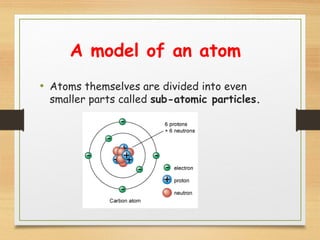
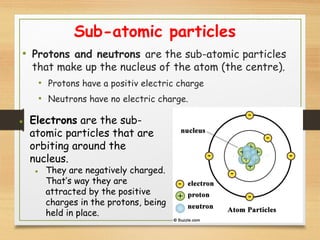
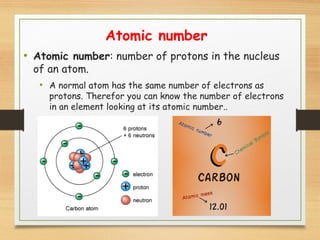
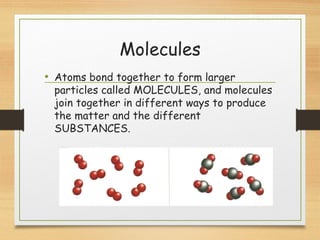
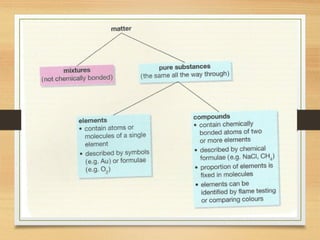
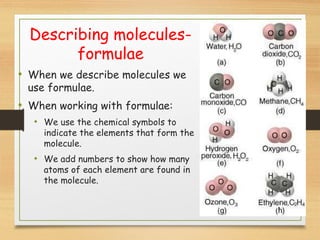
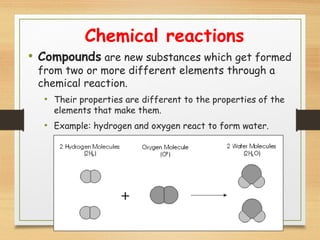
This document provides an overview of atoms, elements, molecules, and compounds. It discusses how everything is made up of atoms, which contain subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons. Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Elements are organized in the periodic table according to their properties and atomic structure. Atoms can bond together to form molecules, which are made of one or more elements. Compounds are molecules made of two or more different elements bonded together. The properties of compounds are different from the individual elements.