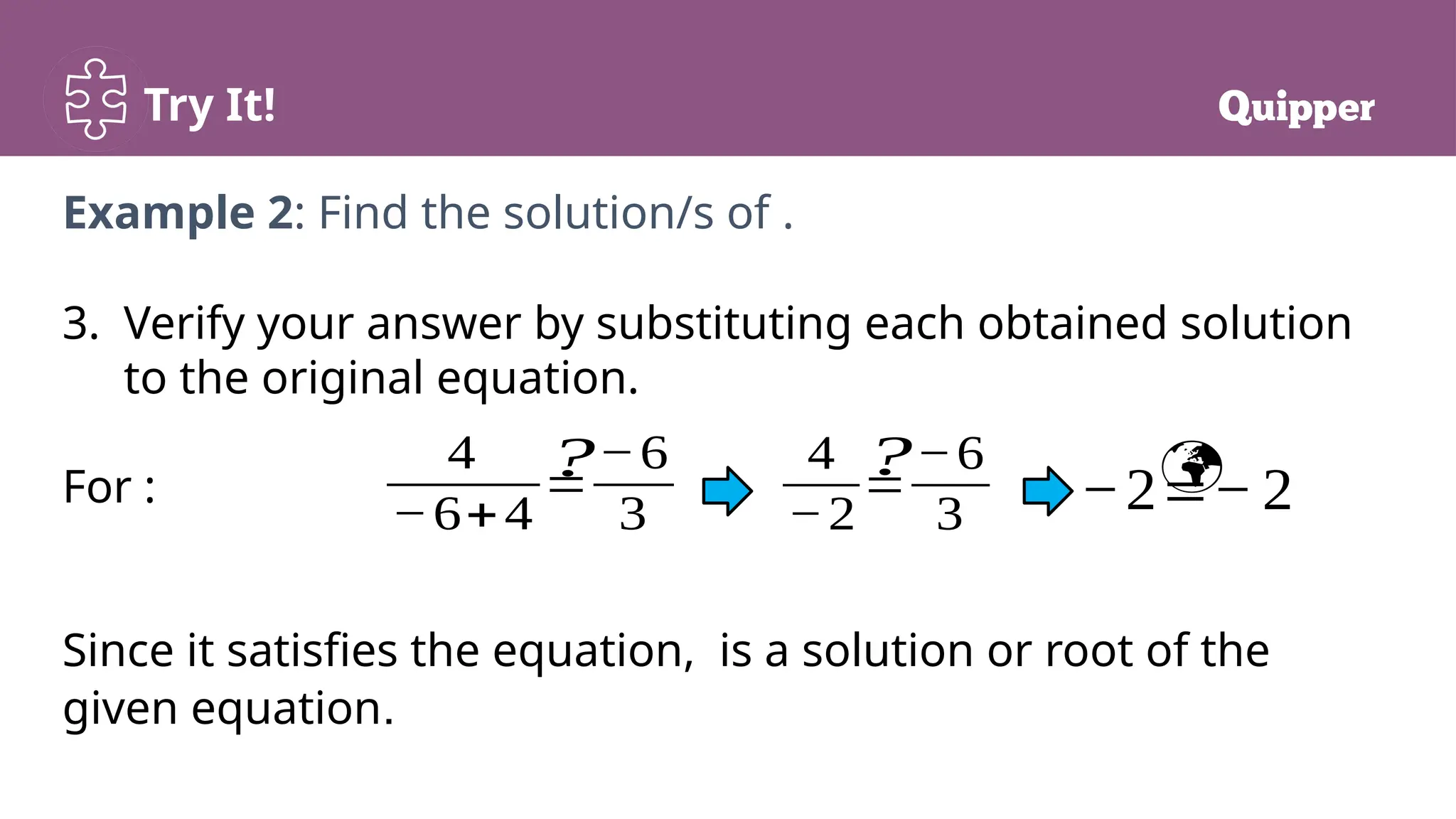
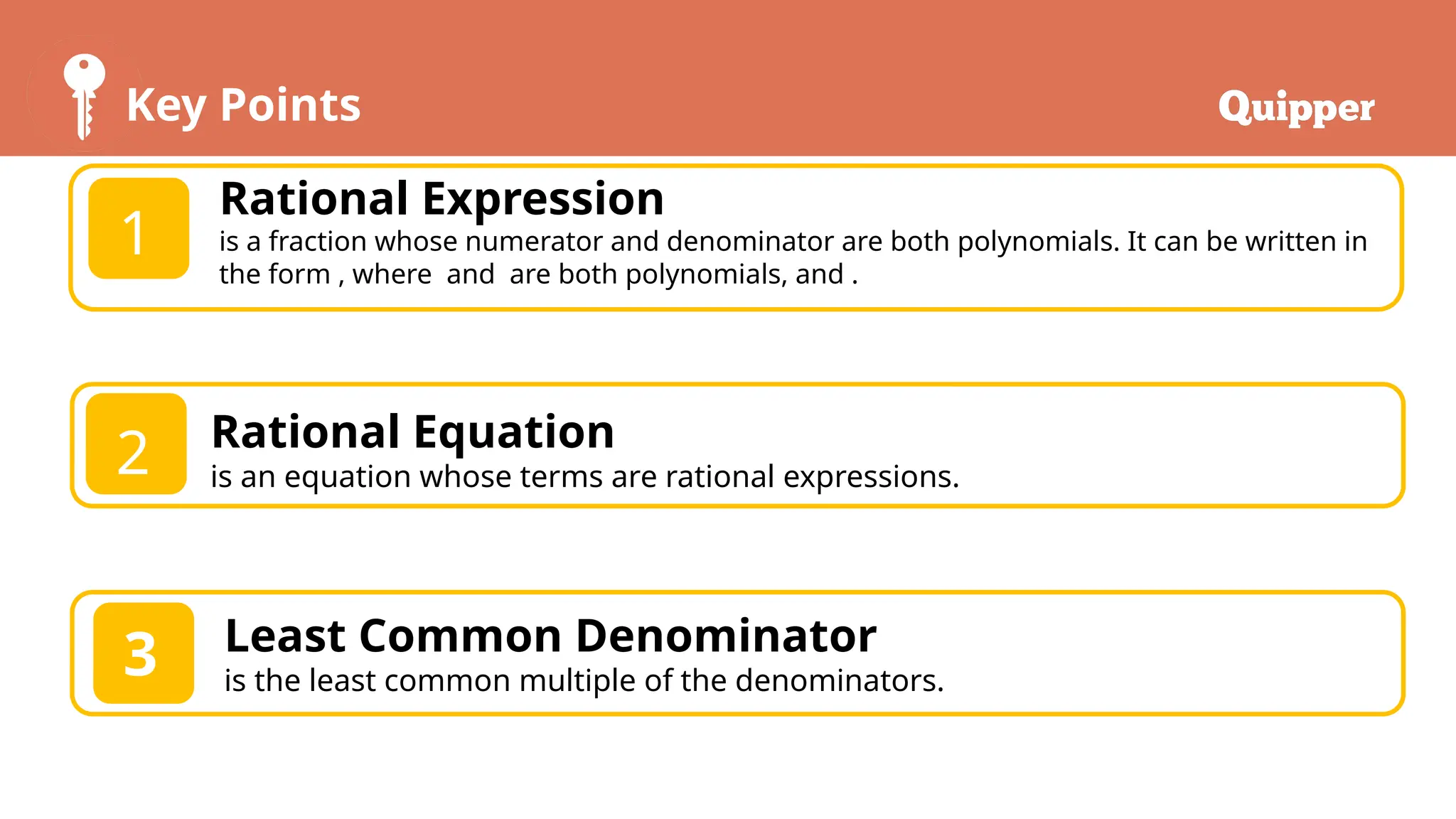
The document outlines the objectives and key concepts related to solving rational equations, including definitions of rational expressions, rational equations, least common denominators, solutions, and extraneous solutions. It provides examples and step-by-step methods for solving rational equations, along with practice exercises for learners. The lesson emphasizes the importance of verifying solutions to ensure their validity.