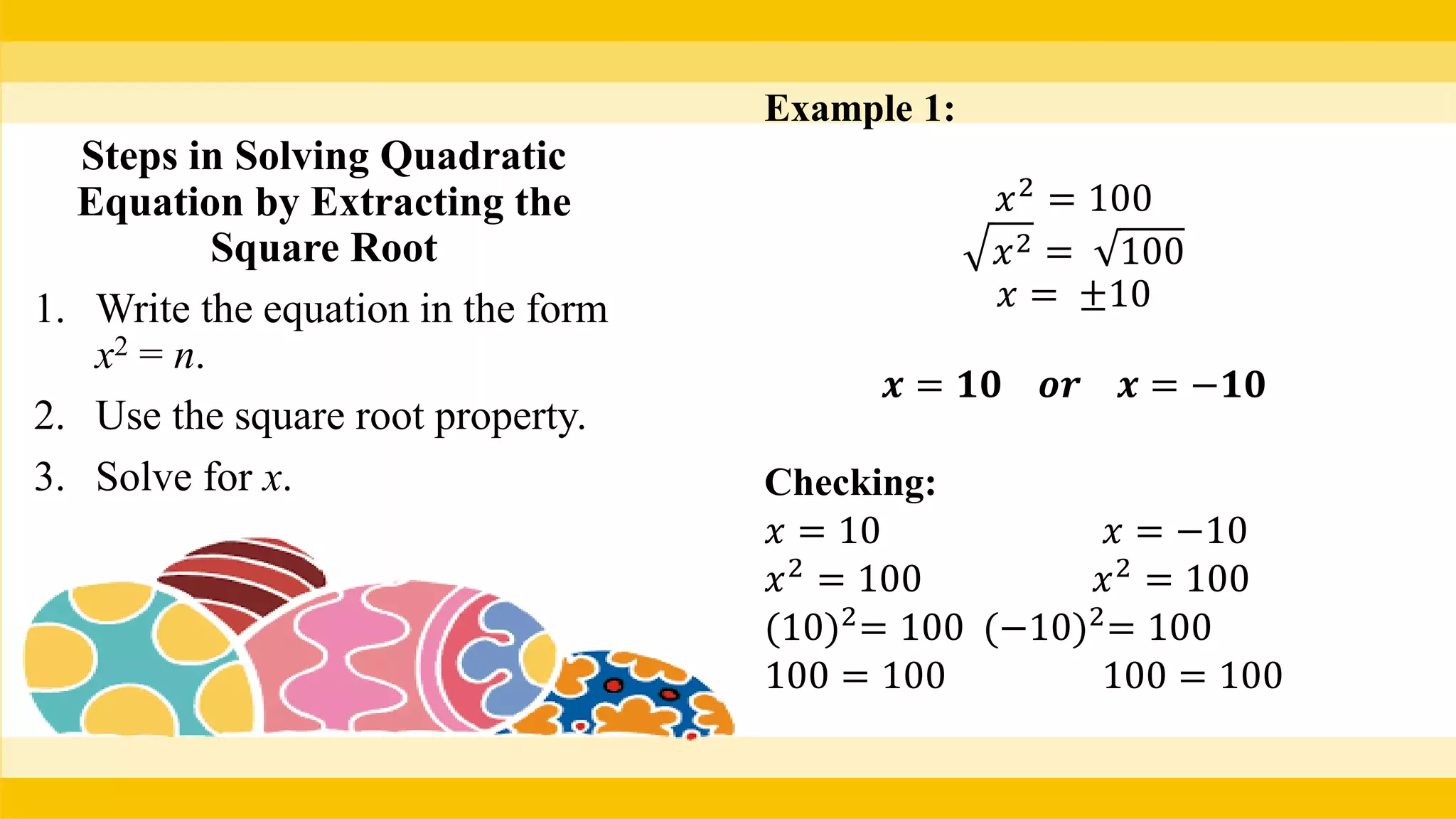
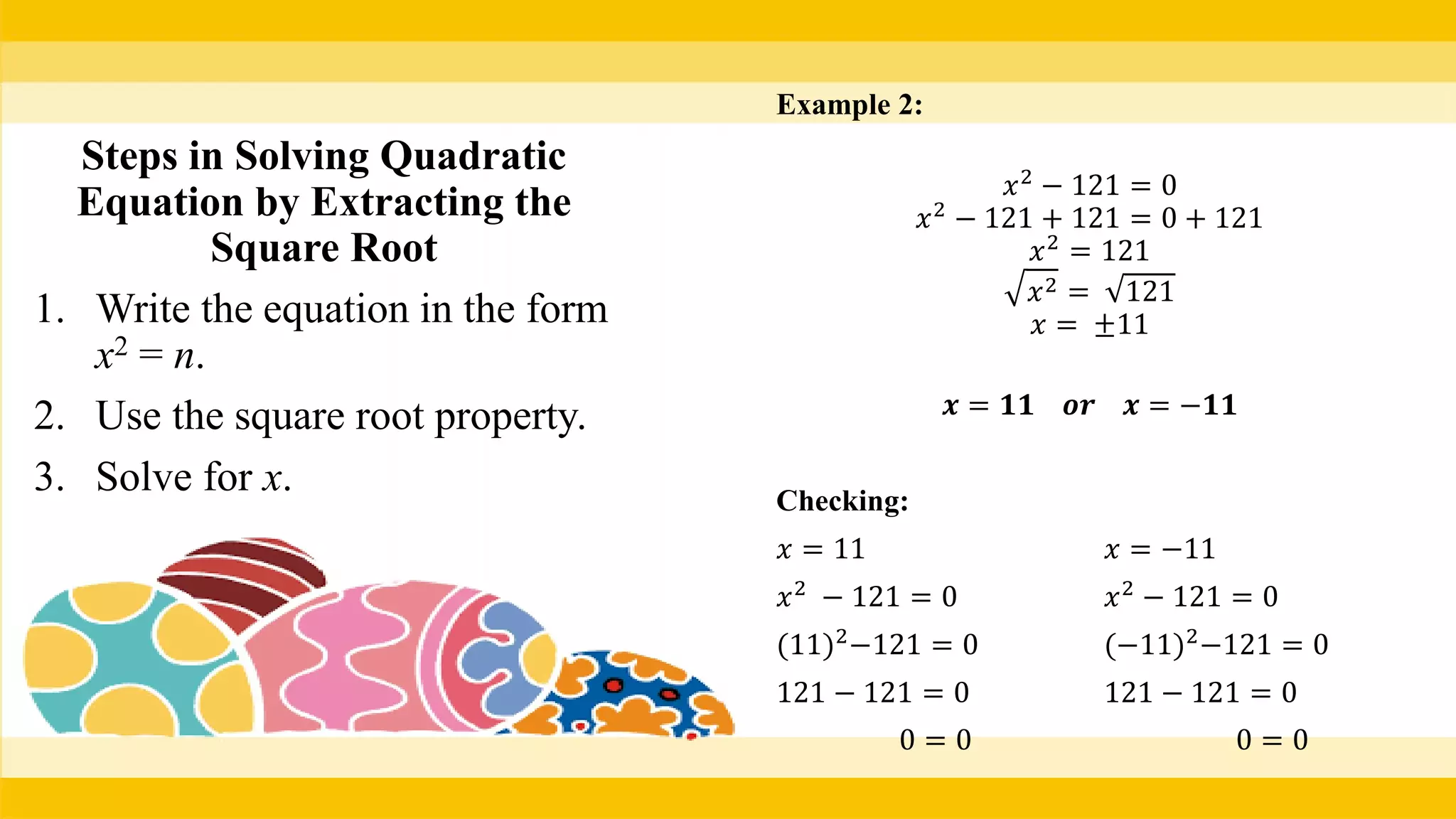
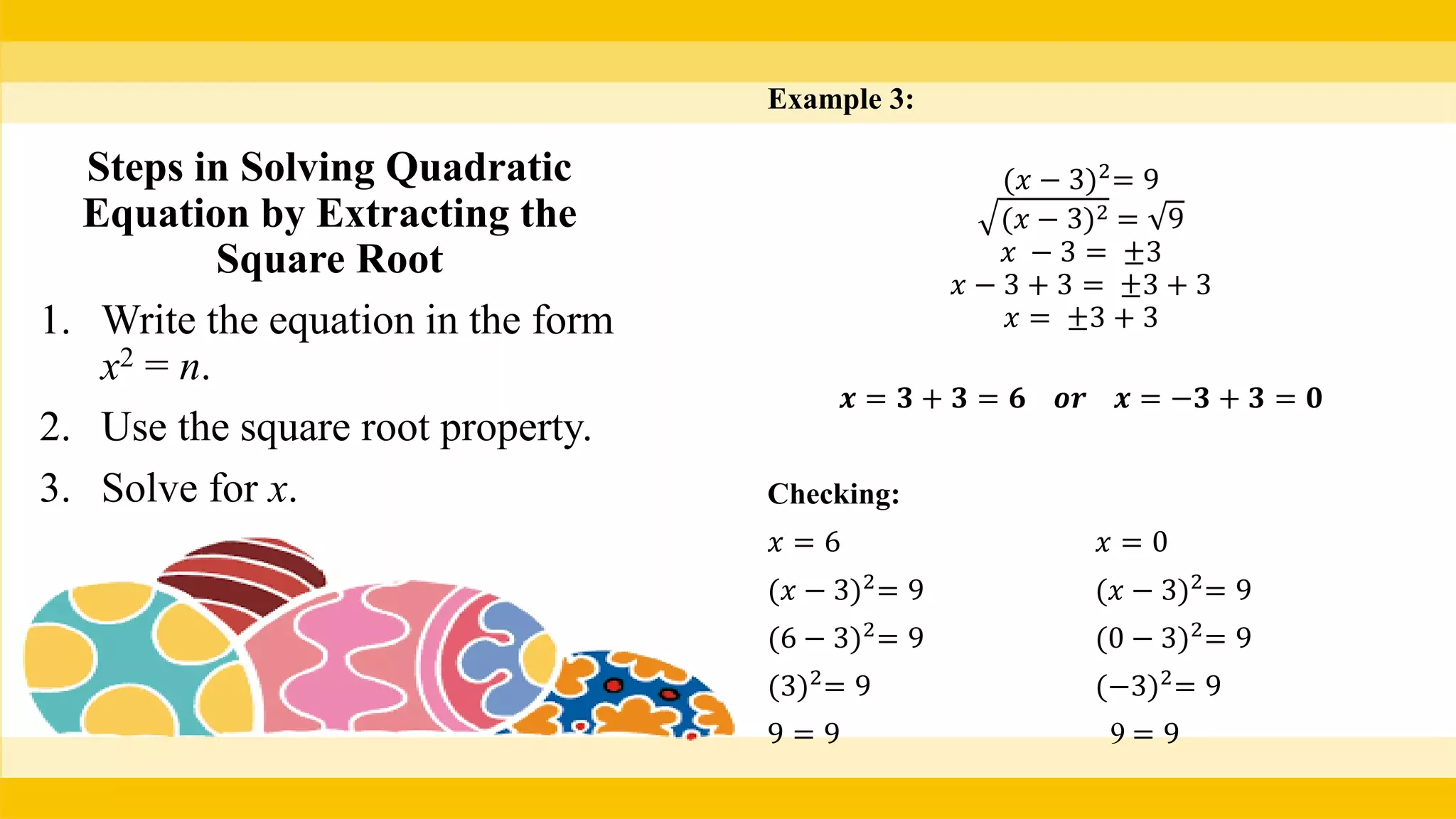
