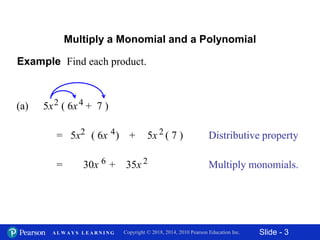
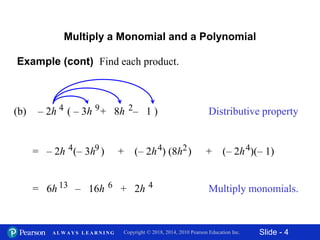
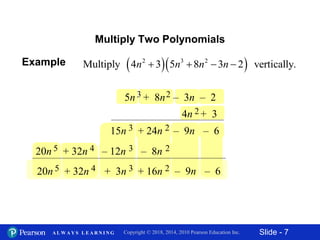
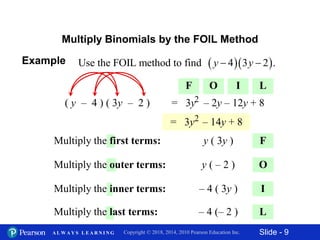
This document discusses different methods for multiplying polynomials, including:
1) Multiplying a monomial and polynomial using the distributive property.
2) Multiplying two polynomials by distributing each term of one polynomial over each term of the other.
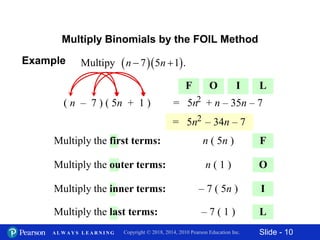
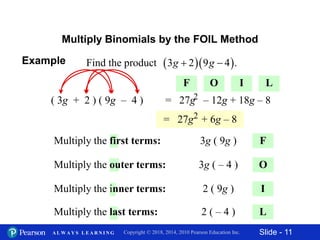
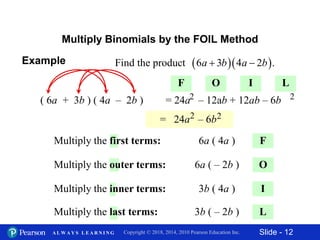
3) Multiplying binomials using the FOIL (First, Outer, Inner, Last) method. FOIL involves multiplying the first, outer, inner, and last terms of each binomial.
The document provides examples of applying each of these multiplication methods to polynomials with variables like x, y, and n.