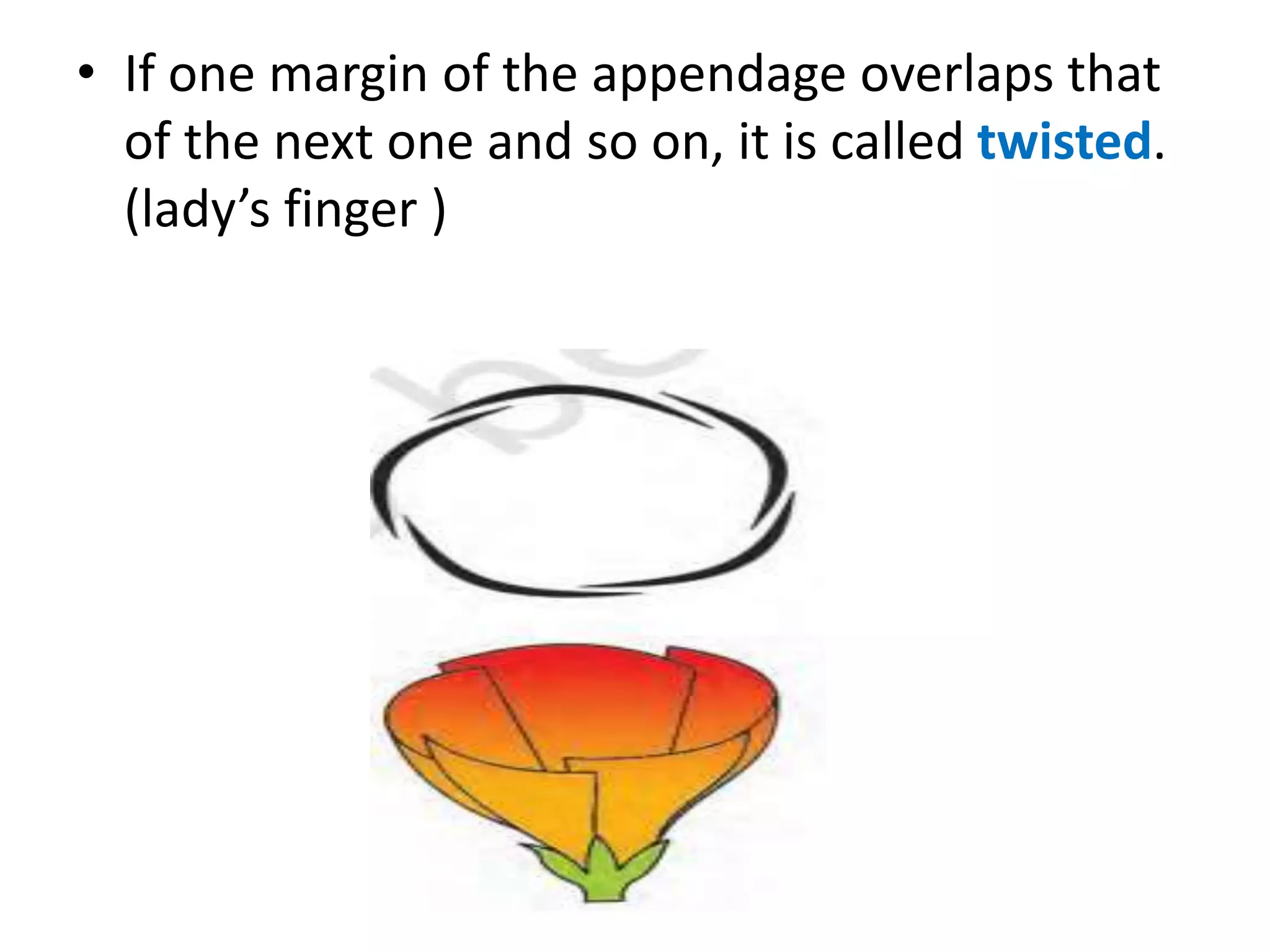
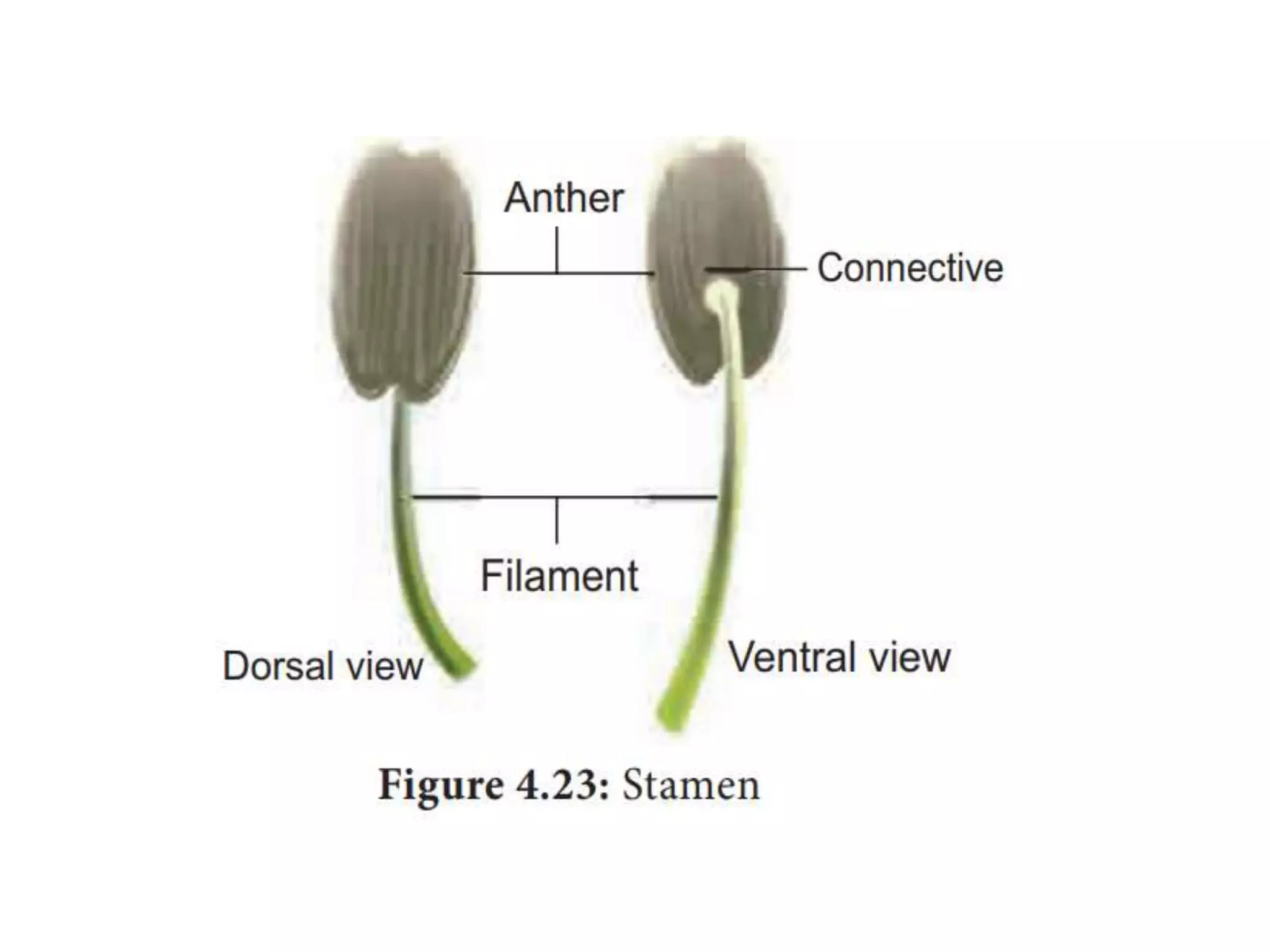
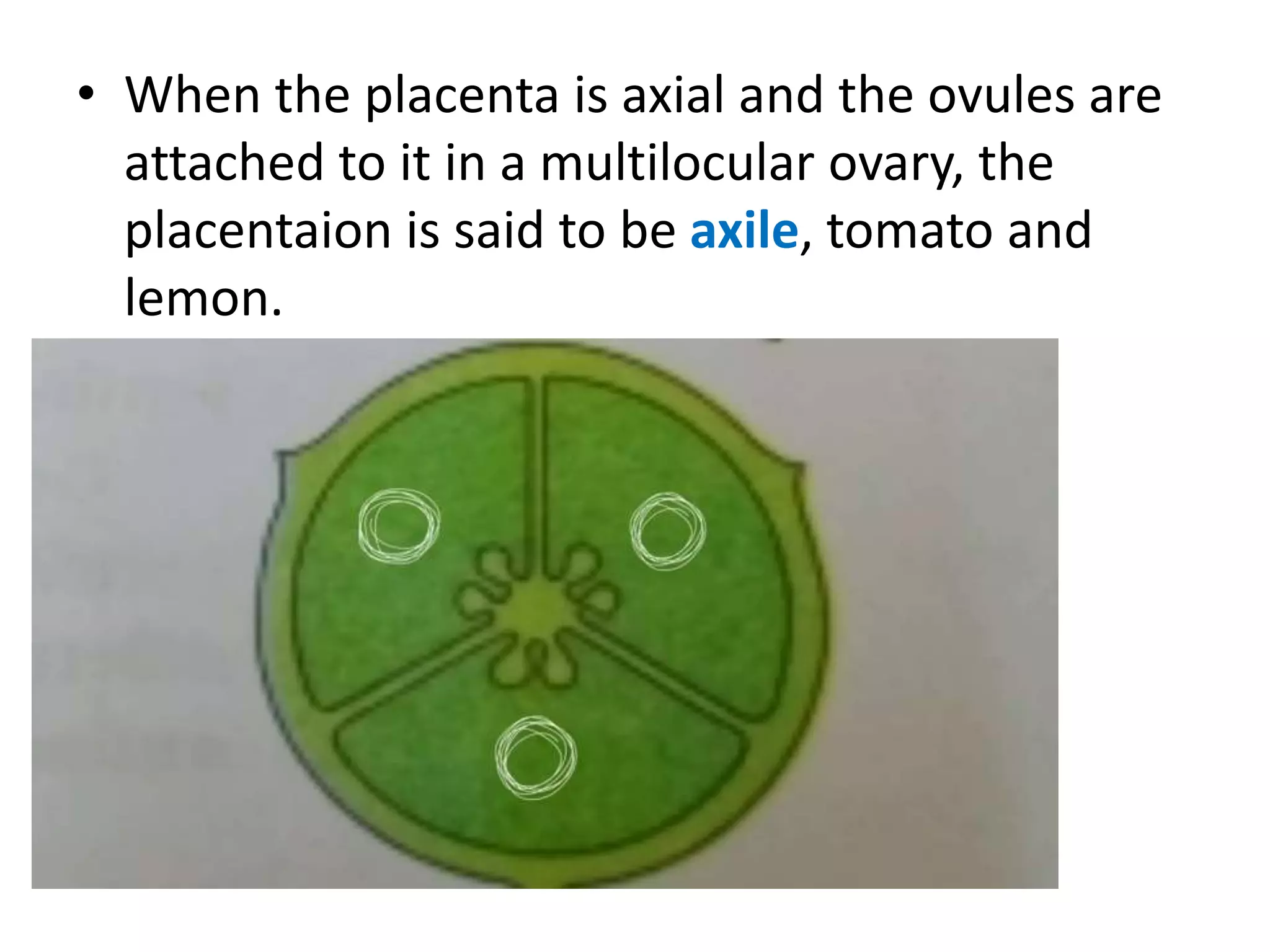
