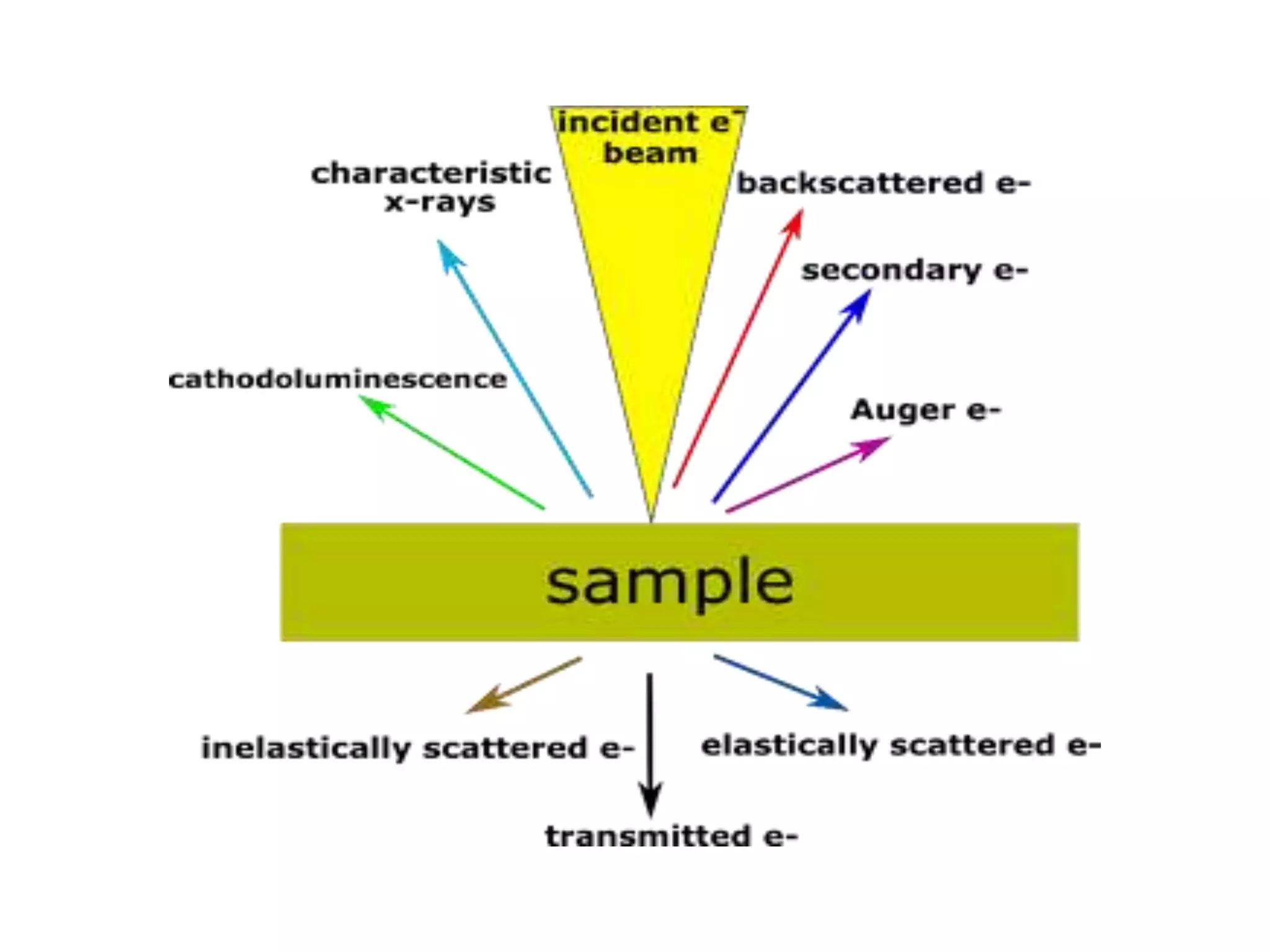
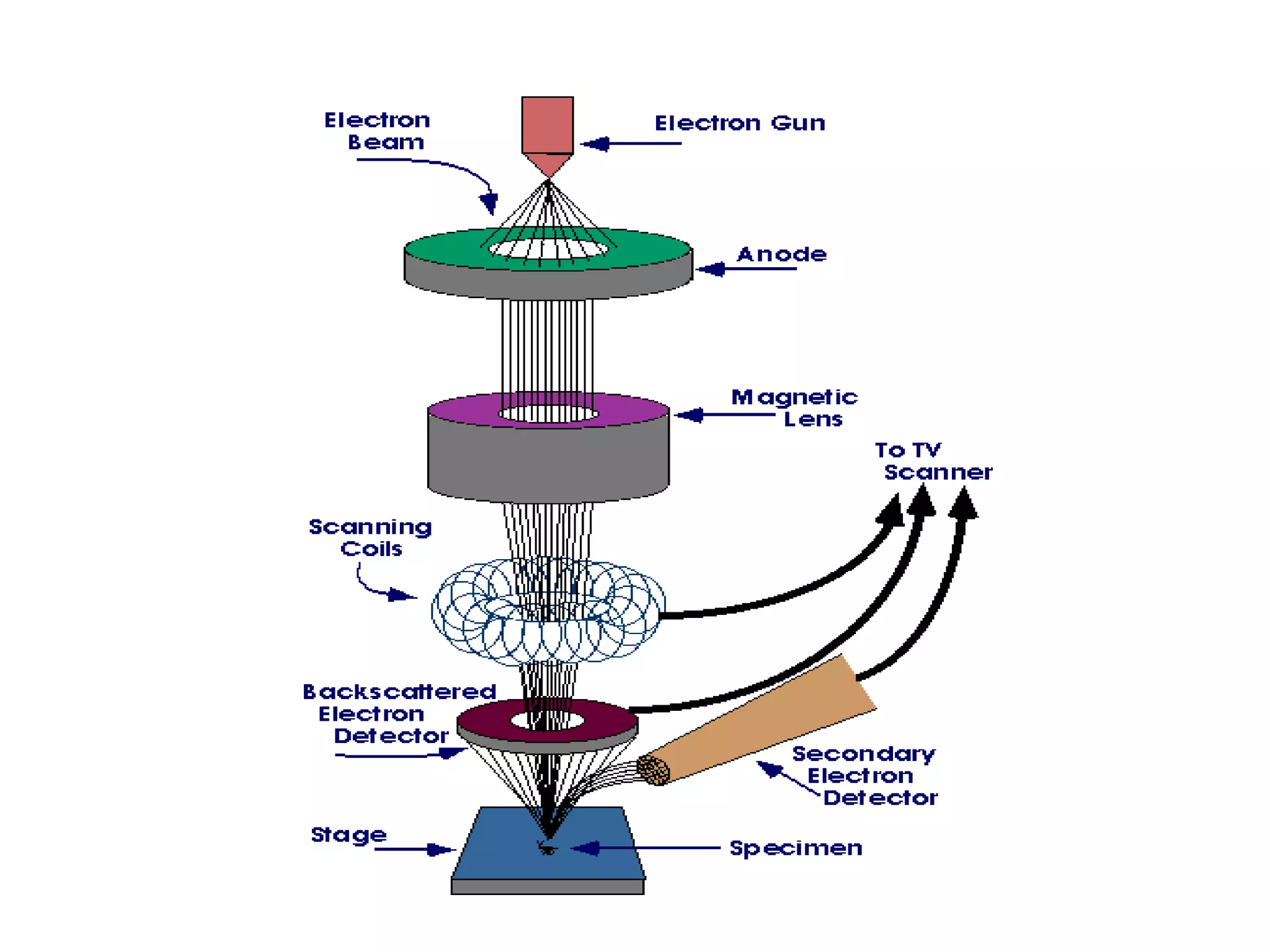
The document provides a comprehensive overview of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), detailing its introduction, types, principles, instrumentation, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It describes how SEM produces high-magnification images of samples through focused electron beams and various interactions with the sample's atoms. Additionally, it discusses the components of SEM, including the electron gun, column, detectors, and the challenges regarding analysis of certain materials.