Science assignment- Form 4 Chapter 4
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
5 likes•3,740 views
The document discusses the kinetic theory of matter and the structure of atoms. It explains that according to the kinetic theory, matter is made of tiny particles that are always moving and their kinetic energy depends on temperature. It also describes how atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons, and how elements are classified in the periodic table based on their proton and nucleon numbers. Purification methods like distillation and crystallization are also summarized.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Chapter 4 Matter and Substances

This document discusses matter and substances. It describes the kinetic theory of matter and states of matter. It explains that all matter is made up of atoms, which contain protons, electrons, and neutrons. The periodic table arranges elements based on proton number and displays their properties. Substances can be made of atoms, molecules, or ions, which determines their physical properties like melting point and electrical conductivity. Metals have properties like shine, malleability, and conductivity, while non-metals have dull surfaces and are brittle. Purification methods like filtration, crystallization, and distillation are used to obtain pure substances. Substances are important in daily life, and their properties allow them to be processed for different uses.
Science form4 - chapter 5

This document discusses physical and chemical changes, heat changes in chemical reactions, the reactivity of metals, electrolysis, and the production of electrical energy from chemical reactions. It defines physical and chemical changes, compares their characteristics, and provides examples of each. It describes how chemical reactions can be exothermic or endothermic and releases or absorbs heat. It also discusses the reactivity series of metals and how the position of a metal determines its reactions with water, acids, oxygen, and in extractions. Electrolysis and its uses in metal extraction and plating are explained. Finally, it covers simple cells and different battery types.
C12 electrochemistry

The document outlines key concepts in electrochemistry including:
1. Electrolysis involves using electricity to break down ionic compounds or solutions into their components. It occurs when ions are able to move freely in molten or aqueous states.
2. During electrolysis, cations move to the cathode where they gain electrons and undergo reduction reactions. Anions move to the anode where they lose electrons and undergo oxidation reactions.
3. The electrolysis of molten ionic compounds produces metals at the cathode and non-metals at the anode. Electrolysis of aqueous solutions can produce hydrogen and oxygen from water or discharge other ions depending on their reactivity.
Chapter 5 chemical changes

This document discusses different types of chemical and physical changes. It explains that physical changes only alter the physical properties of a substance and are reversible, while chemical changes produce new substances through irreversible reactions and often require more energy. Examples of each type of change are provided. The document also covers endothermic and exothermic reactions, noting that endothermic reactions absorb heat while exothermic reactions release heat.
GCSE Chemistry [C3]![GCSE Chemistry [C3]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![GCSE Chemistry [C3]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
The document provides information on the structure of atoms, ionic and covalent bonding, the periodic table, properties of metals and non-metals, and chemical reactions. It discusses how atoms are composed of protons, neutrons and electrons, and how electrons are arranged in shells. It also explains how ionic bonding occurs through transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals, while covalent bonding involves sharing of electrons between non-metals.
C2 revision powerpoint

The document discusses topics related to chemical reactions and the periodic table. It provides information on:
- Mendeleev's creation of the periodic table and how he arranged elements based on their properties.
- The structure of atoms consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons located in electron shells around the nucleus.
- The modern periodic table including atomic number and mass number.
- Ionic bonding forming between metals and non-metals through the transfer of electrons. Ionic compounds have high melting/boiling points and conduct electricity when molten or dissolved.
- Covalent bonding forming when atoms share electrons in covalent molecules. Simple covalent substances have low melting/boiling points while giant
AQA Chemistry C2 Revision

This document provides an overview of key concepts in chemistry including:
1) The structure of atoms including protons, neutrons, and electrons. It also discusses isotopes and electron configuration.
2) The periodic table is introduced including periodic trends in properties and how elements are arranged in groups and periods. Metals, nonmetals, and chemical properties are also covered.
3) Bonding including ionic bonding between metals and nonmetals and covalent bonding between nonmetals is explained through examples like sodium chloride and water. Dot and cross diagrams are used to represent covalent bonds.
4) Compounds and chemical equations are discussed including balancing equations and calculating relative formula mass. Giant ionic structures
Chapter 4 perodic table

The document summarizes key aspects of the periodic table, including:
1) It describes the historical development of the periodic table by scientists like Lavoisier, Dobereiner, Newlands, Meyer, and Mendeleev.
2) It explains the modern arrangement of elements in the periodic table based on proton number and discusses the properties of elements in the same group and period.
3) It provides examples of properties and reactions of representative elements from groups 1, 17, 18 and period 3 of the periodic table. Transition elements and semimetals are also discussed.
Recommended
Chapter 4 Matter and Substances

This document discusses matter and substances. It describes the kinetic theory of matter and states of matter. It explains that all matter is made up of atoms, which contain protons, electrons, and neutrons. The periodic table arranges elements based on proton number and displays their properties. Substances can be made of atoms, molecules, or ions, which determines their physical properties like melting point and electrical conductivity. Metals have properties like shine, malleability, and conductivity, while non-metals have dull surfaces and are brittle. Purification methods like filtration, crystallization, and distillation are used to obtain pure substances. Substances are important in daily life, and their properties allow them to be processed for different uses.
Science form4 - chapter 5

This document discusses physical and chemical changes, heat changes in chemical reactions, the reactivity of metals, electrolysis, and the production of electrical energy from chemical reactions. It defines physical and chemical changes, compares their characteristics, and provides examples of each. It describes how chemical reactions can be exothermic or endothermic and releases or absorbs heat. It also discusses the reactivity series of metals and how the position of a metal determines its reactions with water, acids, oxygen, and in extractions. Electrolysis and its uses in metal extraction and plating are explained. Finally, it covers simple cells and different battery types.
C12 electrochemistry

The document outlines key concepts in electrochemistry including:
1. Electrolysis involves using electricity to break down ionic compounds or solutions into their components. It occurs when ions are able to move freely in molten or aqueous states.
2. During electrolysis, cations move to the cathode where they gain electrons and undergo reduction reactions. Anions move to the anode where they lose electrons and undergo oxidation reactions.
3. The electrolysis of molten ionic compounds produces metals at the cathode and non-metals at the anode. Electrolysis of aqueous solutions can produce hydrogen and oxygen from water or discharge other ions depending on their reactivity.
Chapter 5 chemical changes

This document discusses different types of chemical and physical changes. It explains that physical changes only alter the physical properties of a substance and are reversible, while chemical changes produce new substances through irreversible reactions and often require more energy. Examples of each type of change are provided. The document also covers endothermic and exothermic reactions, noting that endothermic reactions absorb heat while exothermic reactions release heat.
GCSE Chemistry [C3]![GCSE Chemistry [C3]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![GCSE Chemistry [C3]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
The document provides information on the structure of atoms, ionic and covalent bonding, the periodic table, properties of metals and non-metals, and chemical reactions. It discusses how atoms are composed of protons, neutrons and electrons, and how electrons are arranged in shells. It also explains how ionic bonding occurs through transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals, while covalent bonding involves sharing of electrons between non-metals.
C2 revision powerpoint

The document discusses topics related to chemical reactions and the periodic table. It provides information on:
- Mendeleev's creation of the periodic table and how he arranged elements based on their properties.
- The structure of atoms consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons located in electron shells around the nucleus.
- The modern periodic table including atomic number and mass number.
- Ionic bonding forming between metals and non-metals through the transfer of electrons. Ionic compounds have high melting/boiling points and conduct electricity when molten or dissolved.
- Covalent bonding forming when atoms share electrons in covalent molecules. Simple covalent substances have low melting/boiling points while giant
AQA Chemistry C2 Revision