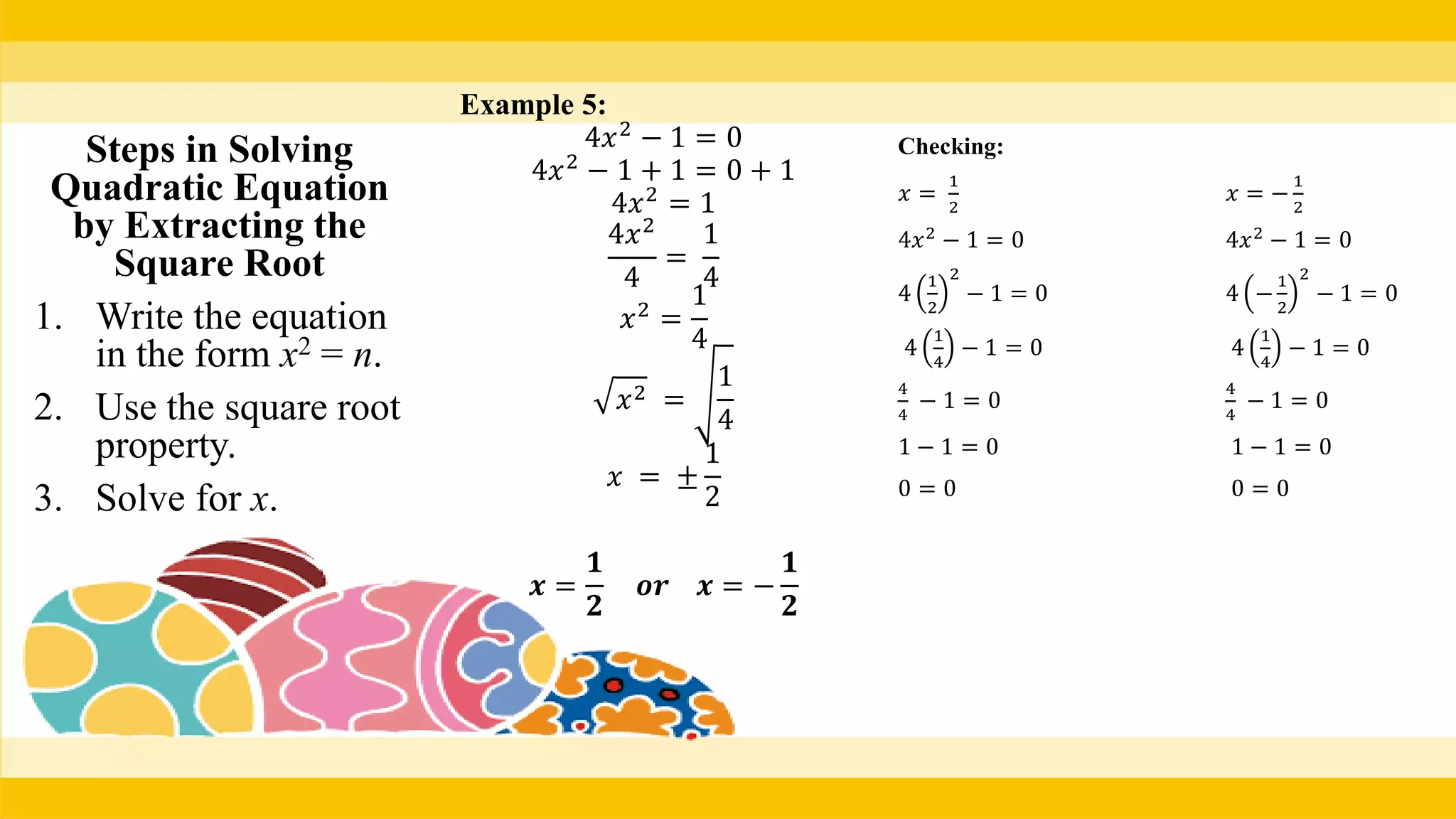
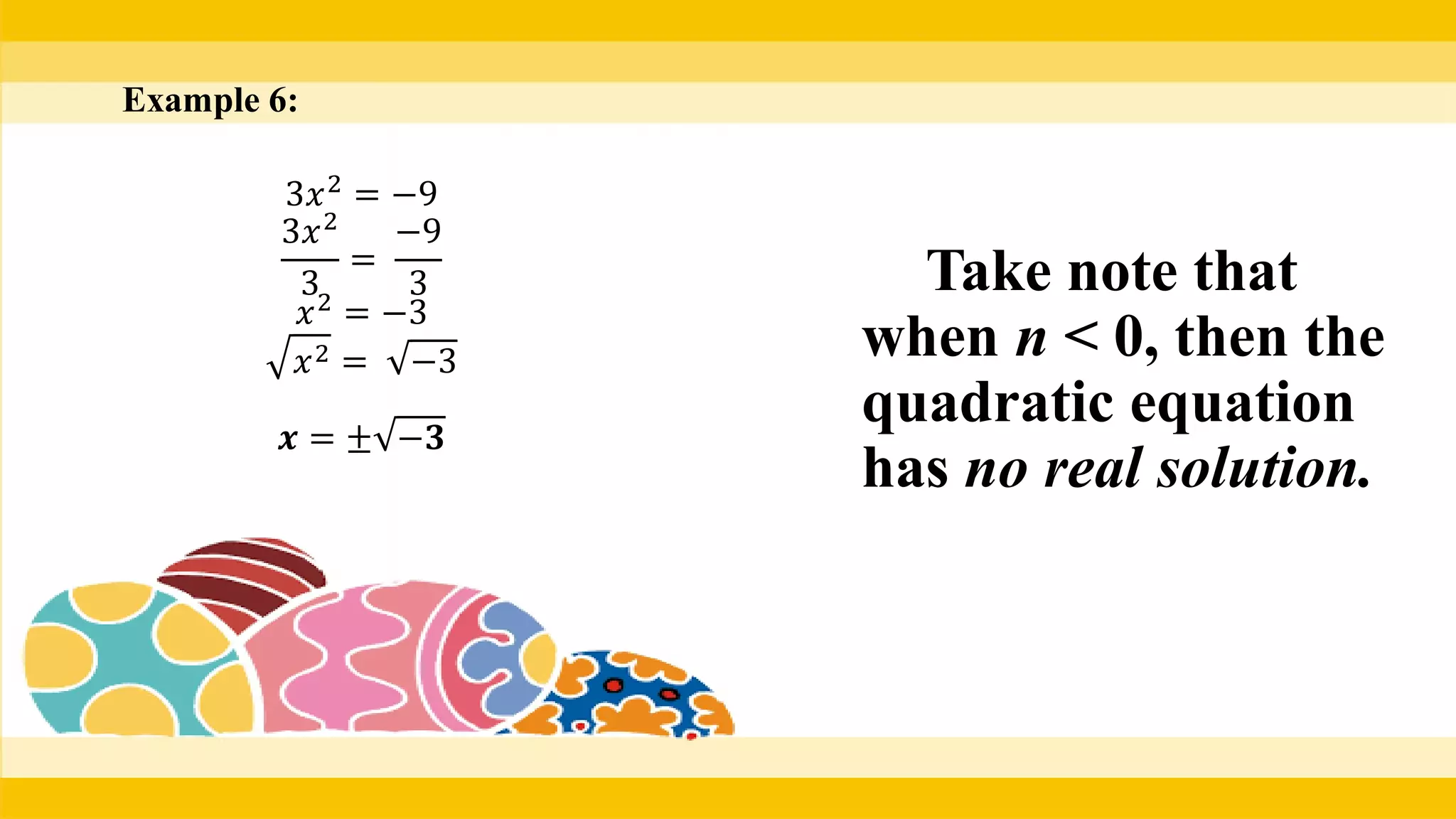
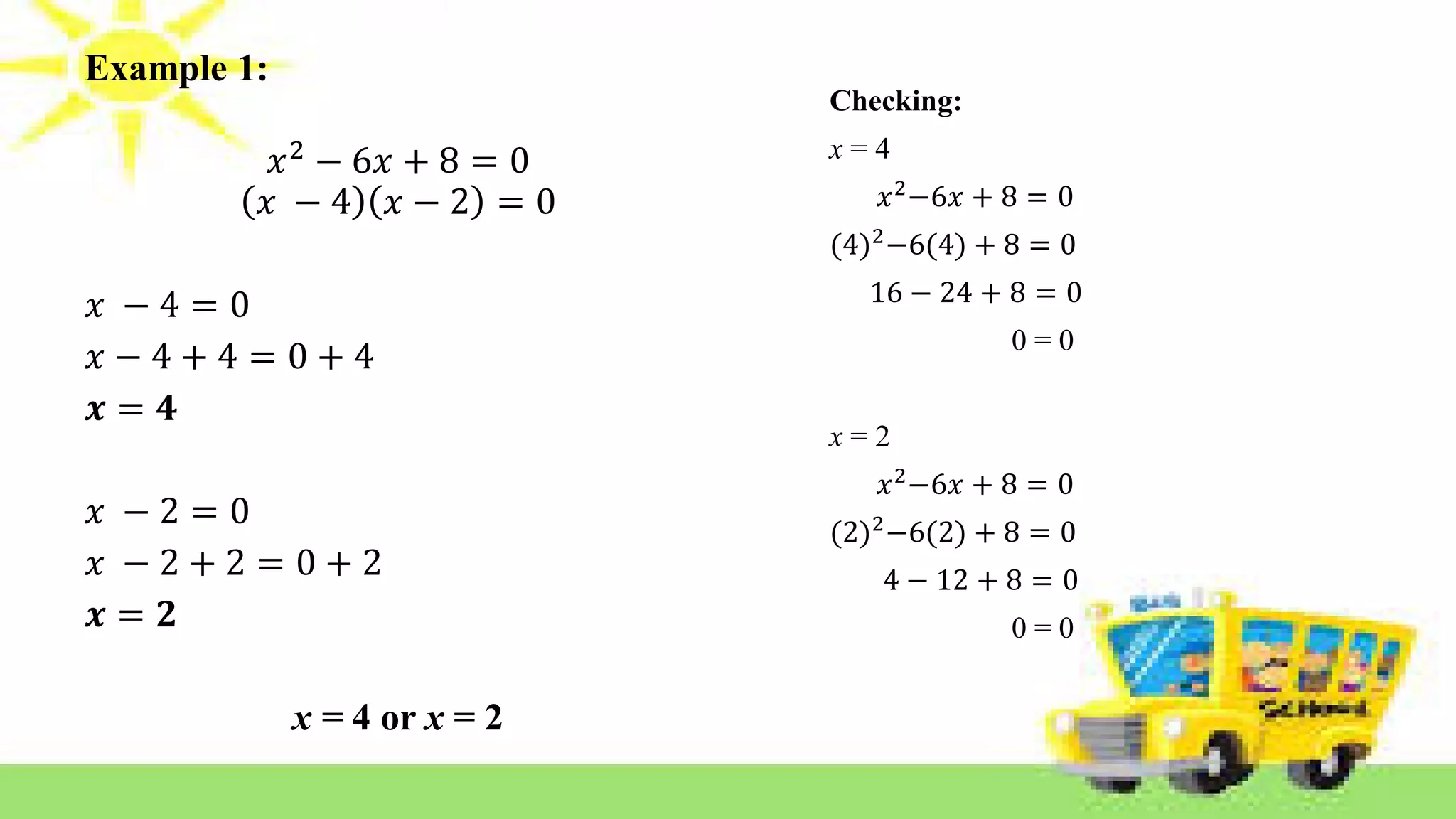
