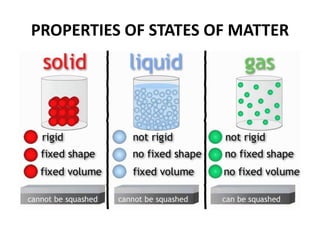
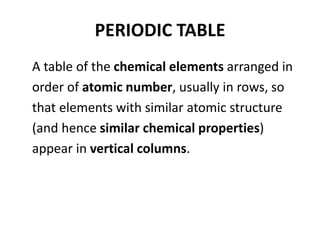
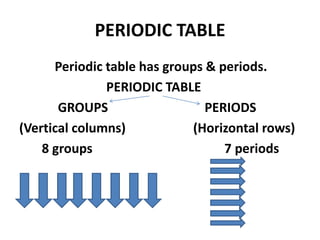
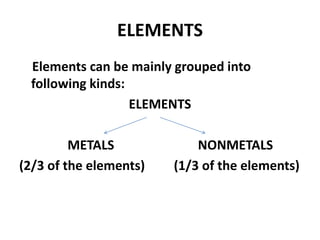
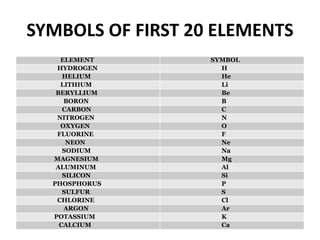
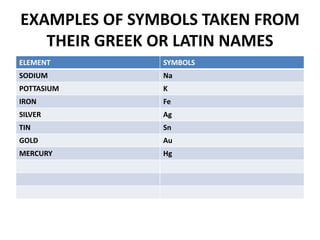
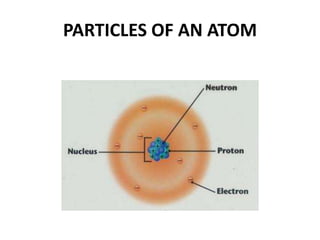
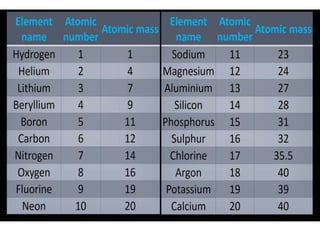
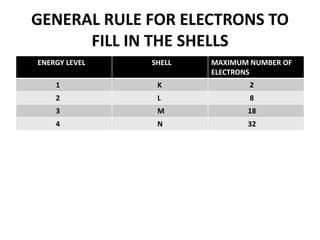
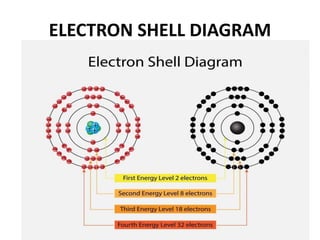
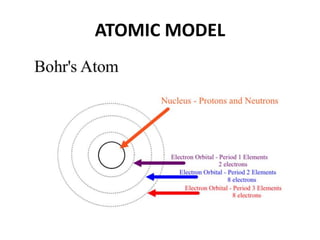
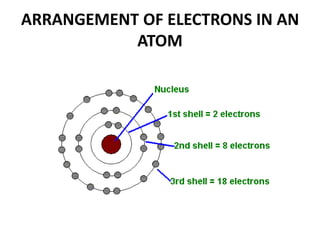
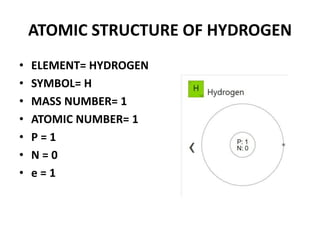
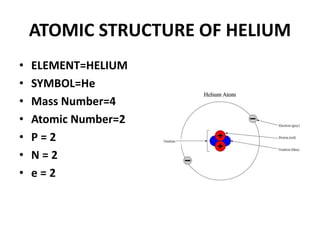
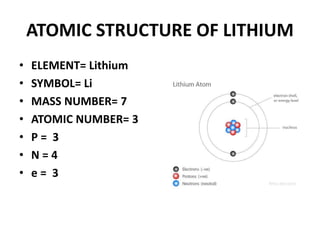
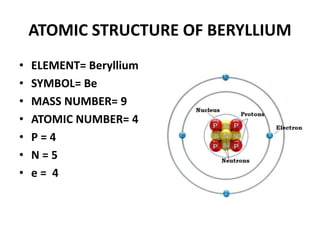
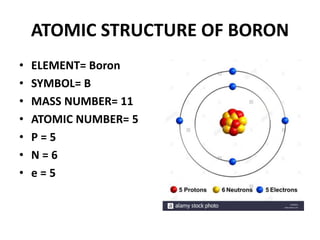
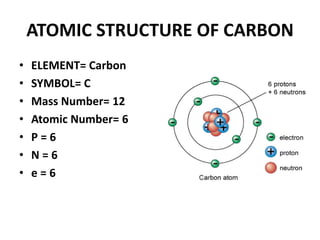
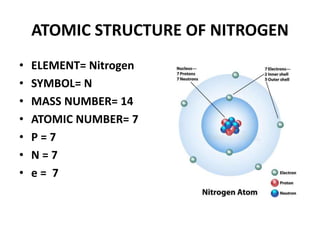
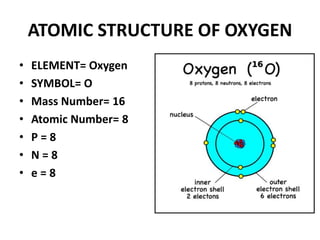
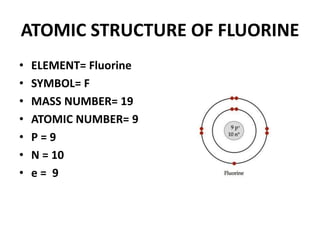
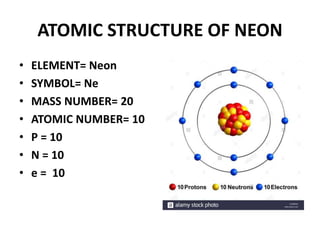
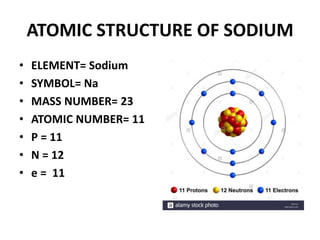