This document provides an overview of key concepts in chemistry including:
1) The structure of atoms including protons, neutrons, and electrons. It also discusses isotopes and electron configuration.
2) The periodic table is introduced including periodic trends in properties and how elements are arranged in groups and periods. Metals, nonmetals, and chemical properties are also covered.
3) Bonding including ionic bonding between metals and nonmetals and covalent bonding between nonmetals is explained through examples like sodium chloride and water. Dot and cross diagrams are used to represent covalent bonds.
4) Compounds and chemical equations are discussed including balancing equations and calculating relative formula mass. Giant ionic structures
Chapter 4 perodic table

The document summarizes key aspects of the periodic table, including:
1) It describes the historical development of the periodic table by scientists like Lavoisier, Dobereiner, Newlands, Meyer, and Mendeleev.
2) It explains the modern arrangement of elements in the periodic table based on proton number and discusses the properties of elements in the same group and period.
3) It provides examples of properties and reactions of representative elements from groups 1, 17, 18 and period 3 of the periodic table. Transition elements and semimetals are also discussed.
CHEMISTRY FORM 4 KSSM CHAPTER 4

The document discusses the properties of two groups of elements - Group 18 noble gases and Group 1 alkali metals.
Group 18 consists of helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and oganesson. Noble gases have full outer electron shells, making them chemically inert. Their melting and boiling points increase down the group as atomic size increases and van der Waals forces strengthen.
Group 1 includes lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, and francium. Alkali metals react by losing one electron to form stable ions. Reactivity increases down the group as the valence electron is more loosely held. They react with water to form hydroxides and oxygen to form ox
Experiment Form 4 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry

Experiment 6.8 investigates displacement reactions between metals and their salt solutions to construct an electrochemical series. The procedure involves placing different metal strips (magnesium, zinc, lead, copper) into separate salt solutions (magnesium nitrate, zinc nitrate, lead nitrate, copper nitrate). Observations are made to check for any color changes in the solutions, solid deposits on the metals, and metal dissolution. It is hypothesized that the greater the number of metals that can displace a metal from its salt solution, the higher its position will be in the electrochemical series.
Periodicity of Elements

This document discusses periodic trends in elements across periods and down groups in the periodic table. It explains that elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and thus similar chemical properties, while periods are related to the number of electron shells. Metals are on the left side of the table and become more nonmetallic from left to right across periods as atomic number increases.
C3 revision (Chemistry unit 3)

The document discusses the history and development of the periodic table. It describes early periodic tables from the 1800s with fewer than 40 known elements arranged based on atomic mass. John Newlands proposed the law of octaves but it only worked for the first few elements. Dmitri Mendeleev arranged elements in a periodic way with gaps for undiscovered elements and was able to predict properties. The modern periodic table arranges elements by atomic number and groups them based on electron configuration in the outer shell leading to similar properties within groups. It also discusses trends in reactivity down groups and across periods.
Aqa gcse chemistry c3 revision

The document discusses the history and modern understanding of the periodic table. It covers how elements are arranged based on proton number and how this explains trends in properties within groups. Specific groups like alkali metals, halogens, and transition metals are examined in terms of their structures, properties, and reactions. Common acid-base reactions and quantitative chemical calculations are also summarized.
Chemistry Note Form 4 & 5

The document provides information on several chemistry concepts and experiments. It includes:
1) A chapter on matter that discusses states of matter, kinetic theory, and heating curves.
2) Chapters on chemical formulas, periodic table, chemical bonds, and electrochemistry.
3) An experiment on determining the end point of a neutralization reaction between potassium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid.
Atomic Structure

The document outlines key concepts about atomic structure including the structure of atoms with protons, neutrons and electrons, atomic number and mass number, electron configuration, isotopes, ions, and molecules of elements and compounds. It also provides learning outcomes for describing atomic structure and properties as well as interpreting atomic symbols and notations.
Chemistry

This document provides a summary of key chemistry concepts covered on the Regents exam, including:
1) Elements cannot be broken down chemically, while mixtures contain two or more physically combined elements or substances.
2) Chemical changes result in new substances with different properties, while physical changes do not alter the identity of the substance.
3) Gas laws relate the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas in chemical reactions and problems.
4) Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The number of protons determines the element.
5) Chemical bonds, including ionic and covalent bonds, result from the transfer or sharing of electrons between atoms.
Chemistry zimsec chapter 9 chemical periodicity

This document summarizes key concepts about chemical periodicity, including the various blocks and periods in the periodic table. It describes trends in atomic properties like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity across periods and down groups. These trends are explained by factors like nuclear charge, atomic size, and shielding effects. Common reactions of representative elements like formation of oxides and chlorides from the third period are presented, along with equations. Structures and bonding of these compounds are discussed as well as their reactions with water.
Chemistry Revision Notes - IGCSE

This document provides an overview of key chemistry concepts including the states of matter, atoms, bonding, and molecular structures.
It begins by explaining the particle nature of matter and defining solids, liquids, and gases. Atoms are introduced as the smallest particles that make up elements, which can combine to form compounds. Bonding types - ionic, covalent, and metallic - are then described along with their characteristic properties. Molecular structures like diamond, graphite, and silica are used as examples of giant covalent networks.
The document concludes by recapping the main differences between ionic, covalent and metallic bonding in terms of structure and properties. Key areas of chemistry are covered concisely with definitions and
Metals and their Reactivity

This document discusses the properties and reactivity of metals. It begins by describing the physical properties of metals, such as their hardness, malleability and conductivity. It then discusses the chemical properties of metals, including how they form positive ions and react with oxygen, water and acids. The document introduces metal alloys and explains why they are stronger than pure metals. It also defines the reactivity series and uses it to predict and describe the reactions of different metals. The document discusses the reactions of various metal compounds and how the position of metals in the reactivity series affects their reactivity and the stability of their compounds.
Elements and Compounds

The document provides information on elements and compounds. It defines an element as a substance that cannot be broken down further by chemical means, while a compound is made up of two or more elements chemically bonded together. Elements are the fundamental building blocks and are made of only one type of atom. Compounds have molecules made of two or more atom types. The document explains how to write chemical formulas and balanced equations to represent elements, compounds and chemical reactions.
C09 periodicity of elements

This chapter discusses the periodic table, explaining that elements are arranged in order of atomic number and grouped into periods and groups based on their electron configuration, with groups having similar properties and periods showing trends down the table. Properties of elements in groups I, VII, and 0 are described, including their physical states, reactivity, and chemical properties.
C07 chemical bonding

The document discusses different types of chemical bonds and macromolecular structures. It explains that ionic bonds form between metals and non-metals via the transfer of electrons, giving ionic compounds high melting points and the ability to conduct electricity when molten or dissolved. Covalent bonds form between non-metals by the sharing of electrons, resulting in covalent compounds having low melting points and the inability to conduct electricity. Some covalent substances exist as macromolecules or giant molecular structures like diamond and graphite. These have very high melting points and different properties compared to simple molecules. Metallic bonding is also described, involving positive metal ions in a "sea of electrons" giving metals properties like malleability and high conductivity
Chemistry zimsec chapter 7 redox reactions and electrolysis