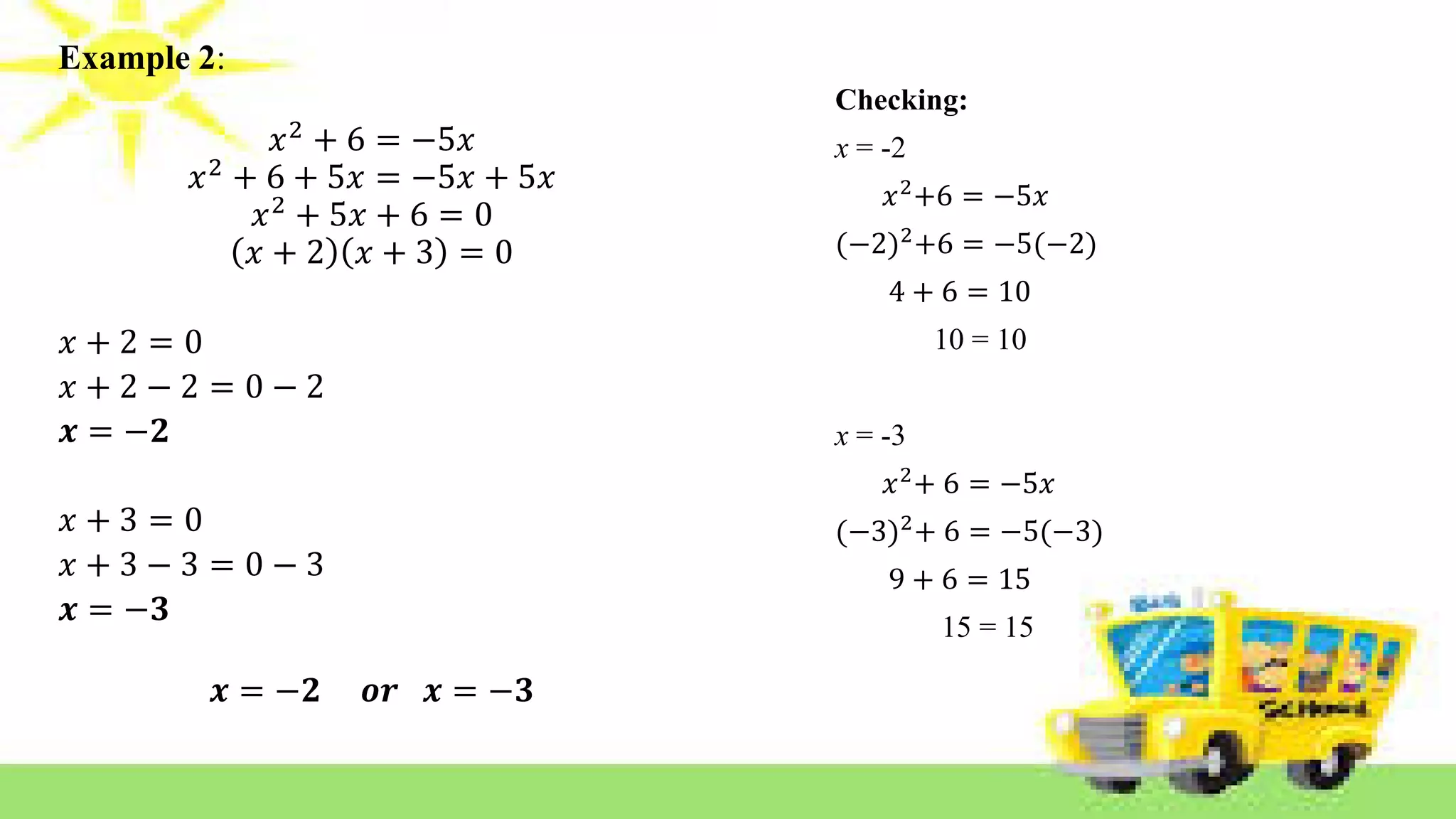
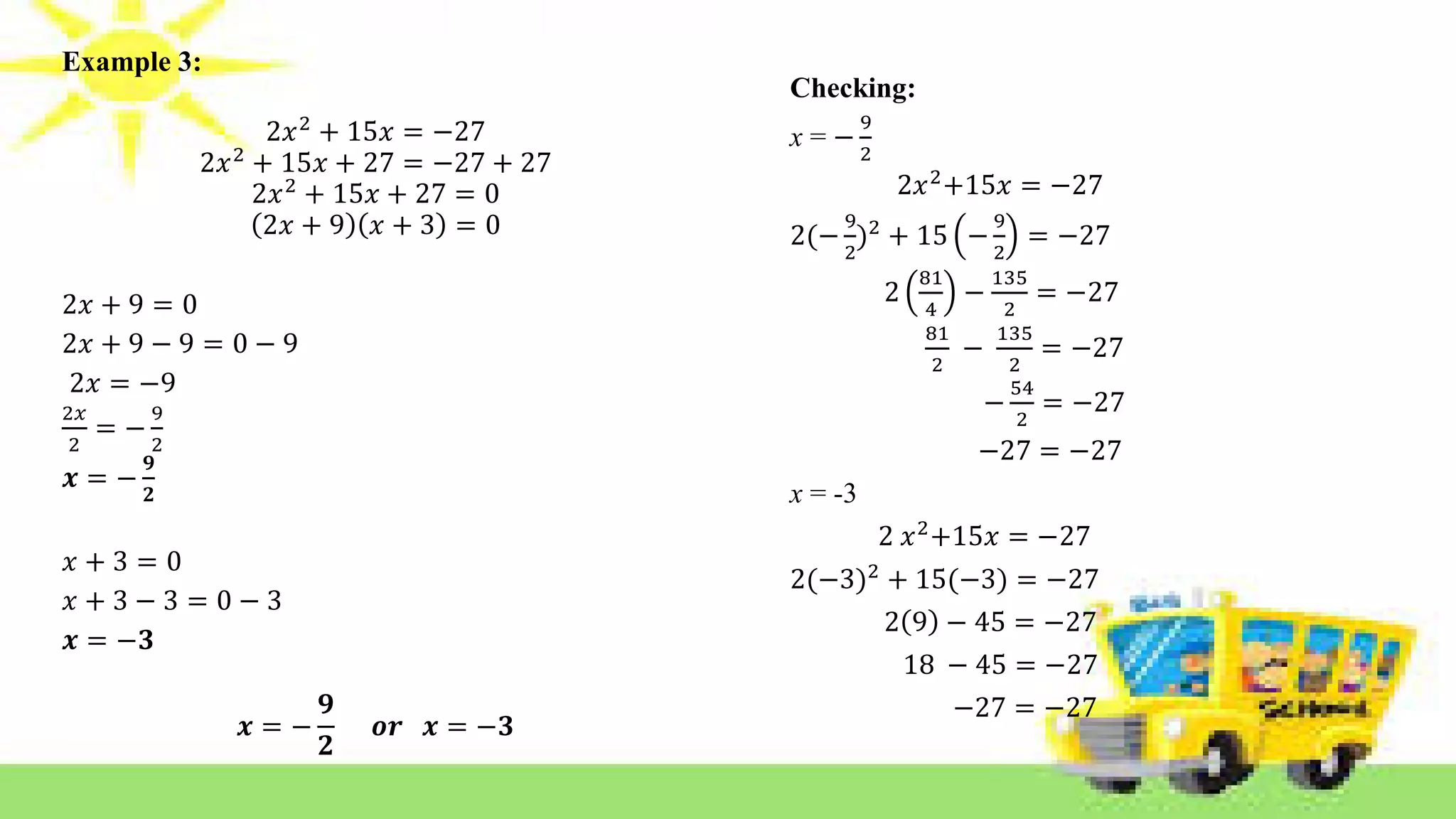
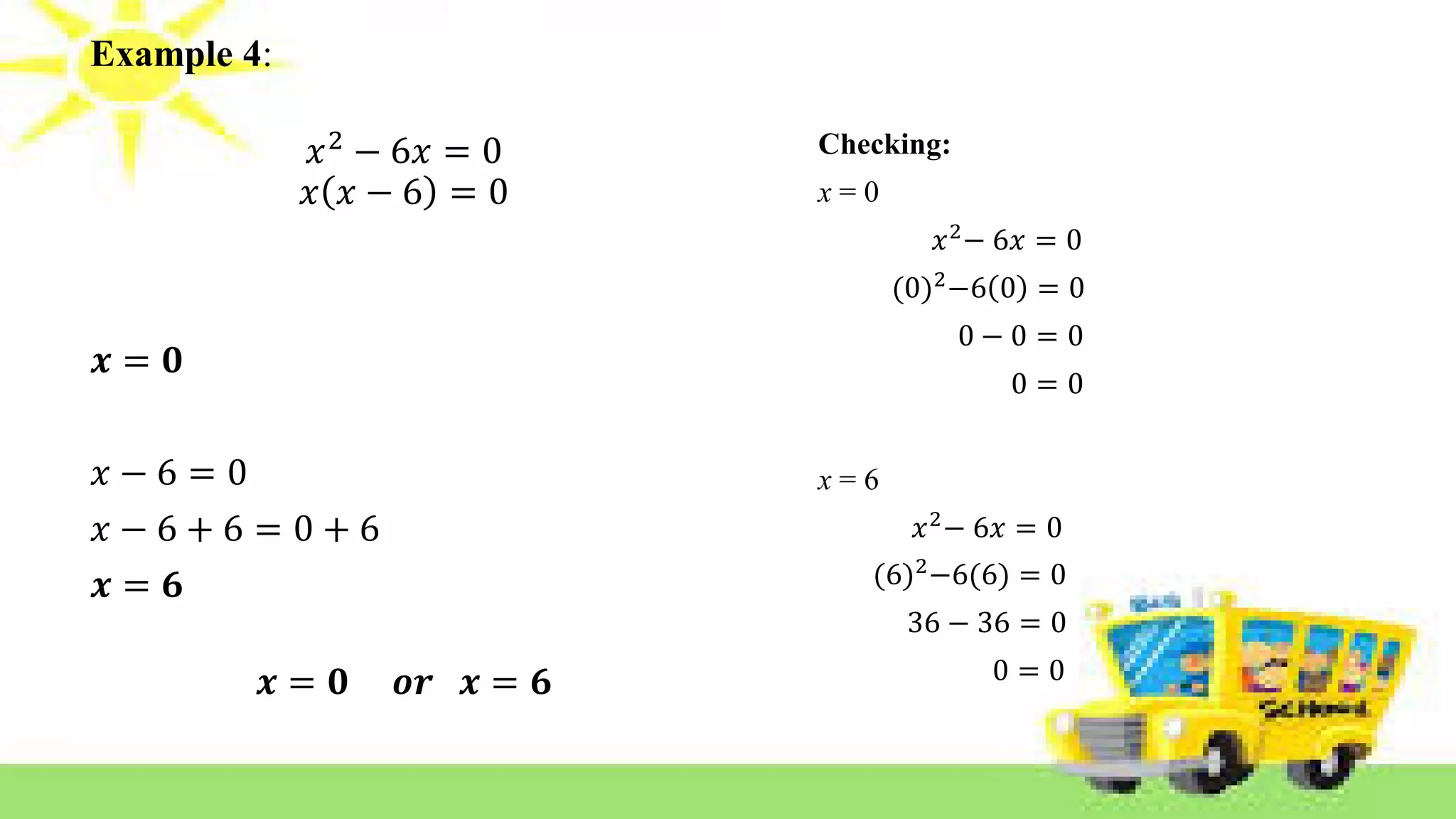
