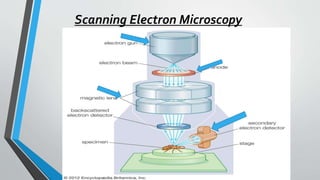
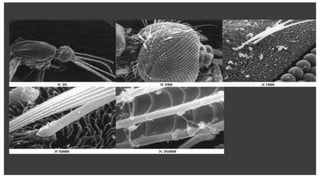
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) utilizes electron beams to produce high-resolution three-dimensional images of various specimens. It is instrumental in fields such as biology, forensics, and materials science, allowing for detailed investigations of sample surfaces and microstructures. While SEM offers significant advantages in terms of magnification and speed, it also has notable disadvantages, including high operational costs and extensive sample preparation requirements.