Chemistry zimsec chapter 7 redox reactions and electrolysis
Advanced Level
Chemistry
Zimsec
Alpro
Elearning
C22 non metals

The document describes non-metals and their properties. It discusses the physical and chemical properties of non-metals, and describes the industrial preparation of chlorine, sulfuric acid, and ammonia. It also lists common uses of non-metals like carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine, and nitrogen and their compounds.
C3 revision powerpoint

This document provides information on qualitative and quantitative analysis of ions in water samples. It discusses common cation and anion tests including flame tests for metals, reactions of halogens with silver nitrate, and tests for ammonium ions. Methods are described for identifying unknown ions in a sample. Ion identification is important in industries such as water treatment and medical testing. The document also covers types of water, calculating concentration, and identification of ions through precipitation reactions and other common tests.
Chapter 4

The document discusses properties of elements in the periodic table. It explains that group 18 elements exist as single particles because they have a stable electron configuration and do not donate, accept or share electrons. It also notes that reactivity increases down group 1 but decreases down group 17 due to changes in proton number, electron configuration and atomic size. Melting points of group 1 elements decrease due to increasing atomic size weakening metallic bonding. Chemical properties of group 17 elements like chlorine are described, including reactions with water and sodium hydroxide. Finally, it explains that across period 3, atomic radius decreases and electronegativity increases because of the increasing proton number and number of valence electrons.
C02 atomic structure

The document outlines key learning outcomes and concepts about atomic structure, including describing the structure of atoms with atomic numbers 1 to 20, defining terms like atomic number and mass number, explaining electron configuration and outer electrons, and distinguishing between isotopes, ions, and molecules of elements and compounds. It also provides illustrations of atomic structure and examples of applying atomic structure concepts.
2. group 1

The document discusses the chemical properties of alkali metals. It explains that alkali metals react vigorously with oxygen and water. The reactivity increases down the group as the atoms get larger, shielding the outer electrons from the nucleus and making them easier to lose. Equations for reactions of lithium, sodium, and potassium with oxygen, water, and other substances are provided. Flame tests for group 2 metals are also discussed.
Form 4 Chapter 4

This chapter discusses the states of matter and their changes, the structure of atoms including protons and nucleon number, classification of elements, and properties of substances based on their particle content. It covers the key topics of matter, atoms, elements, and how their structure determines the properties of different materials.
More Related Content
What's hot
CHEMISTRY FORM 4 KSSM CHAPTER 4

The document discusses the properties of two groups of elements - Group 18 noble gases and Group 1 alkali metals.
Group 18 consists of helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and oganesson. Noble gases have full outer electron shells, making them chemically inert. Their melting and boiling points increase down the group as atomic size increases and van der Waals forces strengthen.
Group 1 includes lithium, sodium, potassium, cesium, and francium. Alkali metals react by losing one electron to form stable ions. Reactivity increases down the group as the valence electron is more loosely held. They react with water to form hydroxides and oxygen to form ox
Experiment Form 4 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry

Experiment 6.8 investigates displacement reactions between metals and their salt solutions to construct an electrochemical series. The procedure involves placing different metal strips (magnesium, zinc, lead, copper) into separate salt solutions (magnesium nitrate, zinc nitrate, lead nitrate, copper nitrate). Observations are made to check for any color changes in the solutions, solid deposits on the metals, and metal dissolution. It is hypothesized that the greater the number of metals that can displace a metal from its salt solution, the higher its position will be in the electrochemical series.
Periodicity of Elements

This document discusses periodic trends in elements across periods and down groups in the periodic table. It explains that elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and thus similar chemical properties, while periods are related to the number of electron shells. Metals are on the left side of the table and become more nonmetallic from left to right across periods as atomic number increases.
C3 revision (Chemistry unit 3)

The document discusses the history and development of the periodic table. It describes early periodic tables from the 1800s with fewer than 40 known elements arranged based on atomic mass. John Newlands proposed the law of octaves but it only worked for the first few elements. Dmitri Mendeleev arranged elements in a periodic way with gaps for undiscovered elements and was able to predict properties. The modern periodic table arranges elements by atomic number and groups them based on electron configuration in the outer shell leading to similar properties within groups. It also discusses trends in reactivity down groups and across periods.
Aqa gcse chemistry c3 revision

The document discusses the history and modern understanding of the periodic table. It covers how elements are arranged based on proton number and how this explains trends in properties within groups. Specific groups like alkali metals, halogens, and transition metals are examined in terms of their structures, properties, and reactions. Common acid-base reactions and quantitative chemical calculations are also summarized.
Chemistry Note Form 4 & 5

The document provides information on several chemistry concepts and experiments. It includes:
1) A chapter on matter that discusses states of matter, kinetic theory, and heating curves.
2) Chapters on chemical formulas, periodic table, chemical bonds, and electrochemistry.
3) An experiment on determining the end point of a neutralization reaction between potassium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid.
Atomic Structure

The document outlines key concepts about atomic structure including the structure of atoms with protons, neutrons and electrons, atomic number and mass number, electron configuration, isotopes, ions, and molecules of elements and compounds. It also provides learning outcomes for describing atomic structure and properties as well as interpreting atomic symbols and notations.
Chemistry

This document provides a summary of key chemistry concepts covered on the Regents exam, including:
1) Elements cannot be broken down chemically, while mixtures contain two or more physically combined elements or substances.
2) Chemical changes result in new substances with different properties, while physical changes do not alter the identity of the substance.
3) Gas laws relate the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas in chemical reactions and problems.
4) Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The number of protons determines the element.
5) Chemical bonds, including ionic and covalent bonds, result from the transfer or sharing of electrons between atoms.
Chemistry zimsec chapter 9 chemical periodicity

This document summarizes key concepts about chemical periodicity, including the various blocks and periods in the periodic table. It describes trends in atomic properties like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity across periods and down groups. These trends are explained by factors like nuclear charge, atomic size, and shielding effects. Common reactions of representative elements like formation of oxides and chlorides from the third period are presented, along with equations. Structures and bonding of these compounds are discussed as well as their reactions with water.
Chemistry Revision Notes - IGCSE

This document provides an overview of key chemistry concepts including the states of matter, atoms, bonding, and molecular structures.
It begins by explaining the particle nature of matter and defining solids, liquids, and gases. Atoms are introduced as the smallest particles that make up elements, which can combine to form compounds. Bonding types - ionic, covalent, and metallic - are then described along with their characteristic properties. Molecular structures like diamond, graphite, and silica are used as examples of giant covalent networks.
The document concludes by recapping the main differences between ionic, covalent and metallic bonding in terms of structure and properties. Key areas of chemistry are covered concisely with definitions and
Metals and their Reactivity

This document discusses the properties and reactivity of metals. It begins by describing the physical properties of metals, such as their hardness, malleability and conductivity. It then discusses the chemical properties of metals, including how they form positive ions and react with oxygen, water and acids. The document introduces metal alloys and explains why they are stronger than pure metals. It also defines the reactivity series and uses it to predict and describe the reactions of different metals. The document discusses the reactions of various metal compounds and how the position of metals in the reactivity series affects their reactivity and the stability of their compounds.
Elements and Compounds

