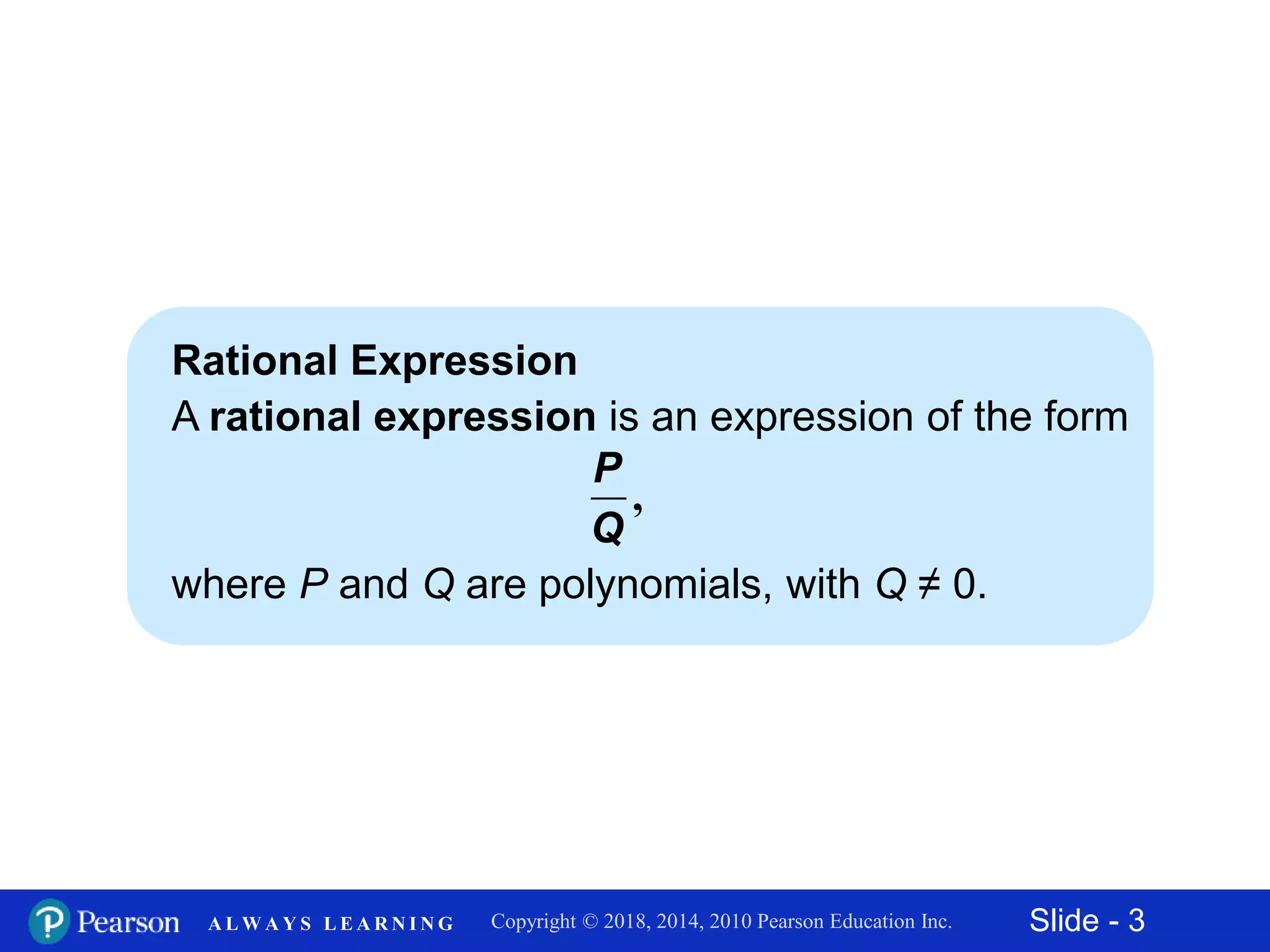
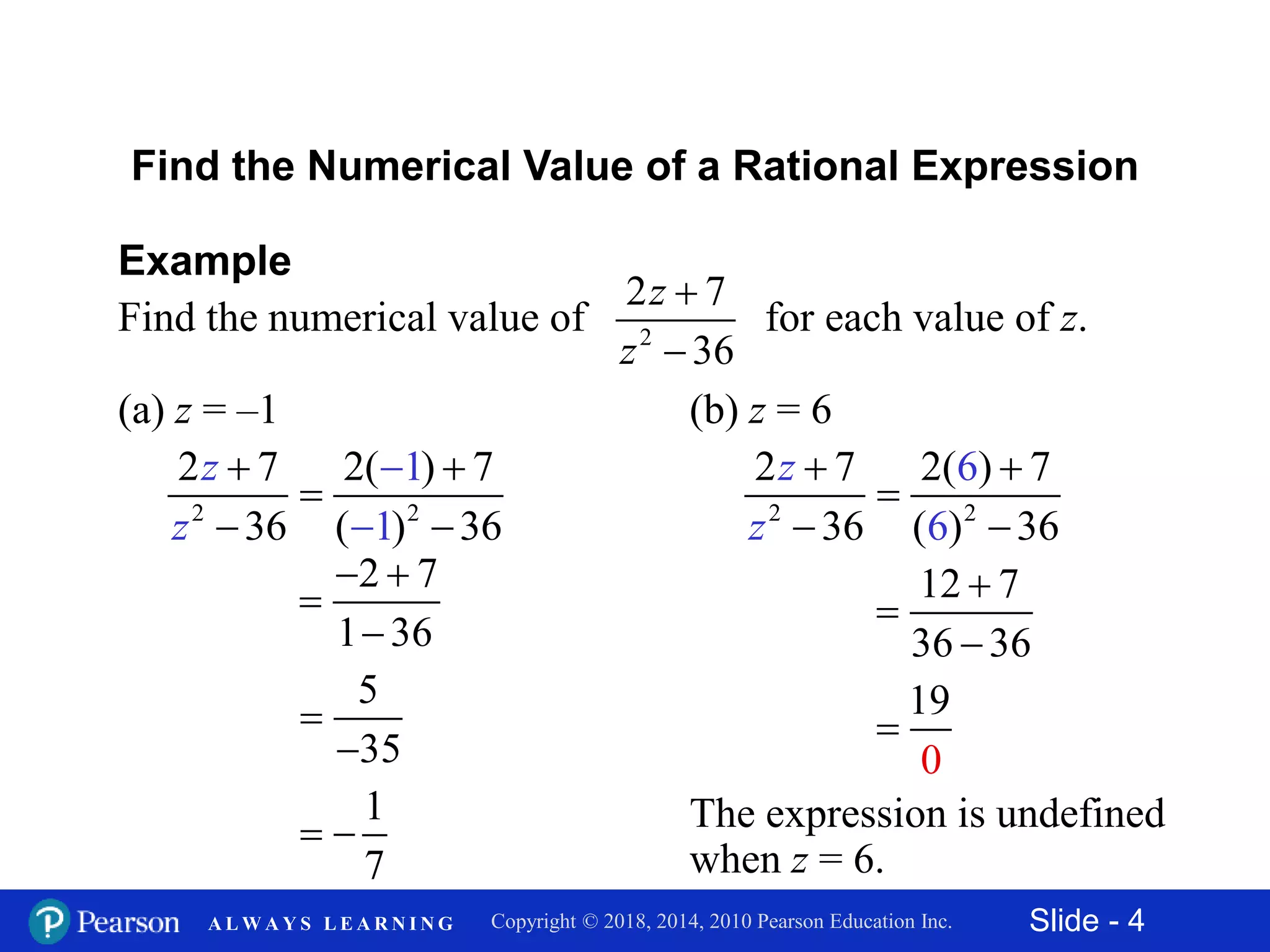
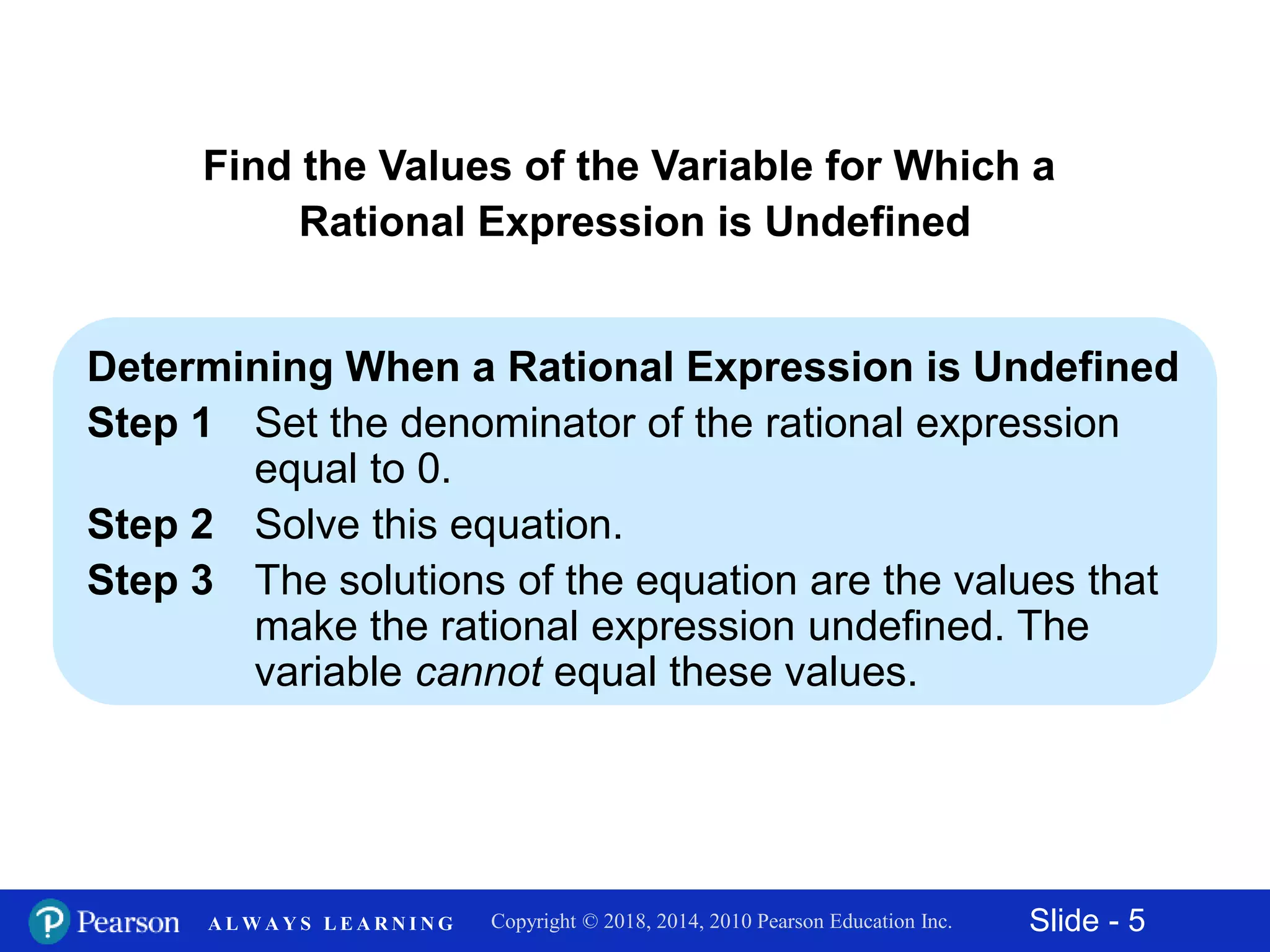
