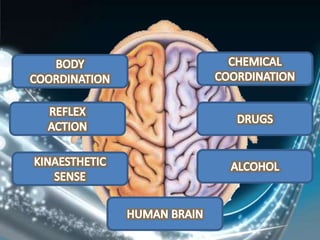
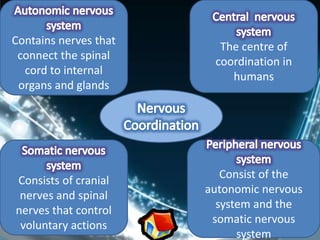
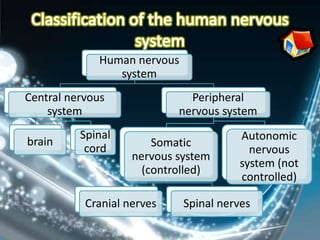
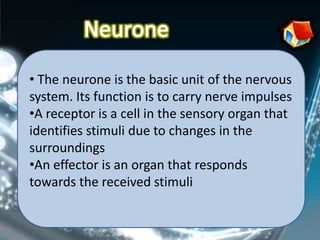
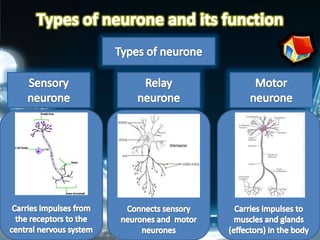
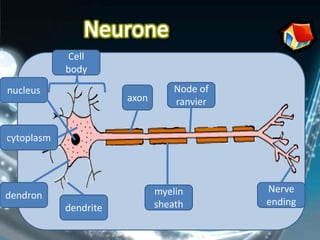
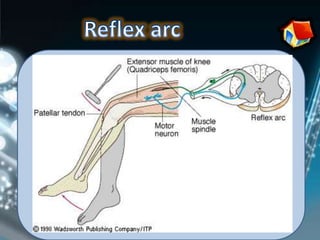
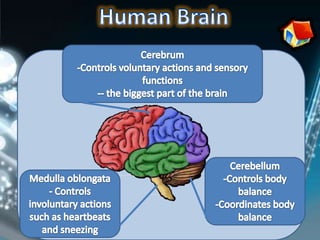
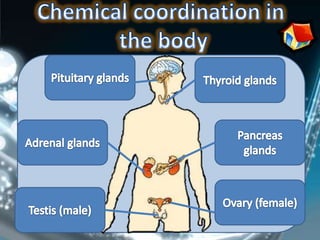
Coordination involves the adjustment and cooperation of various body parts and systems. There are two types of coordination: nervous coordination involving the brain, spinal cord, and nerves; and hormonal coordination involving glands and organs. The document then describes the structure and function of the nervous system including neurons, receptors, effectors, and reflex actions. It also discusses proprioception and kinaesthetic senses which provide awareness of body position and movement. Voluntary actions are controlled by desires while involuntary actions are controlled by the medulla oblongata. Finally, it notes that alcohol can hinder nervous system function and coordination by slowing impulse transmission and potentially damaging liver cells.