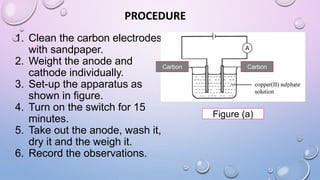
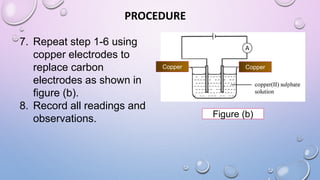
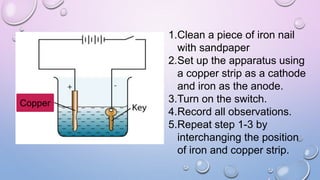
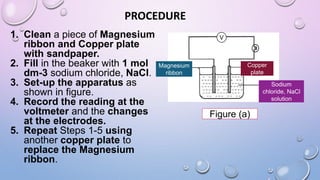
Experiment 6.8 investigates displacement reactions between metals and their salt solutions to construct an electrochemical series. The procedure involves placing different metal strips (magnesium, zinc, lead, copper) into separate salt solutions (magnesium nitrate, zinc nitrate, lead nitrate, copper nitrate). Observations are made to check for any color changes in the solutions, solid deposits on the metals, and metal dissolution. It is hypothesized that the greater the number of metals that can displace a metal from its salt solution, the higher its position will be in the electrochemical series.