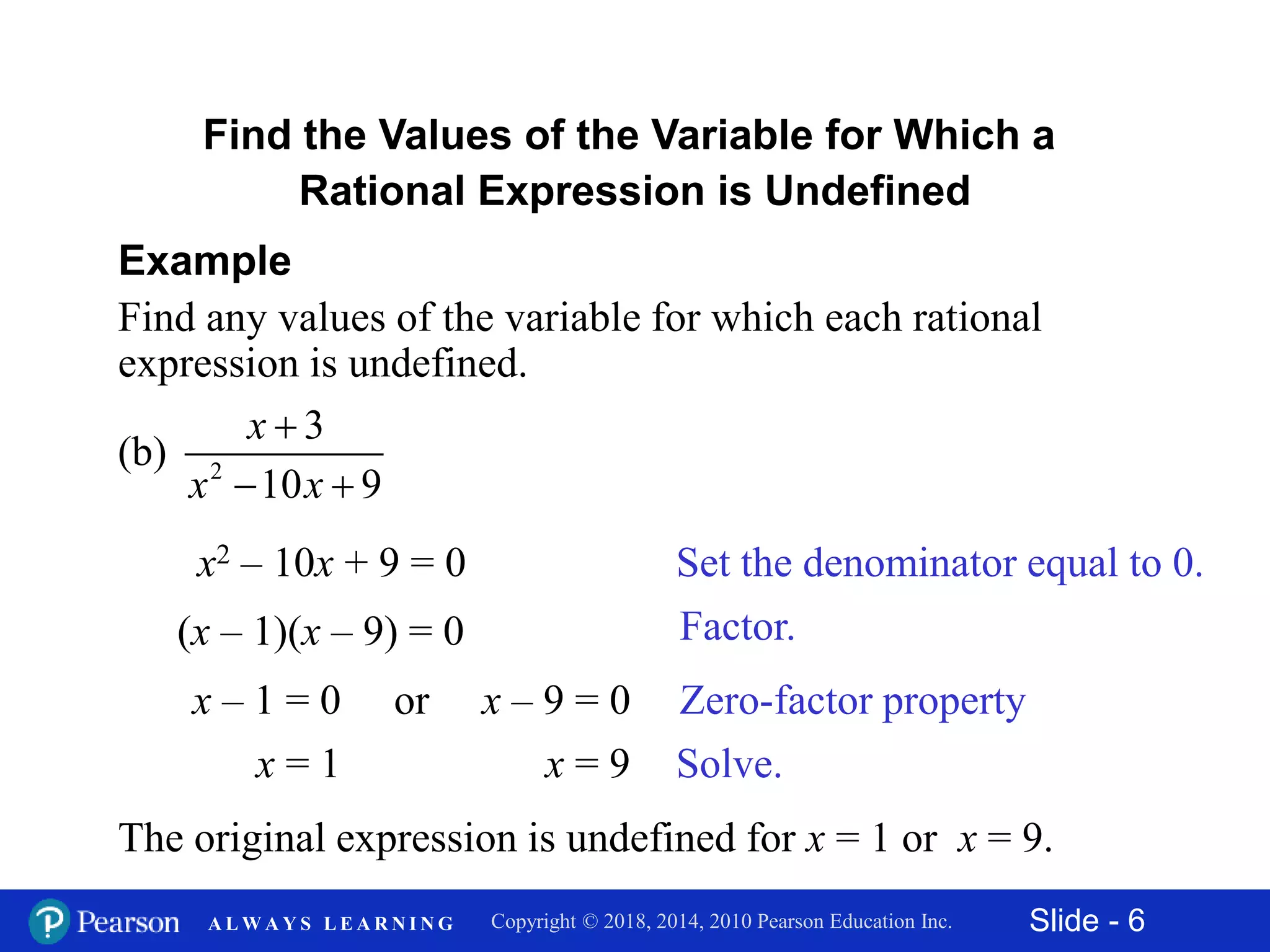
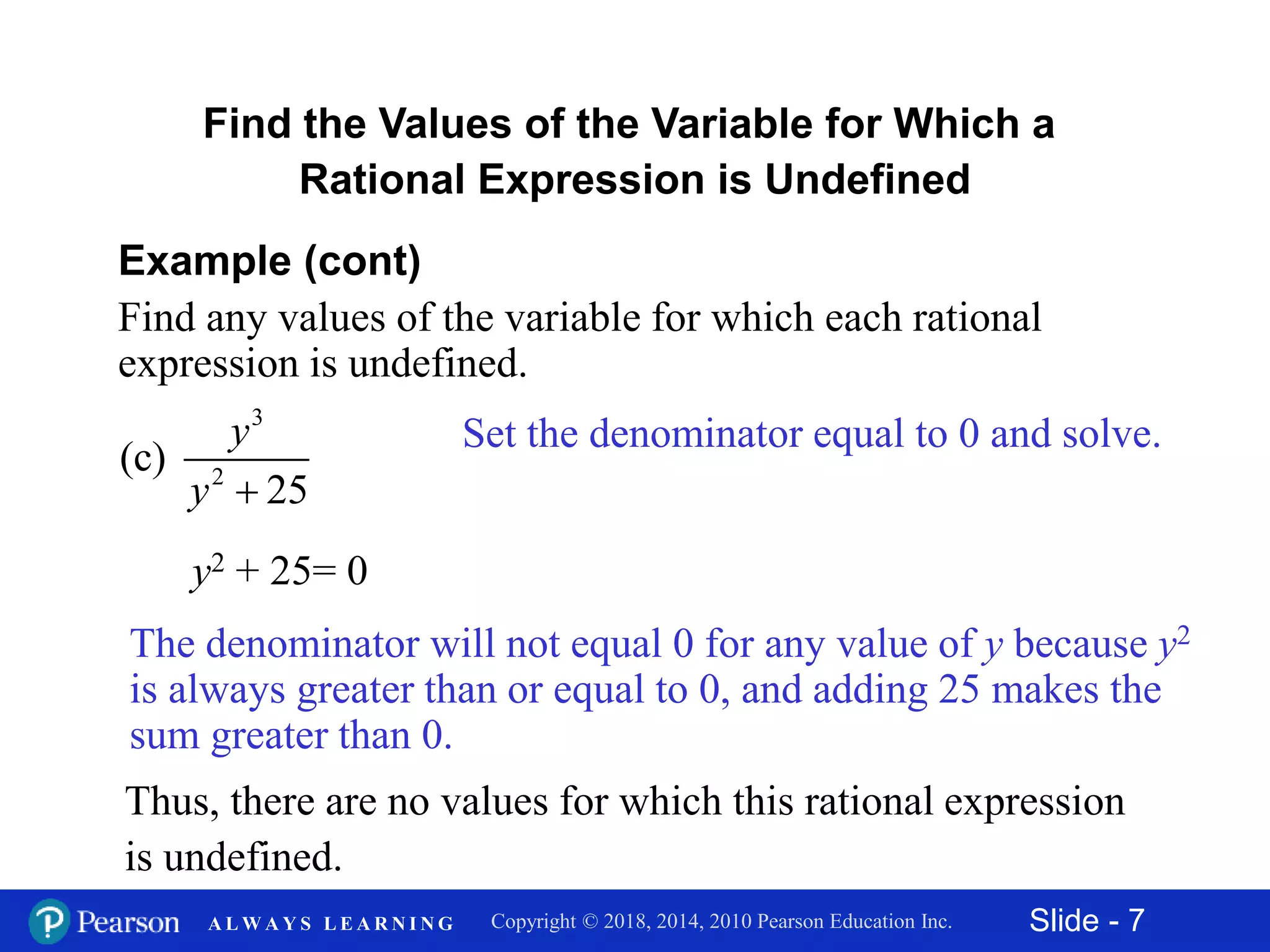
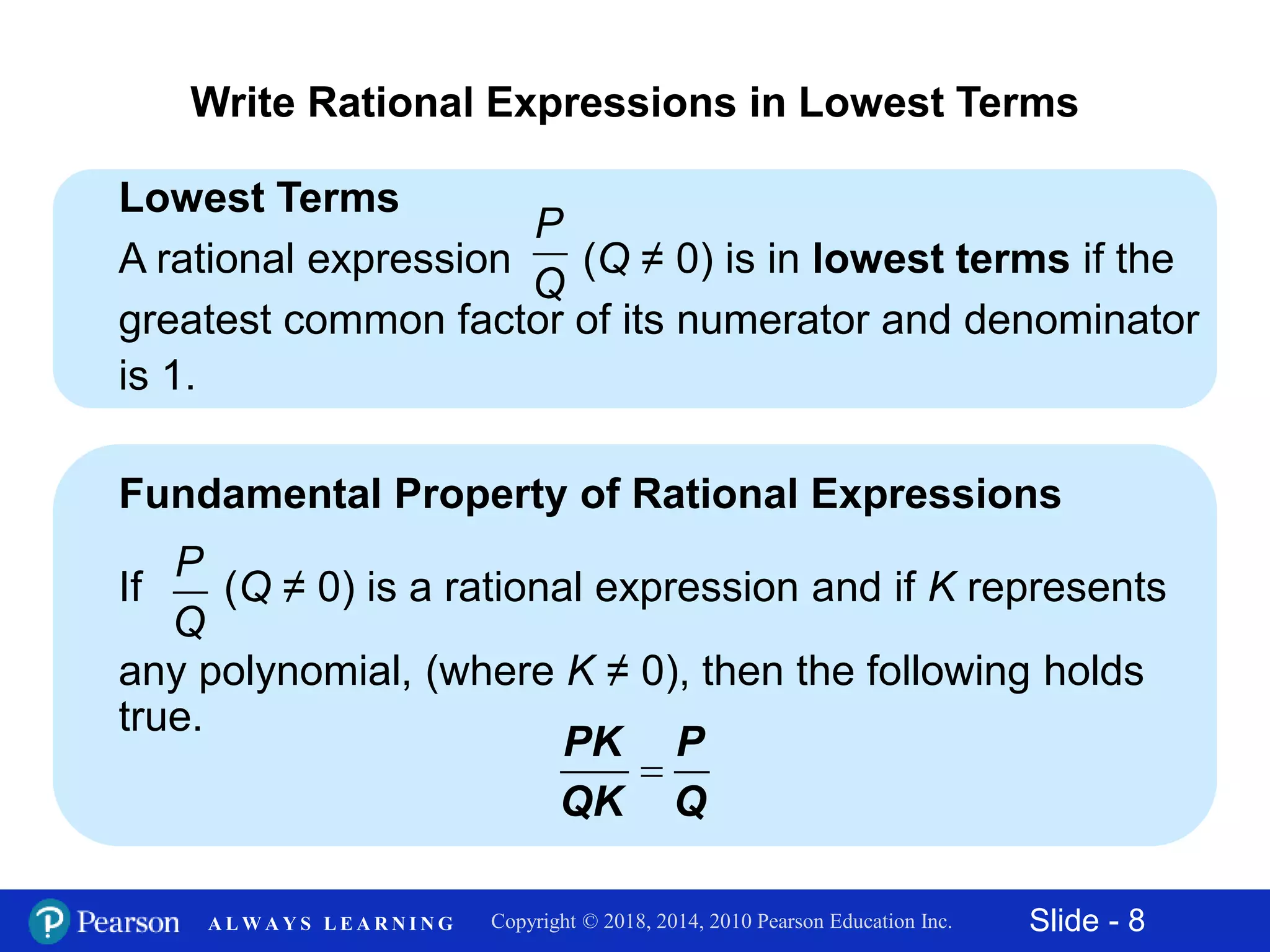