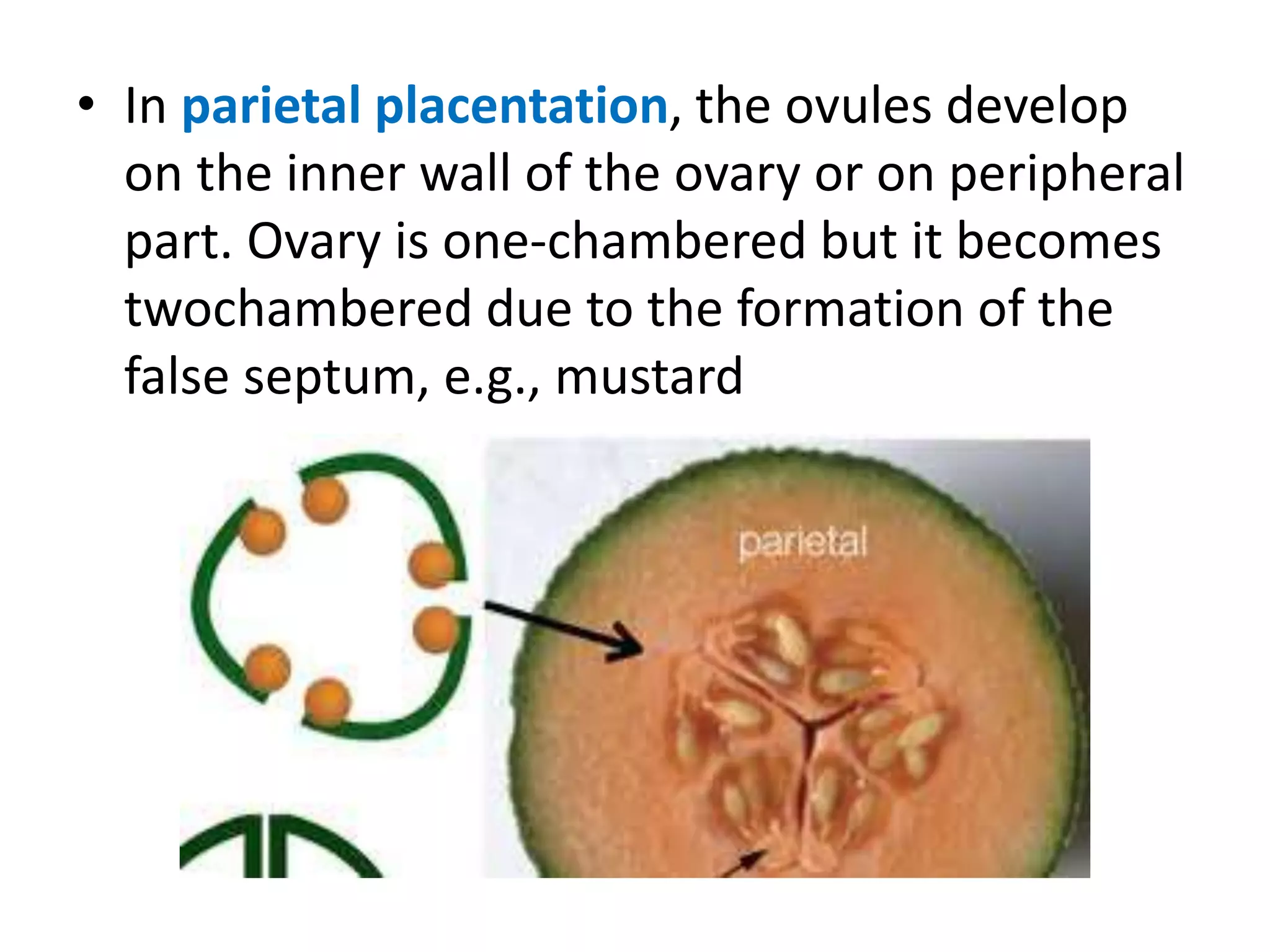
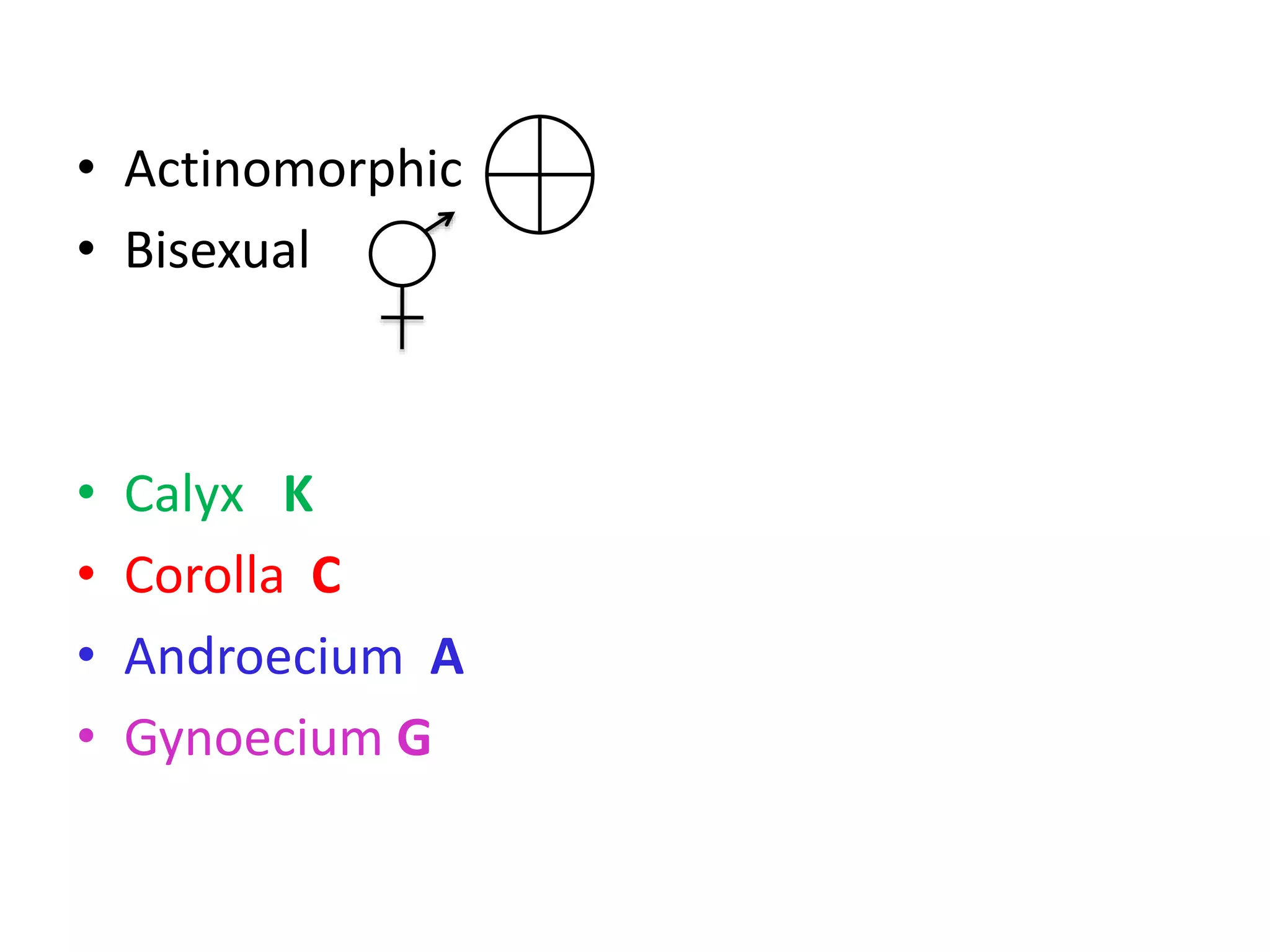
This document summarizes the morphology and structure of flowers in angiosperm plants. It describes the basic parts of a flower including the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. It also discusses flower symmetry, aestivation, placentation, and provides examples of different inflorescence types. As an example, it thoroughly outlines the characteristics of flowers in the Solanaceae family, which includes important crops like tomato, potato, and chili peppers.