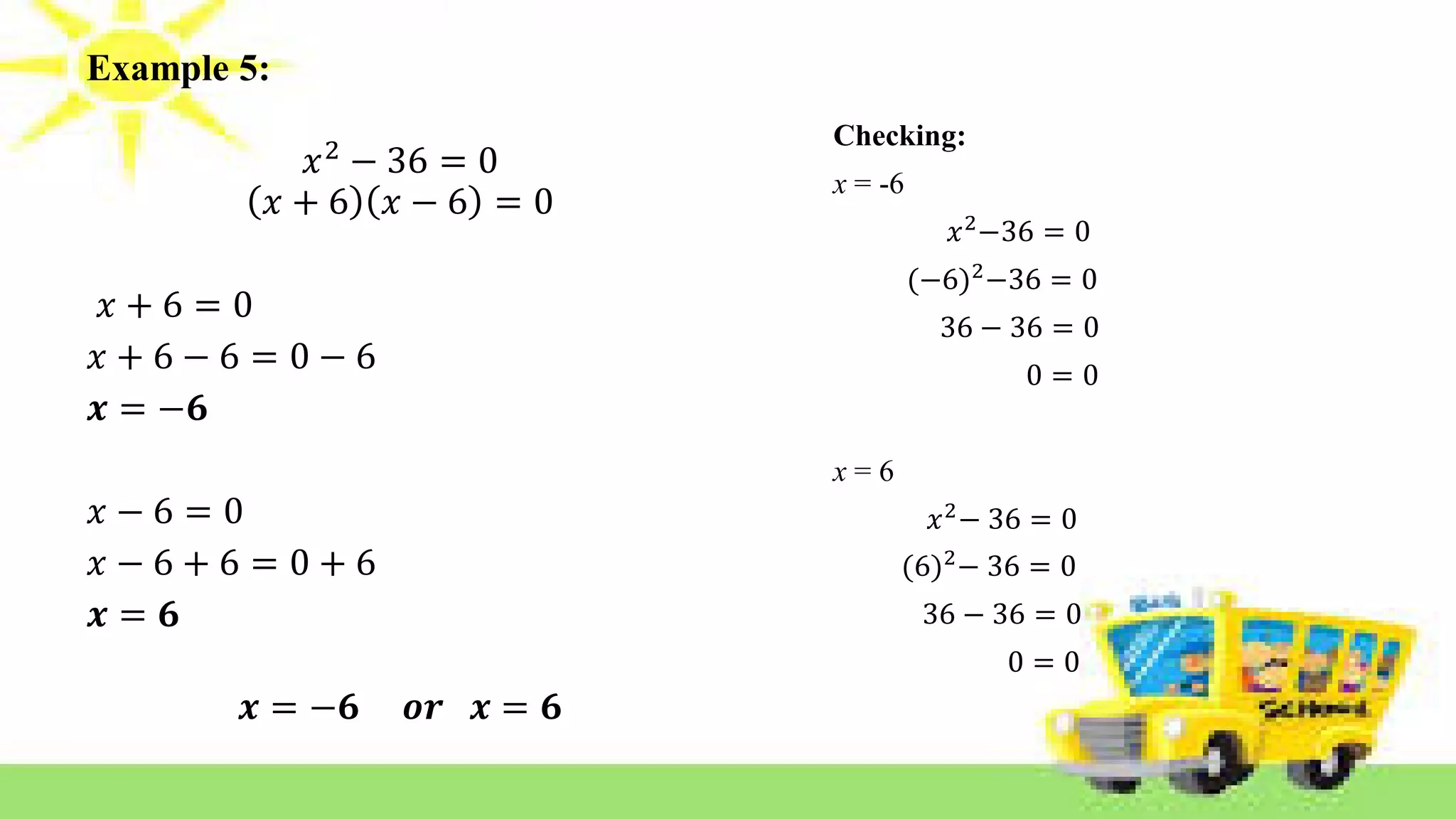
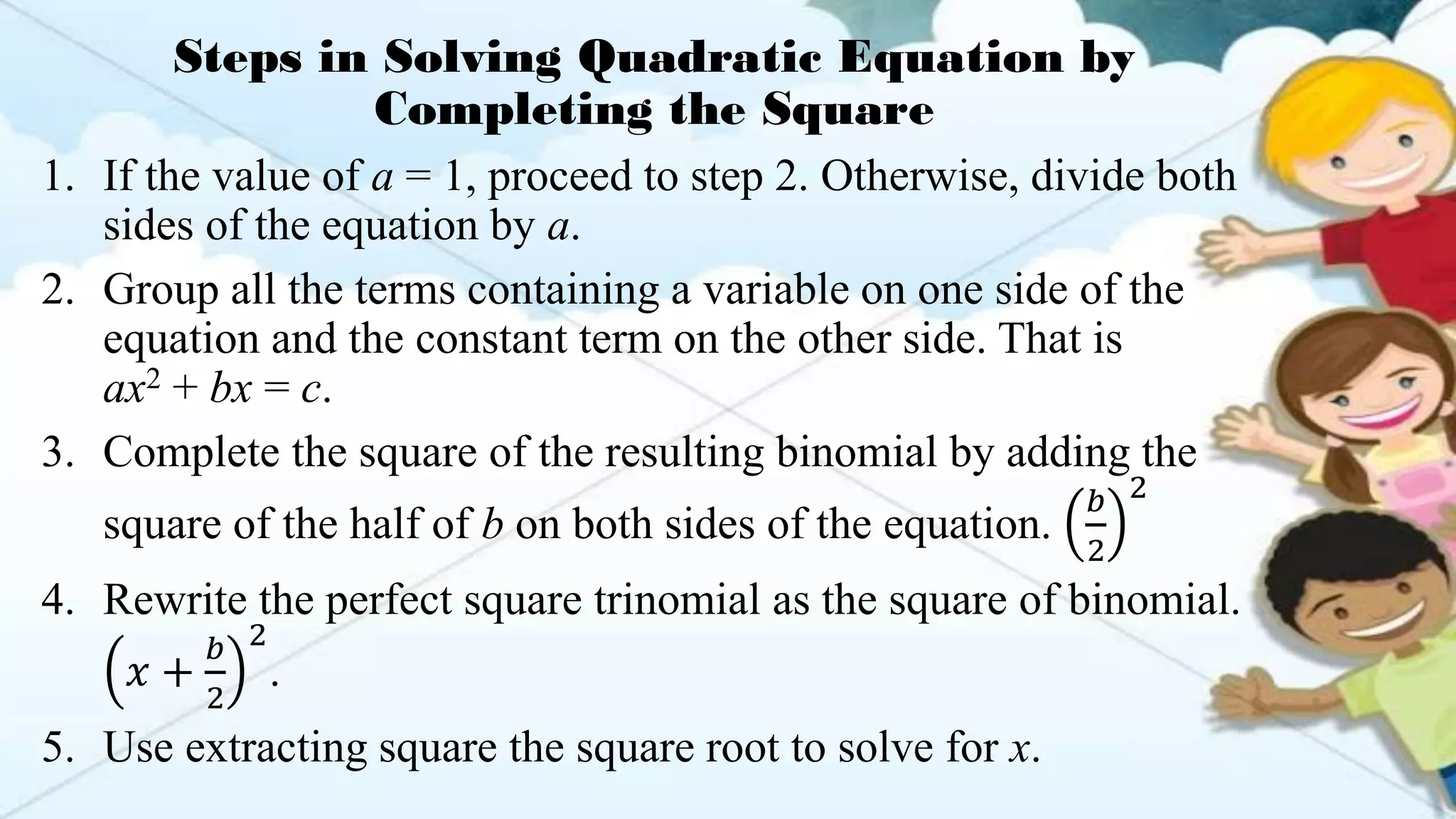
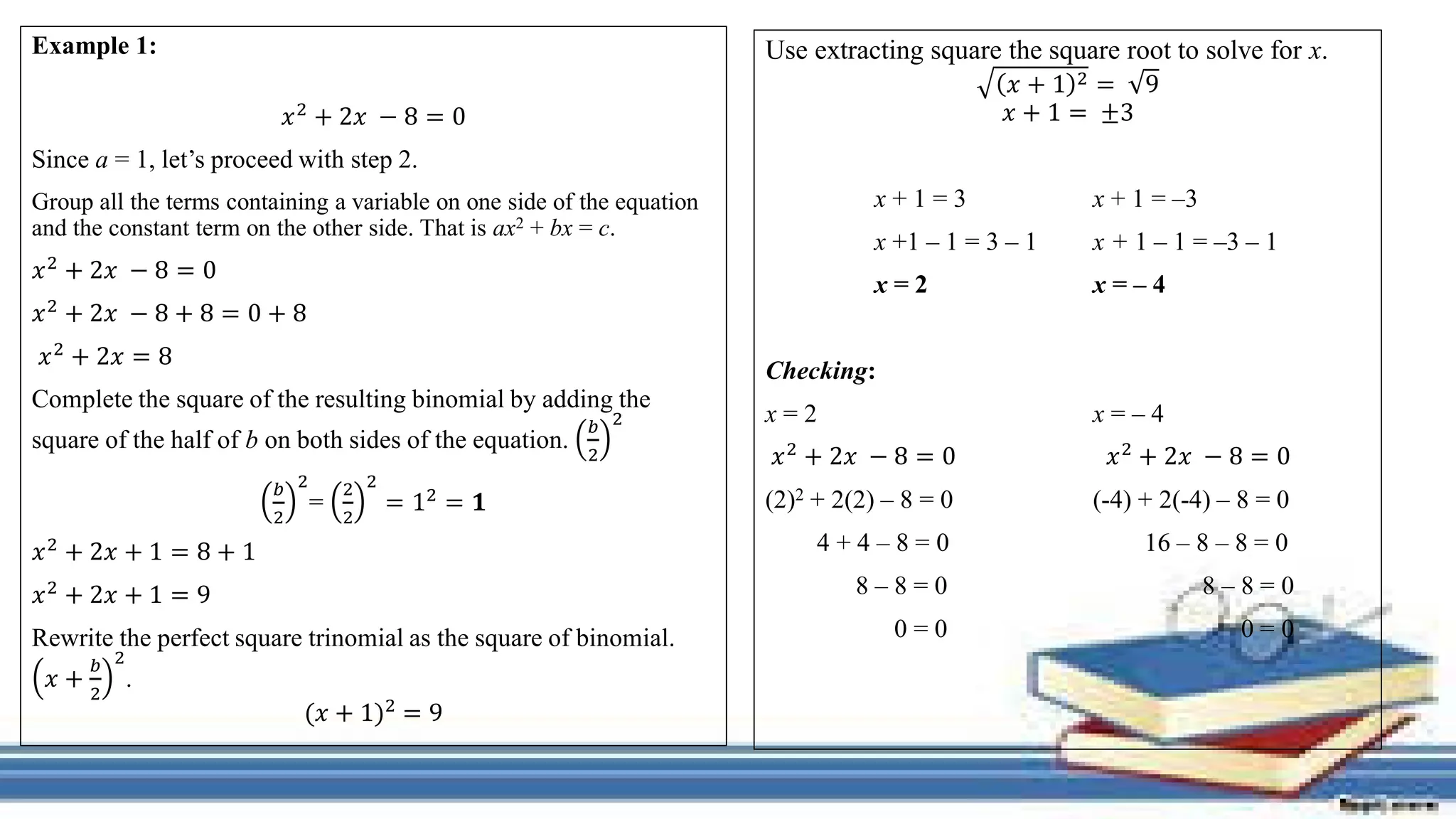