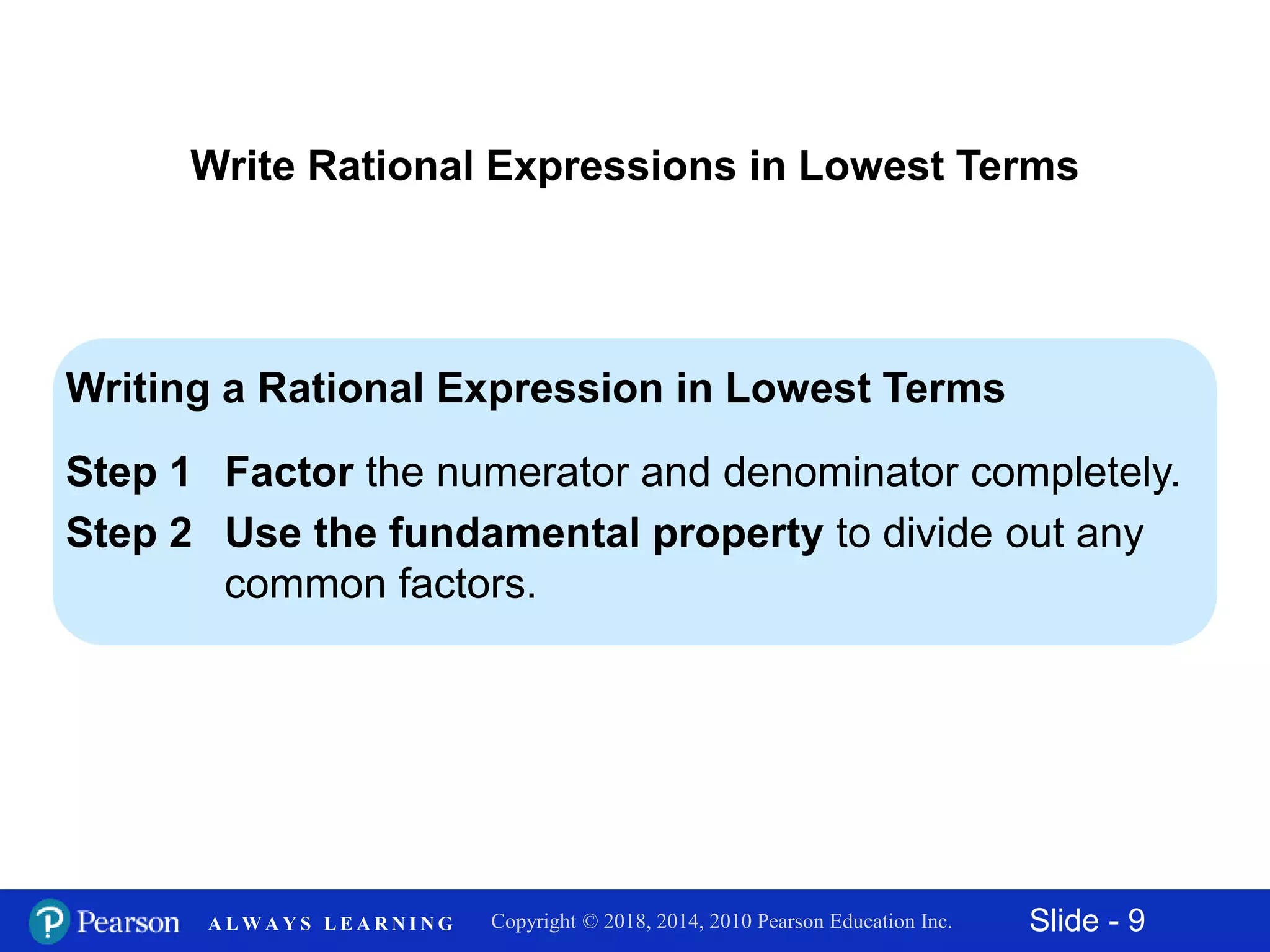
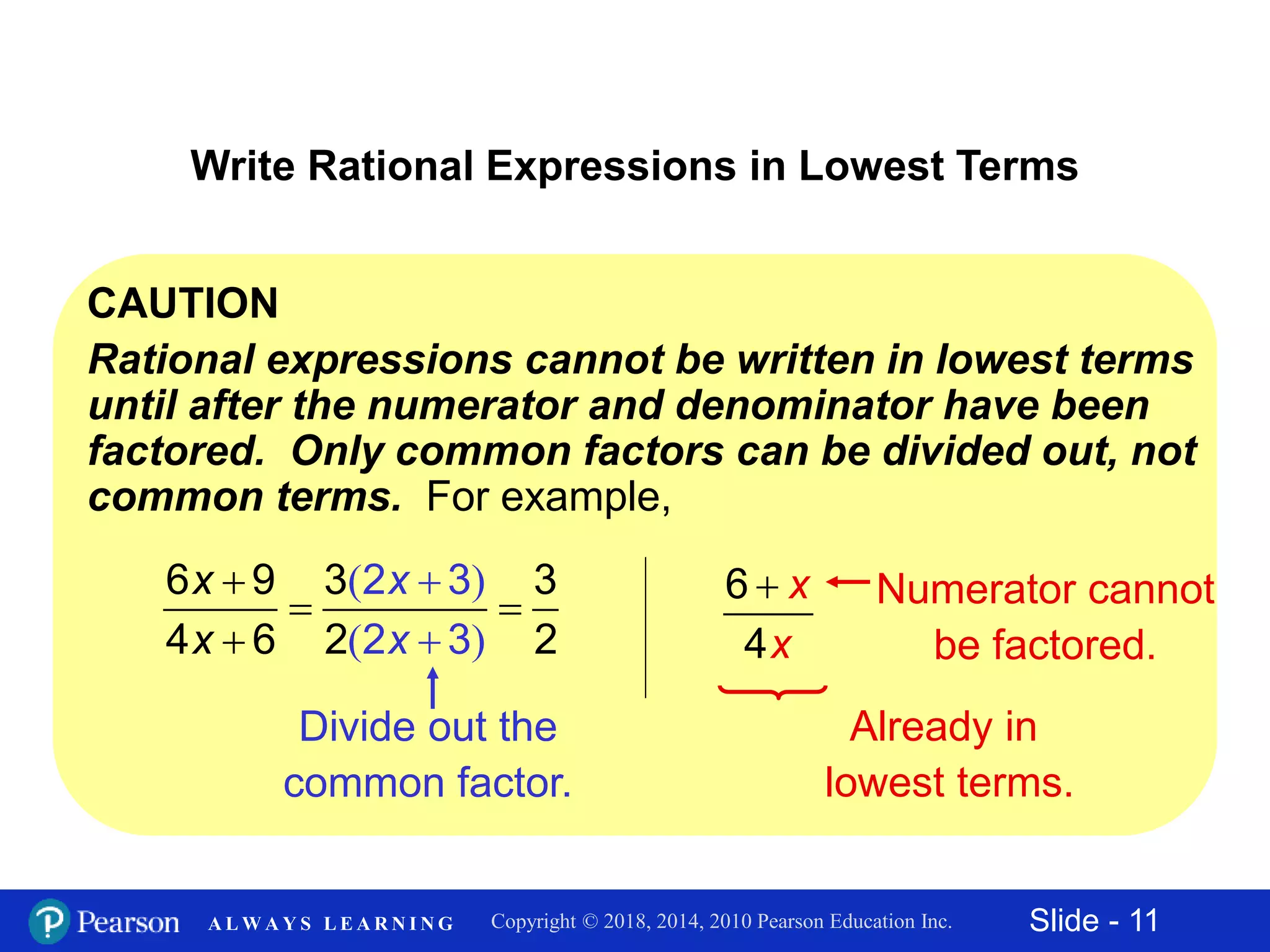
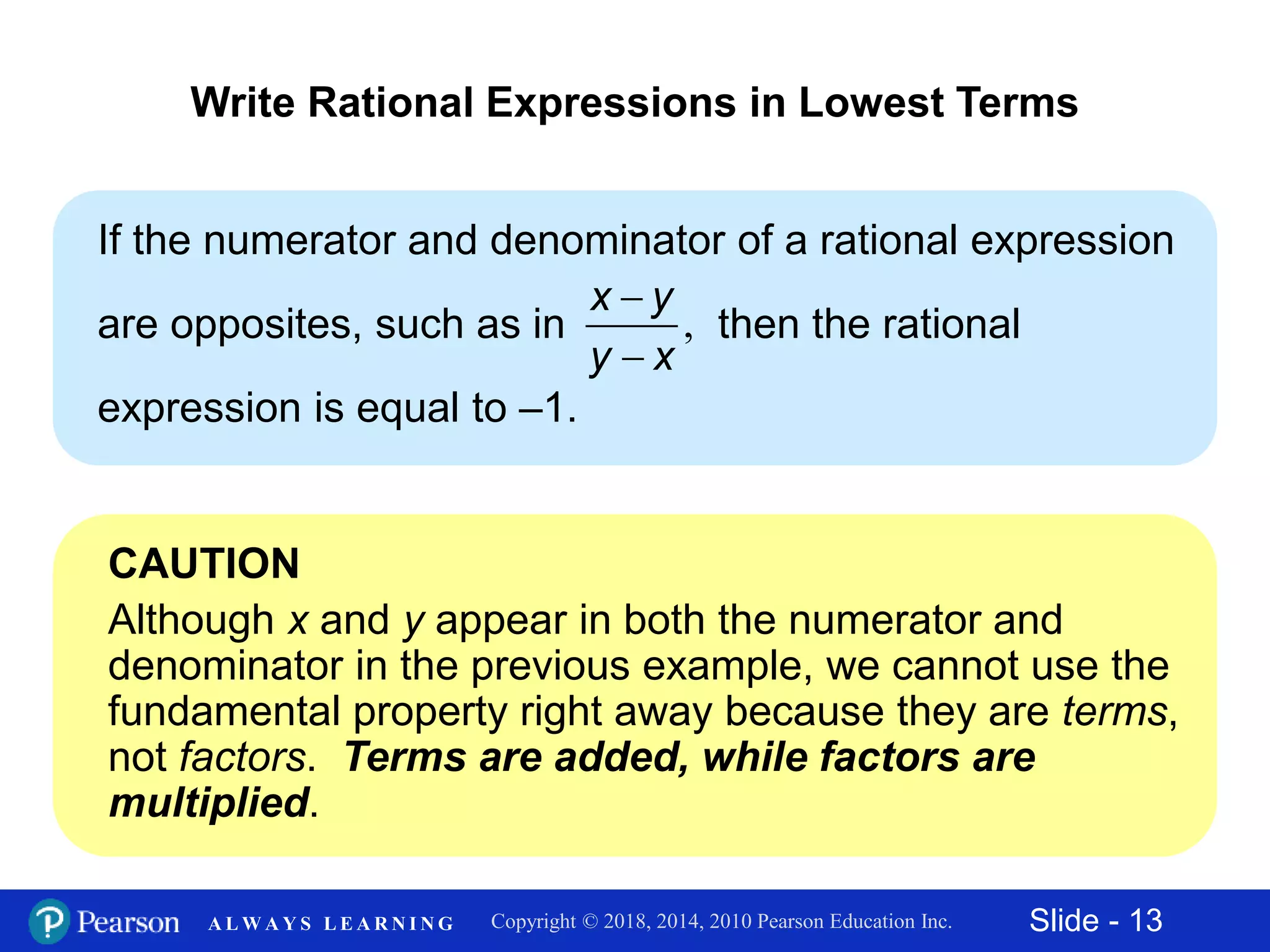
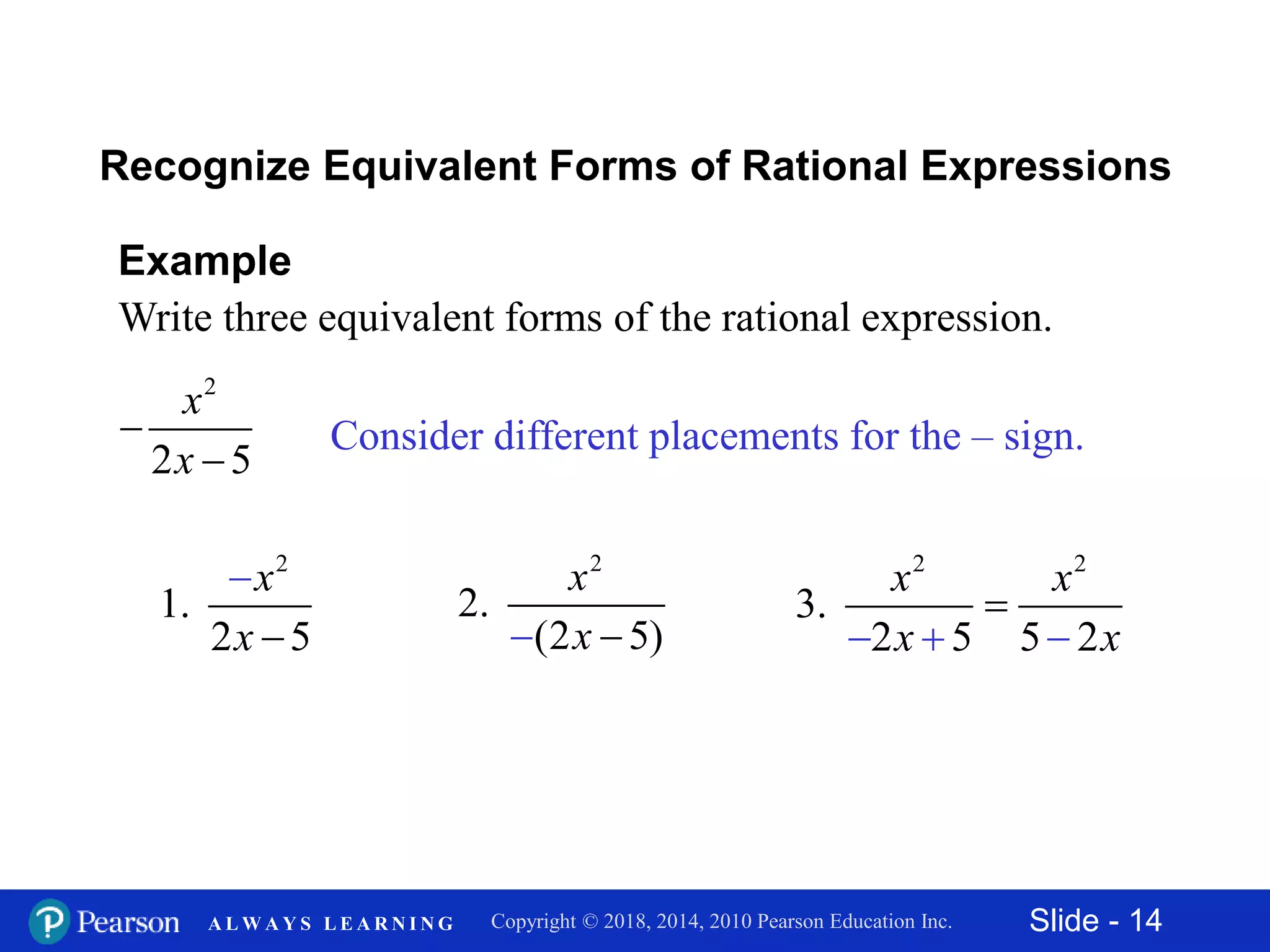
This document discusses rational expressions and their applications. It covers objectives like finding the numerical value of a rational expression, determining values that make a rational expression undefined, writing rational expressions in lowest terms, and recognizing equivalent forms. Some key points include the definition of a rational expression as P/Q where P and Q are polynomials and Q ≠ 0, setting the denominator equal to 0 to find undefined values, and using the fundamental property of rational expressions to write expressions in lowest terms by dividing out common factors. Examples are provided for each concept.