The document provides information on elements and compounds. It defines an element as a substance that cannot be broken down further by chemical means, while a compound is made up of two or more elements chemically bonded together. Elements are the fundamental building blocks and are made of only one type of atom. Compounds have molecules made of two or more atom types. The document explains how to write chemical formulas and balanced equations to represent elements, compounds and chemical reactions.
C09 periodicity of elements

This chapter discusses the periodic table, explaining that elements are arranged in order of atomic number and grouped into periods and groups based on their electron configuration, with groups having similar properties and periods showing trends down the table. Properties of elements in groups I, VII, and 0 are described, including their physical states, reactivity, and chemical properties.
C07 chemical bonding

The document discusses different types of chemical bonds and macromolecular structures. It explains that ionic bonds form between metals and non-metals via the transfer of electrons, giving ionic compounds high melting points and the ability to conduct electricity when molten or dissolved. Covalent bonds form between non-metals by the sharing of electrons, resulting in covalent compounds having low melting points and the inability to conduct electricity. Some covalent substances exist as macromolecules or giant molecular structures like diamond and graphite. These have very high melting points and different properties compared to simple molecules. Metallic bonding is also described, involving positive metal ions in a "sea of electrons" giving metals properties like malleability and high conductivity
Chemistry zimsec chapter 7 redox reactions and electrolysis

Chemistry zimsec chapter 7 redox reactions and electrolysis
Advanced Level
Chemistry
Zimsec
Alpro
Elearning
C22 non metals

The document describes non-metals and their properties. It discusses the physical and chemical properties of non-metals, and describes the industrial preparation of chlorine, sulfuric acid, and ammonia. It also lists common uses of non-metals like carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine, and nitrogen and their compounds.
C3 revision powerpoint

This document provides information on qualitative and quantitative analysis of ions in water samples. It discusses common cation and anion tests including flame tests for metals, reactions of halogens with silver nitrate, and tests for ammonium ions. Methods are described for identifying unknown ions in a sample. Ion identification is important in industries such as water treatment and medical testing. The document also covers types of water, calculating concentration, and identification of ions through precipitation reactions and other common tests.
Chapter 4

The document discusses properties of elements in the periodic table. It explains that group 18 elements exist as single particles because they have a stable electron configuration and do not donate, accept or share electrons. It also notes that reactivity increases down group 1 but decreases down group 17 due to changes in proton number, electron configuration and atomic size. Melting points of group 1 elements decrease due to increasing atomic size weakening metallic bonding. Chemical properties of group 17 elements like chlorine are described, including reactions with water and sodium hydroxide. Finally, it explains that across period 3, atomic radius decreases and electronegativity increases because of the increasing proton number and number of valence electrons.
C02 atomic structure

The document outlines key learning outcomes and concepts about atomic structure, including describing the structure of atoms with atomic numbers 1 to 20, defining terms like atomic number and mass number, explaining electron configuration and outer electrons, and distinguishing between isotopes, ions, and molecules of elements and compounds. It also provides illustrations of atomic structure and examples of applying atomic structure concepts.
2. group 1

The document discusses the chemical properties of alkali metals. It explains that alkali metals react vigorously with oxygen and water. The reactivity increases down the group as the atoms get larger, shielding the outer electrons from the nucleus and making them easier to lose. Equations for reactions of lithium, sodium, and potassium with oxygen, water, and other substances are provided. Flame tests for group 2 metals are also discussed.
What's hot (20)
Chemistry zimsec chapter 7 redox reactions and electrolysis

Chemistry zimsec chapter 7 redox reactions and electrolysis
Viewers also liked
Form 4 Chapter 4

This chapter discusses the states of matter and their changes, the structure of atoms including protons and nucleon number, classification of elements, and properties of substances based on their particle content. It covers the key topics of matter, atoms, elements, and how their structure determines the properties of different materials.
Body coordination (Chapter 2 Form 4)

Coordination involves the adjustment and cooperation of various body parts and systems. There are two types of coordination: nervous coordination involving the brain, spinal cord, and nerves; and hormonal coordination involving glands and organs. The document then describes the structure and function of the nervous system including neurons, receptors, effectors, and reflex actions. It also discusses proprioception and kinaesthetic senses which provide awareness of body position and movement. Voluntary actions are controlled by desires while involuntary actions are controlled by the medulla oblongata. Finally, it notes that alcohol can hinder nervous system function and coordination by slowing impulse transmission and potentially damaging liver cells.
Chapter 3 heredity and variation

The document discusses heredity and variation, including the principles of inheritance. It covers several key topics:
- Cell division through mitosis and meiosis results in the transmission of genes from parents to offspring. Mitosis produces genetically identical cells for growth, while meiosis results in genetic variation through the formation of gametes.
- Genes located on chromosomes carry inherited traits and occur in pairs. One gene from each pair is inherited from the mother and father. Examples of traits determined by genes include eye color and blood type.
- Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants established the principles of dominant and recessive genes. A dominant gene masks the expression of a recessive gene. Monohy
SPM Form 4 Physics - Heat

The document discusses heat and thermal equilibrium. It defines key terms like temperature, heat, and thermal contact. It explains that when two objects at different temperatures come into contact, heat is transferred from the hotter object to the cooler one until they reach the same temperature and thermal equilibrium. Examples are given like a wet towel being used to reduce a fever by transferring heat from the body. The document also discusses specific heat capacity and how it relates to how fast an object's temperature changes when heat is gained or lost. Specific heat capacities of different materials are provided.
Chapter 3 biodiversity

Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including plants, animals and other organisms. There are two main groups of organisms - animals and plants. Animals are further divided into vertebrates and invertebrates, while plants are divided into flowering plants and non-flowering plants. Biodiversity is found in different ecosystems around the world and is important to study and protect.
form 4 biology chap 4 pt1

This document discusses the chemical composition of cells. It states that cells are composed of various elements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and other major and trace elements. The document also lists important organic compounds in cells like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. It explains the roles of these organic compounds like providing energy, forming structures, carrying genetic information and acting as enzymes. Additionally, it highlights the importance of water as the solvent for biochemical reactions in cells.
Form 4 Chapter 5 Part 1

This chapter discusses physical and chemical changes, heat changes during chemical reactions, and the reactivity series of metals. Physical changes alter a substance's physical properties without changing its chemical composition, while chemical changes form new substances. Chemical reactions either absorb or release heat, changing the temperature of the surroundings. Metals exist in a reactivity series based on their tendency to undergo replacement reactions, with more reactive metals displacing less reactive ones.
Topik 3 koordinasi dan gerakbalas

1. Dokumen ini membahas tentang koordinasi dan gerak balas organisme terhadap rangsangan dalam dan luar. Organisme dapat mendeteksi dan memberikan respon terhadap perubahan lingkungan melalui sistem saraf dan endokrin.
2. Sistem saraf bekerja dengan mendeteksi rangsangan, mengirimkan sinyal saraf, dan memicu respon otot atau kelenjar. Sistem endokrin melibatkan pelepasan hormon untuk mengatur aktivitas organ dan jaringan.
Chapter 2 Body Coordination

