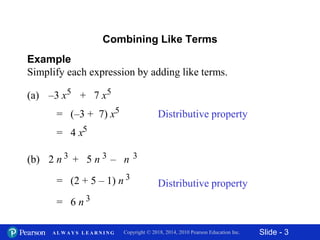
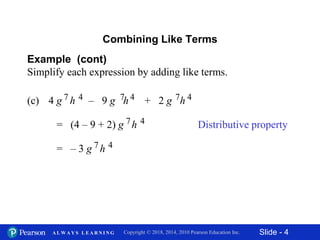
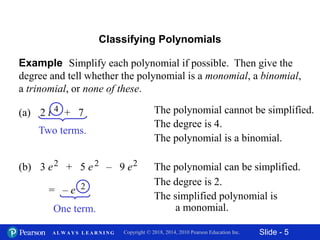
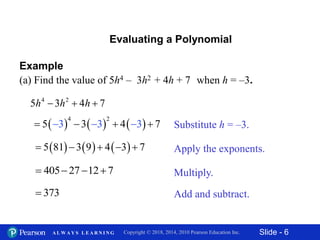
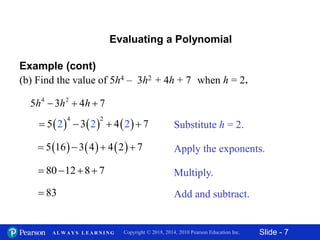
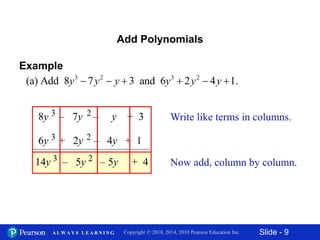
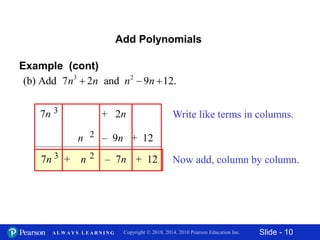
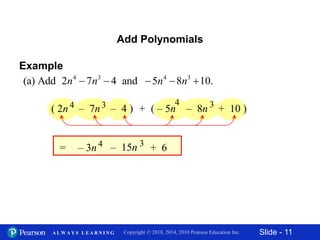
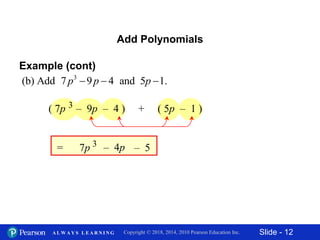
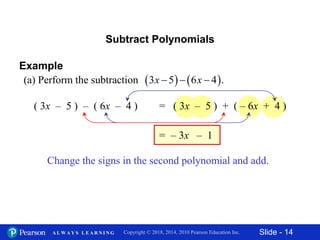
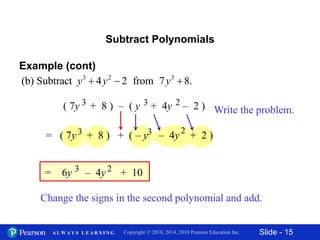
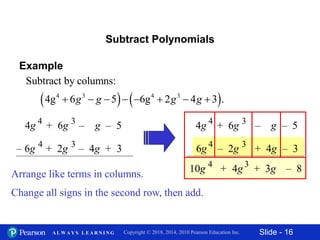
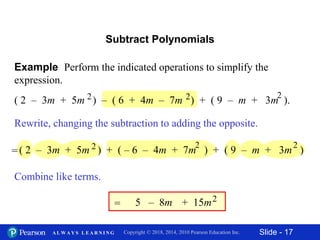
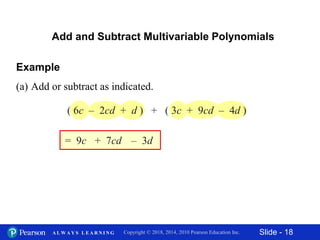
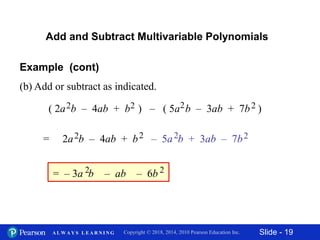
This document contains slides about adding and subtracting polynomials. It begins with objectives for the lesson and examples of combining like terms and evaluating polynomials. Subsequently, it demonstrates how to add and subtract polynomials by writing like terms in columns and combining them. This includes examples of adding and subtracting multivariable polynomials. The document provides step-by-step workings for solving polynomial expressions.