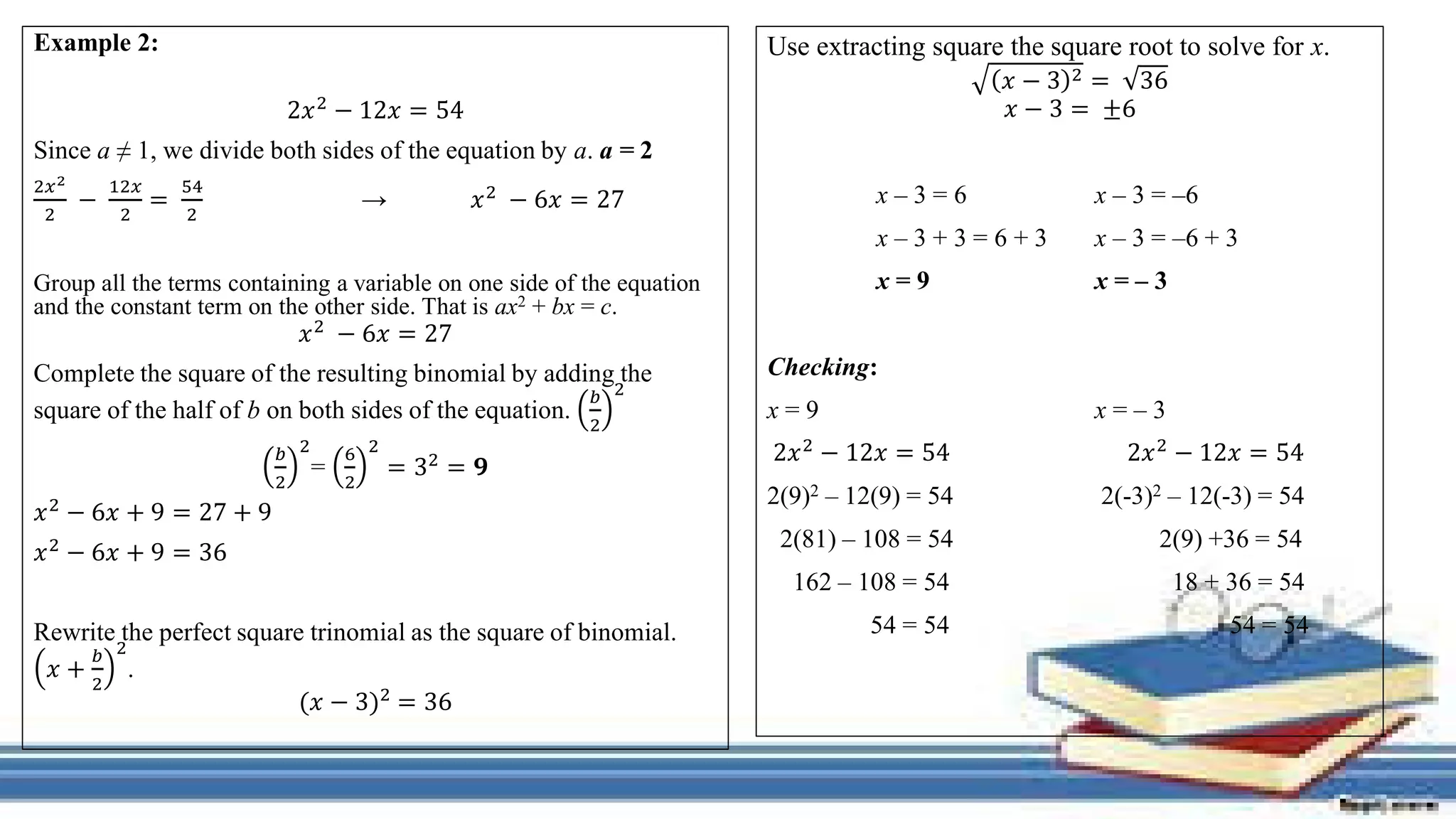
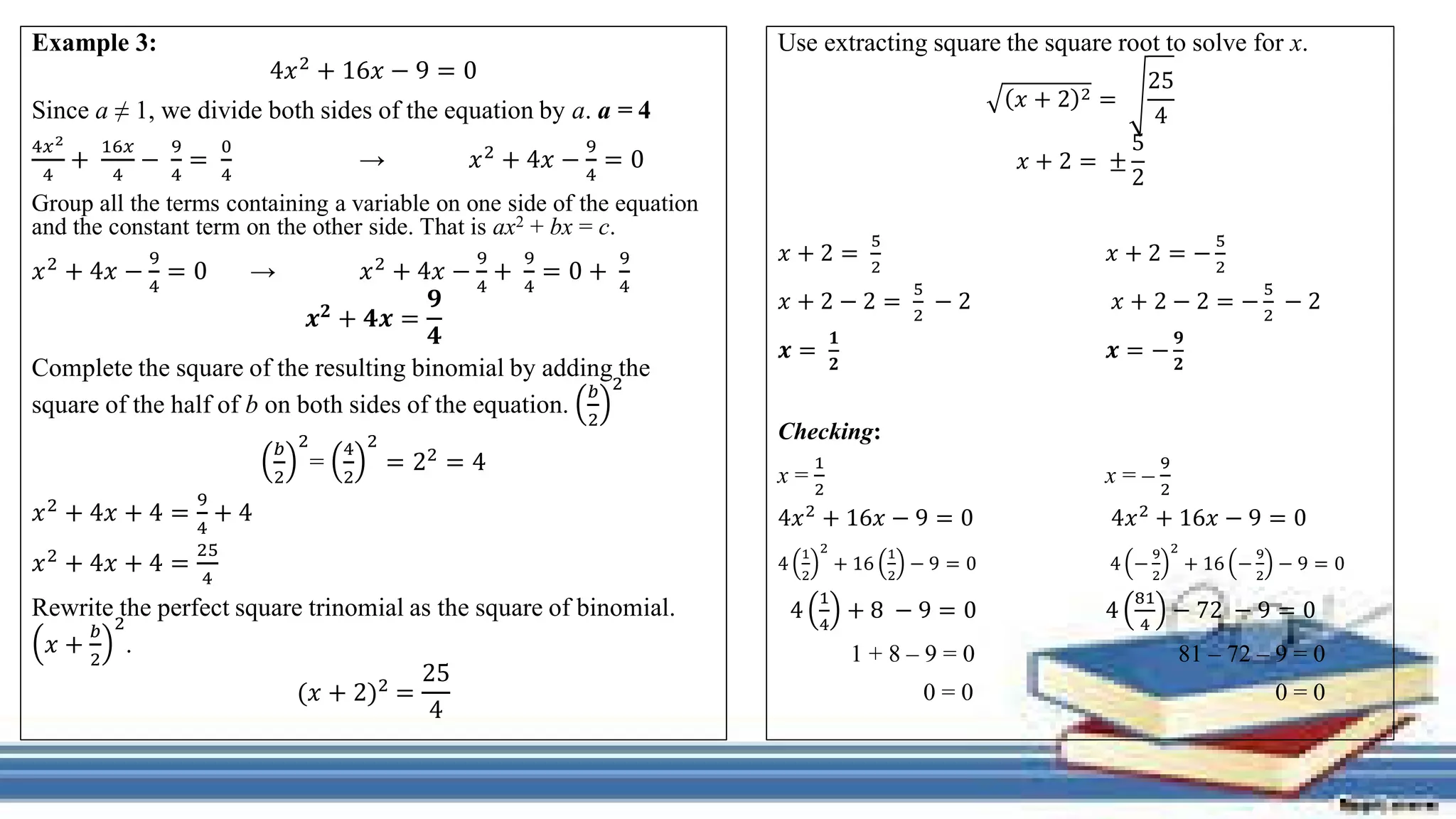
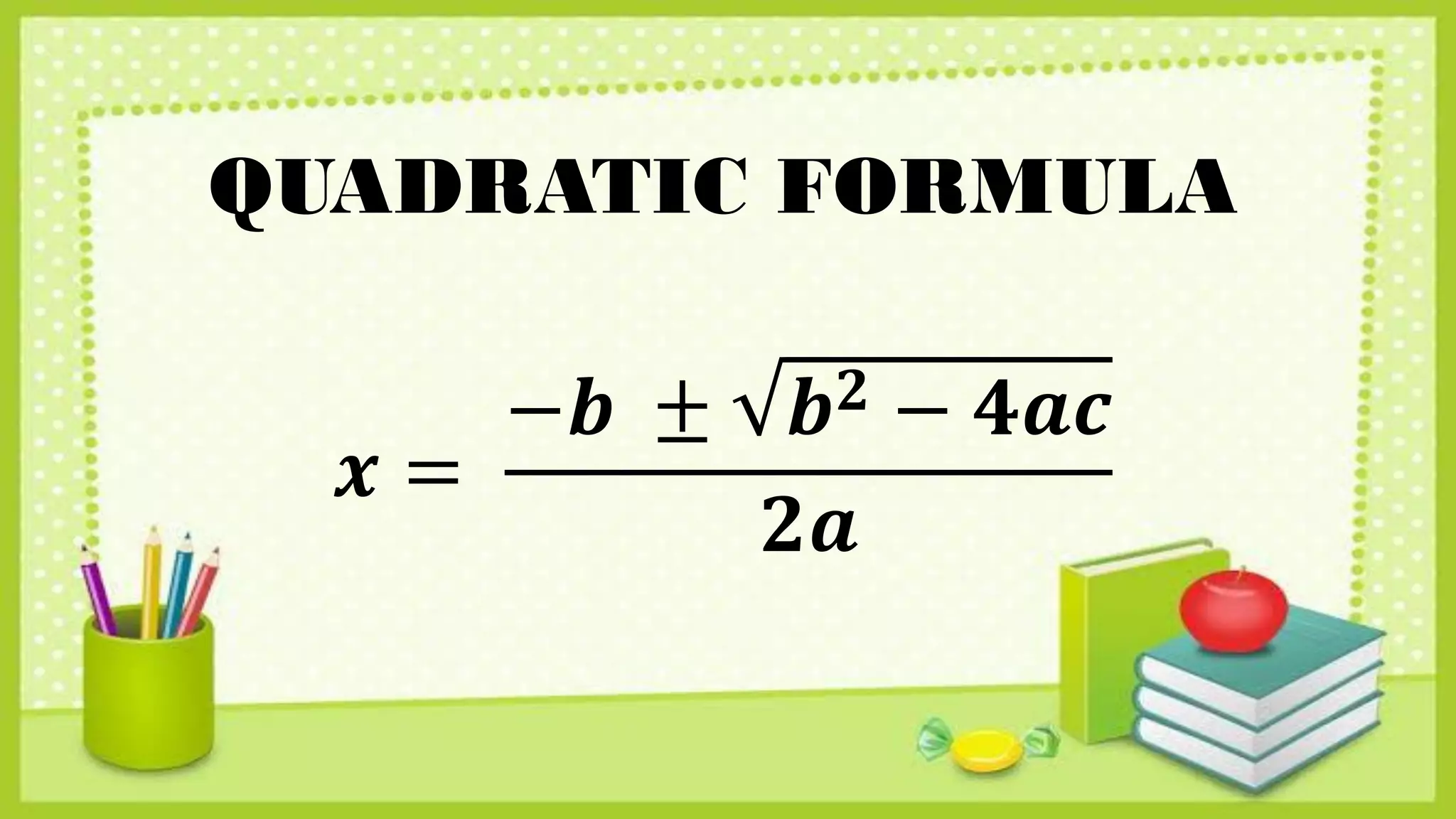