This document summarizes the nervous and endocrine systems that coordinate the human body. It discusses:
- Nervous coordination is controlled by the nervous system and examples include walking and writing. Hormonal coordination is controlled by the endocrine system and examples include body growth and food digestion.
- The nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (spinal and cranial nerves). Stimuli are received by receptors and transmitted via neurons to the CNS which coordinates responses by effectors.
- The endocrine system consists of glands like the pituitary, thyroid and ovaries/testes that secrete hormones to regulate functions like metabolism and growth. Disorders can result
Chapter 4 - Carbon Compound

The document outlines six section dividers for a presentation on various topics relating to carbon compounds, alcohol and its health effects, fats and health, the oil palm industry, the soap making process, and natural polymers. Each section divider can be moved within the presentation and will group subsequent slides under the given label.
Chapter 2 form 4

- Matter is composed of particles called atoms and molecules. Atoms are the smallest particles that make up elements, and molecules are made of two or more bonded atoms.
- The structure of the atom has been discovered over time by scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, and Chadwick. We now know atoms have a tiny, dense nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons.
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Some isotopes are unstable and radioactive, while others are stable. Radioactive isotopes have important applications in medicine, agriculture, and industry.
Effect of flow coefficient and loading coefficient on

IJRET : International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology is an international peer reviewed, online journal published by eSAT Publishing House for the enhancement of research in various disciplines of Engineering and Technology. The aim and scope of the journal is to provide an academic medium and an important reference for the advancement and dissemination of research results that support high-level learning, teaching and research in the fields of Engineering and Technology. We bring together Scientists, Academician, Field Engineers, Scholars and Students of related fields of Engineering and Technology.
Derecho laboral

El documento describe los principios fundamentales del Derecho Laboral en Colombia. Estos incluyen la libertad de trabajo, la obligatoriedad del trabajo, y la protección del trabajo. También describe mecanismos como la conciliación, la acción de tutela, y la transacción que garantizan los derechos laborales de los trabajadores.
Proof of payment

This transaction history from November 1, 2013 through December 9, 2013 shows currency conversions between US dollars and Vietnamese dong, as well as transfers of funds between PayPal and the recipient's bank account. There are also payments received from various individuals and companies, as well as one temporary hold and one reversal recorded during this period.
Construction Industry Snapshot Package-November 2014

Construction starts in November 2014 were 2.7% lower than in October but up 2.4% compared to the average over the previous ten months. Year-to-date construction starts are up 7.4% compared to the same period in 2013. Engineering/civil and institutional construction starts have increased the most year-to-date at 9.9% and 8.4% respectively. The U.S. economy continues to improve with GDP growth of 3.9% and strong job growth, benefiting the construction industry.
About skyries

Skyries Innovations Pvt Ltd is a software/ product company that is currently engaged in developing products for education, healthcare, consumer electronics, agriculture, business enterprises.
Our Specialization: School Automation, Office Automation , Process Automation , Product Innovation , Mobile & Cloud Technology , Product Development , R&D , Migration to Cloud , Custom Business Solutions,Software based Security Solutions , Products for Agriculture , Healthcare , Film & Entertainment , Music , Education & Logistics .
Viewers also liked (20)
Effect of flow coefficient and loading coefficient on

Effect of flow coefficient and loading coefficient on
Construction Industry Snapshot Package-November 2014

Construction Industry Snapshot Package-November 2014
Similar to Science assignment- Form 4 Chapter 4
Atoms and atomic theory review

This document provides information about classifying matter and its composition. It defines pure substances as elements or compounds made of uniform particles and mixtures as substances with two or more types of particles. Pure substances undergo physical or chemical changes, which respectively involve changes in properties or the formation of new substances. The document also discusses atoms as the basic building blocks of matter, containing subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons. It introduces the periodic table as organizing the elements by their chemical properties and number of protons.
Atoms, elements and compounds

This document provides an overview of atoms, elements, molecules, and compounds. It discusses how everything is made up of atoms, which contain subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons. Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Elements are organized in the periodic table according to their properties and atomic structure. Atoms can bond together to form molecules, which are made of one or more elements. Compounds are molecules made of two or more different elements bonded together. The properties of compounds are different from the individual elements.
Structure of matter atoms and molecules

- An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. All atoms of the same element are identical.
- Atoms are very small, not visible even under a powerful microscope. Models like the ball-and-stick model are used to represent atoms and molecules.
- Atoms consist of even smaller subatomic particles - protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus. The number of protons determines the element.
A++ mission 6 notes part i 2012

The document provides information about atoms and the structure of matter in three sections:
1. Atoms are the building blocks of matter and consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The arrangement of atoms determines the properties of different types of matter.
2. Atoms can combine to form compounds and molecules through chemical bonds. Compounds have unique properties that differ from their constituent elements.
3. Matter exists in four states - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. The state depends on how tightly or freely the atoms and molecules are able to move. Solids have a fixed structure while gases spread freely.
Chemistry short notes of civilstap summary

The document discusses the key concepts of elements, compounds, atoms, molecules, and ions. It defines elements as basic forms of matter that cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed by chemical bonds between different elements. Atoms are the basic building blocks that make up elements and can combine to form molecules or ions. Molecules may contain atoms of the same or different elements, while ions are charged particles that form when atoms gain or lose electrons.
NOTES OF ELEMENTS COMPOUNDS AND MIXTURES GRADE 5.pptx

This document provides information about the structure and properties of matter. It defines key terms like atomic theory, atom, element, compound, and molecule. It describes the basic structure of an atom including protons, neutrons, electrons, and electron shells. It provides examples of the atomic structure of various elements like hydrogen, helium, lithium, oxygen, and calcium. It also discusses how elements can form compounds by chemical bonding and how compounds have different properties than their constituent elements. Compounds are made of molecules, the smallest units that exhibit a compound's properties, as illustrated by examples of water and sodium chloride molecules.
Human Impact on Ozone in the Environment

This is the lecture for Ozone, Oxygen, Atomic Structure, Bonding and Human Impact. For best results, listen to my podcast while looking at the slides.
General Biology. LECTURE 2. THE CHEMICAL FOUNDATION OF LIFE.pptx

This document provides an overview of the chemical foundations of life. It discusses that biochemistry is the study of the structures and roles of chemicals in living organisms. The key points made are:
- Life depends on chemistry as living things are composed of chemical elements like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen.
- Atoms are the basic unit of matter and combine to form molecules and chemical compounds. The four most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element that vary in neutron number. There are three isotopes of hydrogen: protium, deuterium, and tritium.
Chapter 2 - Chemistry of Life

This document provides information on the structure and composition of matter. It discusses the basic units that make up all matter including atoms, elements, molecules, compounds, and mixtures. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Elements are composed of only one type of atom, while compounds contain at least two elements chemically bonded together. Chemical and physical properties depend on how atoms are arranged and bonded. The document also covers states of matter, chemical reactions, energy, and the role of catalysts like enzymes in biological reactions.
Atoms, Elements and compounds.pptx 2023 2024

The document discusses the basic concepts of atoms, elements, compounds, and mixtures. It defines atoms as the smallest particles that make up elements. Elements are composed of only one type of atom, while compounds contain two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together. Mixtures are combinations of substances that are not chemically bonded and can be separated. The periodic table is introduced as a way to identify elements based on atomic number and mass. Examples are provided to illustrate compounds and both homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Ch8 the atom-part 3