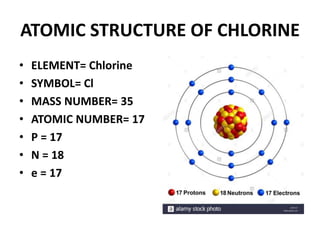
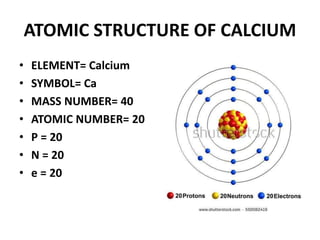
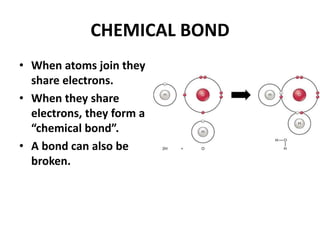
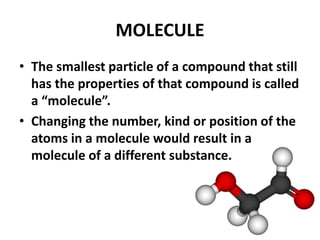
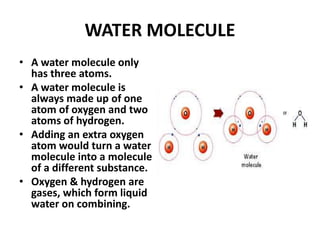
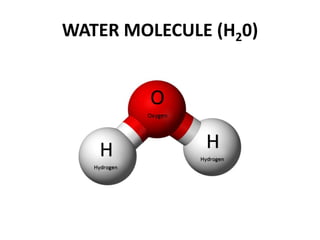
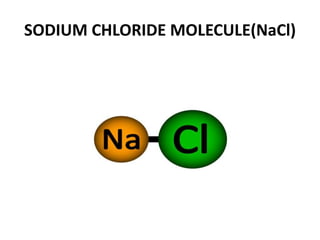
This document provides information about the structure and properties of matter. It defines key terms like atomic theory, atom, element, compound, and molecule. It describes the basic structure of an atom including protons, neutrons, electrons, and electron shells. It provides examples of the atomic structure of various elements like hydrogen, helium, lithium, oxygen, and calcium. It also discusses how elements can form compounds by chemical bonding and how compounds have different properties than their constituent elements. Compounds are made of molecules, the smallest units that exhibit a compound's properties, as illustrated by examples of water and sodium chloride molecules.