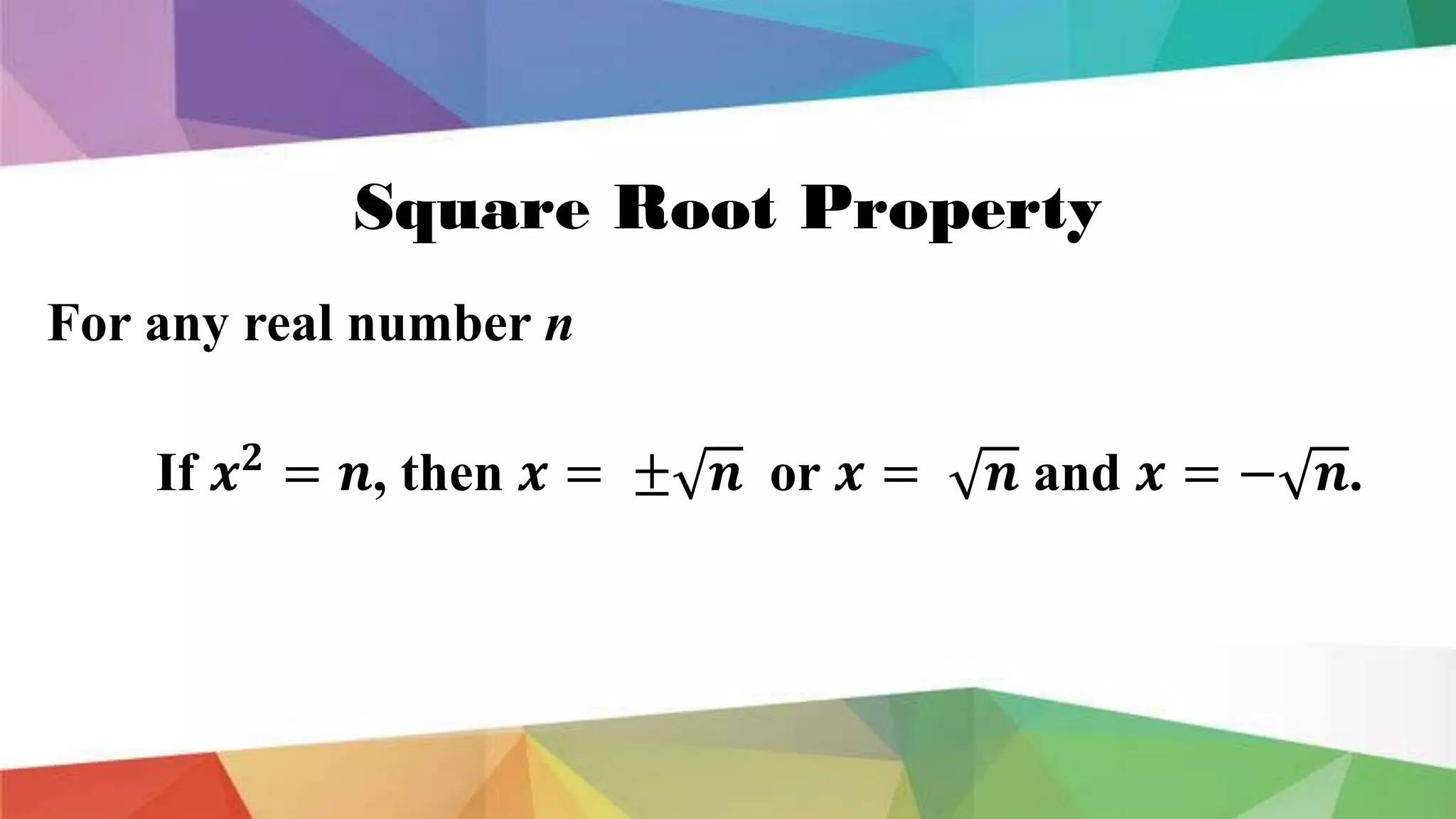The document provides methods for solving quadratic equations including extracting square roots, factoring, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula. It includes detailed steps, examples, and checks for each method to verify solutions. Key concepts such as the solution set and the zero product property are also explained.