The document provides an overview of the periodic table and classification of elements and matter. It discusses how elements are classified based on their properties, including metals and nonmetals. Key periodic patterns are described, such as how the chemical behavior of elements is determined by their electron configuration. The periodic law is explained, as well as the development of the modern periodic table with periods and families.
Basic Science of Materials-1 (9).ppt

- Atoms are the smallest particles that make up elements and exhibit their properties. They are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Electrons determine electrical, magnetic, and chemical properties. Their distribution in orbits or shells differs for each element.
- The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged while neutrons have no charge. Electrons are negatively charged and have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons.
- Elements are pure substances made of one type of material that cannot be broken down further. There are over 120 known elements. Metals conduct electricity well and are hard, heavy solids.
Chapter 4 notes

The Rutherford gold foil experiment discovered the atomic nucleus. In this experiment, Rutherford beamed particles at a gold foil and observed some particles bouncing back at large angles, indicating a small, dense nucleus at the center of the atom. Dalton's atomic theory proposed that atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them the same atomic number but different atomic mass numbers. The periodic table arranges elements into groups based on repeating properties and allows easy comparison of elemental properties.
Mecchapter2 120815075639-phpapp02

The document summarizes key concepts about atomic structure and the periodic table. It discusses the composition of atoms including electrons, protons, and neutrons. It describes Dalton's atomic theory and the discoveries of subatomic particles. The periodic table is introduced, including its organization by family and period. The periodic law is explained. Electron configuration and arrangements are covered, including energy levels, subshells, orbitals, and electron spin.
Human Physiology Chemistry

Human physiology involves the study of molecules, cells, tissues, organs and organ systems that make up the human body. At the most basic level, atoms combine through chemical bonds like ionic and covalent bonds to form molecules, which then organize into cells. Cells further organize into tissues and organs to carry out specific functions and form organ systems that allow the human body to function as a whole.
CH1000 Fundamentals of ChemistryModule 1 – Chapter 3

CH1000
Fundament
als of
Chemistry
Module 1 – Chapter 3
Elements and Atoms
• What is an element?
• An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical
means into a simpler substance.
• Elements are the building blocks of matter.
• Elements can occur naturally or be synthesized in labs.
• The smallest unit of an element that retains its properties and chemical
behavior is called an atom.
• Atoms are made up of subatomic particles, but they do not have the properties of the
element
Elements
•Ten elements make up
almost 99 % of the mass of
the Earth’s crust, seawater
and atmosphere.
•Oxygen accounts for about
20 % of the atmosphere
and is found in nearly all
rocks, sand and soil.
Symbols
of the
Elements
•Each element has an
abbreviation called a symbol.
•The first letter of a symbol
must always be capitalized.
•If a second letter is needed, it
should be lowercase.
Introduction to
the Periodic Table
•Elements with similar
chemical properties are placed
in columns called groups.
•Four groups have special
identifying names, like Noble
Gases, in group 8A, which are
all unreactive gases.
Introduction to
the Periodic
Table
•The eight tall columns are called representative elements, or main group
elements. These are shown in red.
•The elements in the center are called the transition metals, or sometimes
the “inner transition metals.” These are shown in purple.
Introduction to the Periodic
Table
•Elements can be further classified
as metals, metalloids and
nonmetals.
•Notice the bold, black “staircase”
on the table. Everything to the left
of the staircase is a metal and
everything to the right of the
staircase is a non metal.
• The exception is Hydrogen,
which is why some periodic
tables will show hydrogen
disconnected from the main
body of the table.
•The elements in grey touching the
“staircase” are called metalloids, or
semiconductor metals. These metals
are used in the semiconductor
industry.
Metals,
Nonmetal
s and
Metalloids
• Solid at room temperature (except mercury)
• Shiny
• Good conductors of heat and electricity
• Malleable (can be shaped)
• Ductile (can be drawn into wires)
• Most metals have a high melting point and density
Metals
• Not shiny
• Have fairly low melting points and densities
• Are poor conductors of heat and electricity
Non
Metals
• Metalloids have properties between metals and
nonmetals.
• These elements are positioned diagonally on the Periodic
Table separating the metals and nonmetals.
Metalloid
s
Diatomic Elements
•Diatomic molecules
contain exactly two atoms
•Seven elements exist as
diatomic molecules and are
shown in the table to the
left
•Diatomic elements can be
separated.
Compounds
•A compound is a substance
containing two or more
elements that are chemically
combined in a definite
proportion by mass
•Compounds, unlike elements,
can be decomposed chemically
into simpler substances
...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules

This document discusses atoms, ions, and molecules. It defines atoms as the smallest particle of an element that cannot be broken down further. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, giving them a positive or negative charge. The document also defines molecules as two or more atoms chemically bonded together, and can be made of the same or different elements. Chemical formulas indicate the types of elements and number of each atom in a substance.
atomsionsandmolecules-120805032310-phpapp01.pdf

This document discusses atoms, ions, and molecules. It defines atoms as the smallest particle of an element that cannot be broken down further. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, giving them a positive or negative charge. The document also defines isotopes as atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Molecules are two or more atoms joined together, and can be made of the same or different elements. Chemical formulas indicate the types and numbers of atoms in a substance.
Basic concepts of chemistry

This document provides an overview of basic concepts in chemistry. It discusses that chemistry is the science of molecules and their transformations, and involves the study of elements and compounds. Key concepts covered include the branches of chemistry, atoms and molecules, physical and chemical properties of matter, states of matter, classification of matter as elements, compounds and mixtures, and separation techniques. Important historical figures and advancements in the field are also mentioned.
PPT ATOMS AND MOLECULE 

This document provides an overview of atoms and molecules. It defines key terms like atom, molecule, ion, and discusses Dalton's atomic theory and its postulates. The document explains that atoms are the smallest particles that make up matter and combine to form molecules or ions. It discusses how elements are represented by symbols and how atomic mass is measured in atomic mass units relative to carbon-12. The document also summarizes laws of chemical combination and provides examples of writing chemical formulas based on valencies of elements.
Similar to Science assignment- Form 4 Chapter 4 (20)
NOTES OF ELEMENTS COMPOUNDS AND MIXTURES GRADE 5.pptx

NOTES OF ELEMENTS COMPOUNDS AND MIXTURES GRADE 5.pptx
General Biology. LECTURE 2. THE CHEMICAL FOUNDATION OF LIFE.pptx

General Biology. LECTURE 2. THE CHEMICAL FOUNDATION OF LIFE.pptx
CH1000 Fundamentals of ChemistryModule 1 – Chapter 3

CH1000 Fundamentals of ChemistryModule 1 – Chapter 3
Recently uploaded
Equivariant neural networks and representation theory

Or: Beyond linear.
Abstract: Equivariant neural networks are neural networks that incorporate symmetries. The nonlinear activation functions in these networks result in interesting nonlinear equivariant maps between simple representations, and motivate the key player of this talk: piecewise linear representation theory.
Disclaimer: No one is perfect, so please mind that there might be mistakes and typos.
dtubbenhauer@gmail.com
Corrected slides: dtubbenhauer.com/talks.html
Describing and Interpreting an Immersive Learning Case with the Immersion Cub...

