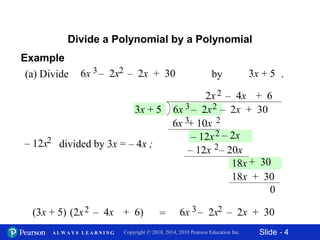
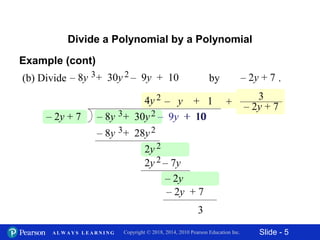
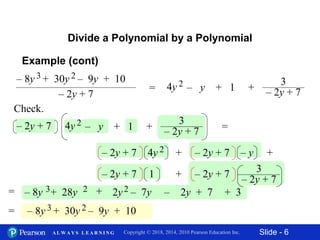
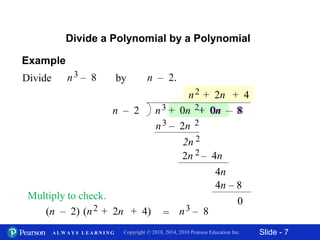
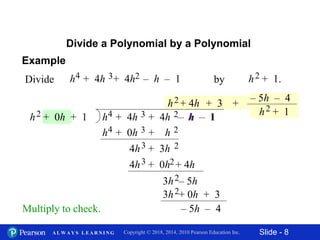
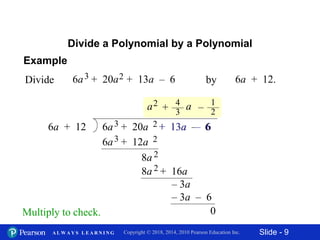
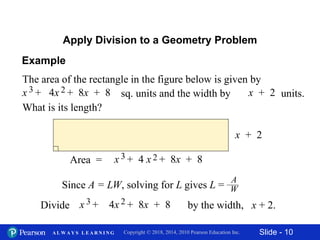
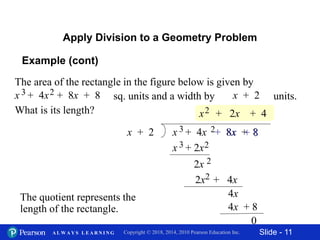
This document contains 11 slides about dividing polynomials by polynomials. It provides examples of dividing polynomials with variables like x, y, h, a by other polynomials. It demonstrates setting up the long division and checking the work by multiplication. One slide applies the division concept to find the length of a rectangle given its area and width as polynomials. The overall document teaches how to divide polynomials and applies it to a geometry problem.