Current descriptions of immersive learning cases are often difficult or impossible to compare. This is due to a myriad of different options on what details to include, which aspects are relevant, and on the descriptive approaches employed. Also, these aspects often combine very specific details with more general guidelines or indicate intents and rationales without clarifying their implementation. In this paper we provide a method to describe immersive learning cases that is structured to enable comparisons, yet flexible enough to allow researchers and practitioners to decide which aspects to include. This method leverages a taxonomy that classifies educational aspects at three levels (uses, practices, and strategies) and then utilizes two frameworks, the Immersive Learning Brain and the Immersion Cube, to enable a structured description and interpretation of immersive learning cases. The method is then demonstrated on a published immersive learning case on training for wind turbine maintenance using virtual reality. Applying the method results in a structured artifact, the Immersive Learning Case Sheet, that tags the case with its proximal uses, practices, and strategies, and refines the free text case description to ensure that matching details are included. This contribution is thus a case description method in support of future comparative research of immersive learning cases. We then discuss how the resulting description and interpretation can be leveraged to change immersion learning cases, by enriching them (considering low-effort changes or additions) or innovating (exploring more challenging avenues of transformation). The method holds significant promise to support better-grounded research in immersive learning.
3D Hybrid PIC simulation of the plasma expansion (ISSS-14)

3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) algorithm,
Plasma expansion in the dipole magnetic field.
Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf

When I was asked to give a companion lecture in support of ‘The Philosophy of Science’ (https://shorturl.at/4pUXz) I decided not to walk through the detail of the many methodologies in order of use. Instead, I chose to employ a long standing, and ongoing, scientific development as an exemplar. And so, I chose the ever evolving story of Thermodynamics as a scientific investigation at its best.
Conducted over a period of >200 years, Thermodynamics R&D, and application, benefitted from the highest levels of professionalism, collaboration, and technical thoroughness. New layers of application, methodology, and practice were made possible by the progressive advance of technology. In turn, this has seen measurement and modelling accuracy continually improved at a micro and macro level.
Perhaps most importantly, Thermodynamics rapidly became a primary tool in the advance of applied science/engineering/technology, spanning micro-tech, to aerospace and cosmology. I can think of no better a story to illustrate the breadth of scientific methodologies and applications at their best.
Cytokines and their role in immune regulation.pptx

This presentation covers the content and information on "Cytokines " and their role in immune regulation .
The use of Nauplii and metanauplii artemia in aquaculture (brine shrimp).pptx

Although Artemia has been known to man for centuries, its use as a food for the culture of larval organisms apparently began only in the 1930s, when several investigators found that it made an excellent food for newly hatched fish larvae (Litvinenko et al., 2023). As aquaculture developed in the 1960s and ‘70s, the use of Artemia also became more widespread, due both to its convenience and to its nutritional value for larval organisms (Arenas-Pardo et al., 2024). The fact that Artemia dormant cysts can be stored for long periods in cans, and then used as an off-the-shelf food requiring only 24 h of incubation makes them the most convenient, least labor-intensive, live food available for aquaculture (Sorgeloos & Roubach, 2021). The nutritional value of Artemia, especially for marine organisms, is not constant, but varies both geographically and temporally. During the last decade, however, both the causes of Artemia nutritional variability and methods to improve poorquality Artemia have been identified (Loufi et al., 2024).
Brine shrimp (Artemia spp.) are used in marine aquaculture worldwide. Annually, more than 2,000 metric tons of dry cysts are used for cultivation of fish, crustacean, and shellfish larva. Brine shrimp are important to aquaculture because newly hatched brine shrimp nauplii (larvae) provide a food source for many fish fry (Mozanzadeh et al., 2021). Culture and harvesting of brine shrimp eggs represents another aspect of the aquaculture industry. Nauplii and metanauplii of Artemia, commonly known as brine shrimp, play a crucial role in aquaculture due to their nutritional value and suitability as live feed for many aquatic species, particularly in larval stages (Sorgeloos & Roubach, 2021).
Immersive Learning That Works: Research Grounding and Paths Forward

We will metaverse into the essence of immersive learning, into its three dimensions and conceptual models. This approach encompasses elements from teaching methodologies to social involvement, through organizational concerns and technologies. Challenging the perception of learning as knowledge transfer, we introduce a 'Uses, Practices & Strategies' model operationalized by the 'Immersive Learning Brain' and ‘Immersion Cube’ frameworks. This approach offers a comprehensive guide through the intricacies of immersive educational experiences and spotlighting research frontiers, along the immersion dimensions of system, narrative, and agency. Our discourse extends to stakeholders beyond the academic sphere, addressing the interests of technologists, instructional designers, and policymakers. We span various contexts, from formal education to organizational transformation to the new horizon of an AI-pervasive society. This keynote aims to unite the iLRN community in a collaborative journey towards a future where immersive learning research and practice coalesce, paving the way for innovative educational research and practice landscapes.
Unlocking the mysteries of reproduction: Exploring fecundity and gonadosomati...

The pygmy halfbeak Dermogenys colletei, is known for its viviparous nature, this presents an intriguing case of relatively low fecundity, raising questions about potential compensatory reproductive strategies employed by this species. Our study delves into the examination of fecundity and the Gonadosomatic Index (GSI) in the Pygmy Halfbeak, D. colletei (Meisner, 2001), an intriguing viviparous fish indigenous to Sarawak, Borneo. We hypothesize that the Pygmy halfbeak, D. colletei, may exhibit unique reproductive adaptations to offset its low fecundity, thus enhancing its survival and fitness. To address this, we conducted a comprehensive study utilizing 28 mature female specimens of D. colletei, carefully measuring fecundity and GSI to shed light on the reproductive adaptations of this species. Our findings reveal that D. colletei indeed exhibits low fecundity, with a mean of 16.76 ± 2.01, and a mean GSI of 12.83 ± 1.27, providing crucial insights into the reproductive mechanisms at play in this species. These results underscore the existence of unique reproductive strategies in D. colletei, enabling its adaptation and persistence in Borneo's diverse aquatic ecosystems, and call for further ecological research to elucidate these mechanisms. This study lends to a better understanding of viviparous fish in Borneo and contributes to the broader field of aquatic ecology, enhancing our knowledge of species adaptations to unique ecological challenges.
如何办理(uvic毕业证书)维多利亚大学毕业证本科学位证书原版一模一样

原版纸张【微信:741003700 】【(uvic毕业证书)维多利亚大学毕业证】【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原海外各大学 Bachelor Diploma degree, Master Degree Diploma
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
Phenomics assisted breeding in crop improvement

As the population is increasing and will reach about 9 billion upto 2050. Also due to climate change, it is difficult to meet the food requirement of such a large population. Facing the challenges presented by resource shortages, climate
change, and increasing global population, crop yield and quality need to be improved in a sustainable way over the coming decades. Genetic improvement by breeding is the best way to increase crop productivity. With the rapid progression of functional
genomics, an increasing number of crop genomes have been sequenced and dozens of genes influencing key agronomic traits have been identified. However, current genome sequence information has not been adequately exploited for understanding
the complex characteristics of multiple gene, owing to a lack of crop phenotypic data. Efficient, automatic, and accurate technologies and platforms that can capture phenotypic data that can
be linked to genomics information for crop improvement at all growth stages have become as important as genotyping. Thus,
high-throughput phenotyping has become the major bottleneck restricting crop breeding. Plant phenomics has been defined as the high-throughput, accurate acquisition and analysis of multi-dimensional phenotypes
during crop growing stages at the organism level, including the cell, tissue, organ, individual plant, plot, and field levels. With the rapid development of novel sensors, imaging technology,
and analysis methods, numerous infrastructure platforms have been developed for phenotyping.
在线办理(salfor毕业证书)索尔福德大学毕业证毕业完成信一模一样

学校原件一模一样【微信:741003700 】《(salfor毕业证书)索尔福德大学毕业证》【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)原件一模一样纸张工艺/offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原。
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微741003700】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证【q/微741003700】
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf

Isolation of pure culture, its various method.
Recently uploaded (20)
Equivariant neural networks and representation theory

Equivariant neural networks and representation theory
Describing and Interpreting an Immersive Learning Case with the Immersion Cub...

Describing and Interpreting an Immersive Learning Case with the Immersion Cub...
3D Hybrid PIC simulation of the plasma expansion (ISSS-14)

3D Hybrid PIC simulation of the plasma expansion (ISSS-14)
Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf

Applied Science: Thermodynamics, Laws & Methodology.pdf
Cytokines and their role in immune regulation.pptx

Cytokines and their role in immune regulation.pptx
The use of Nauplii and metanauplii artemia in aquaculture (brine shrimp).pptx

The use of Nauplii and metanauplii artemia in aquaculture (brine shrimp).pptx
Immersive Learning That Works: Research Grounding and Paths Forward

Immersive Learning That Works: Research Grounding and Paths Forward
Unlocking the mysteries of reproduction: Exploring fecundity and gonadosomati...

Unlocking the mysteries of reproduction: Exploring fecundity and gonadosomati...
Basics of crystallography, crystal systems, classes and different forms

Basics of crystallography, crystal systems, classes and different forms
aziz sancar nobel prize winner: from mardin to nobel

aziz sancar nobel prize winner: from mardin to nobel
8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf

8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf
mô tả các thí nghiệm về đánh giá tác động dòng khí hóa sau đốt

mô tả các thí nghiệm về đánh giá tác động dòng khí hóa sau đốt
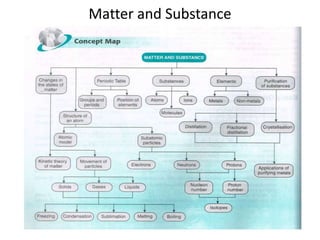
Science assignment- Form 4 Chapter 4
- 2. Kinetic Theory of Matter 1) Kinetic Theory of Matter states that • Matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles. • The particles are always moving in random motion. • The moving energy is called the kinetic energy of particles. • The kinetic energy of particles depends on the temperature of matter and increases when the temperature increases. 2) Importance of Kinetic Theory of Matter: a) It explains the movement of particles in three states, which are solid, liquid and gaseous states. b) It explains the basic structure of matter.
- 3. Interconversion of the Three States of Matter
- 5. Kinetic Theory of Matter can be applied to explain the changes in the states of matter through the processes as shown.
- 8. Structure of an Atom •Matter is made up of tiny, discrete particles called atoms. •An atom is the smallest particle in an element which is able to react chemically. •An atom is indivisible. •It is impossible to observe an atom with the naked eye. However, you may be able to see a crude picture of atoms taken with an electron microscope called the scanning tunnelling microscope. The atoms are magnified millions of times as shown in Photograph 4.1.
- 9. Subatomic Particles of Atoms • An atom is made up of three subatomic particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. • The atom consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by subatomic particles known as electrons as shown in the Figure 4.8.
- 10. Properties of Subatomic Particles
- 11. 4.3 Proton Number and Nucleon Number in Atoms of Elements • An element is a substance which cannot be split by any known chemical method into two or more simpler substances. • An element is made up of atoms, for example, element iron contains iron atoms. • The element either occur naturally or are man-made by scientists. • A neutral atom contains an equal number of protons and electrons as shown in Table 4.5. Element Number of protons Number of electrons Hydrogen 1 1 Oxygen 8 8 Iron 26 26 Table 4.5 Neutral atoms
- 12. • Proton number = number of protons = number of electrons of a neutral atom • Nucleon number = number of protons + number of neutrons • Number of neutrons = nucleon number – proton number • An atom can be represented by the symbol as shown in Figure 4.10 :
- 13. Isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element and contain the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. • Each isotopes is named by inserting the nucleon number after the name of the element. • Example of hydrogen isotopes include a) Hydrogen-1 : a hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutron b) Hydrogen-2 : a hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 1 neutron c) Hydrogen-3 : a hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 2 neutrons
- 14. Table below shows the isotopes for different elements.
- 15. Classification of Elements in the Periodic Table • In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, introduced a table which was known as the Periodic Table. It contained all 63 elements in the table were arranged from left to right in the order of their increasing atomic masses. • The importance of the Periodic Table : – Important in systematic and methodical study of elements. – Help us to determine the properties of elements. – Uses to forecast the properties and uses of particular element.
- 17. Properties of Substances – Atoms, Molecules and Ions • An atom is the smallest, indivisible particle of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction. • A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same type or different types which are chemically combined together. • There are two types of molecules : – Molecules of an element ( combination of the same type of atoms. For example : oxygen, hydrogen and chlorine) – Molecules of a compound ( combination of the different types of atoms. For example : water, carbon dioxide and ammonia) • An ion is when an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes a charged particle. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positive ion and it has more protons than electrons but if gains electrons, it becomes a negative ion which has more electrons than protons.
- 18. Comparison of properties among three groups of substances
- 19. Metals and non-metals • Most elements can be classified as metals or non-metals. • Examples of metals include iron, sliver, copper, aluminium, gold and tin. • Argon, hydrogen gas and diamonds are examples of non-metals. • Uses of metals and non-metals in daily life : Examples of Metals • Iron is used in making cars, bridges and railway tracks. • Sliver is often used to make jewellery. • Copper is used in make wires for electric circuits. • Aluminium is used to make power lines as it is very light. Examples of non-metals •Diamond are mostly used to make beautiful jewellery. •Phosphorus is used to make matchstick tips. •Sulphur is a key ingredient in making paint. •Graphite is used to manufacture lubricants.
- 20. Similarities and differences between metals and non-metals
- 21. Method of Purification • Purification is a process in which impurities are separated from a particular substance so that it becomes a pure substance. • Purification is carried out using diverse physical techniques. No chemical changes take place. • Purification is carried out through: – Distillation – Crystallisation
- 22. Distillation • Distillation involves the evaporation of a liquid to form a gas or a vapour. The vapour is then condensed to obtain a pure liquid known as distillation. © TutorVista (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xxNfJLMNS4E)
- 23. Crystallisation • Crystallisation is a process carried out to obtain crystals from a saturated solution. © KClassScienceChannel (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QdwKhbtzsug)
- 24. Characteristics of substances to the purification methods used.
- 25. Conclusion • As conclude, matter exists in three states – solid, liquid and gas. • Heat energy is absorbed during boiling, melting and sublimation ; Heat energy is released during freezing and condensation. • An atom is made of three subatomic particles – protons, neutrons and electrons. • Isotopes are atoms of an element that have the same proton number but different nucleon numbers. • The Periodic Table is a table of elements arranged from left to right in the order of their increasing proton numbers. • Metals are hard, shiny, ductile, malleable and can conduct electricity and heat. • Non-metals are dull, brittle and poor conductors of electricity and heat. • Purification carried out through distillation and crystallisation.