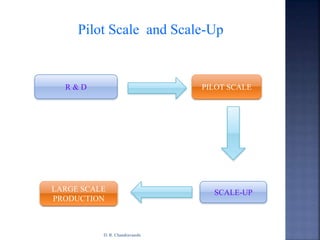
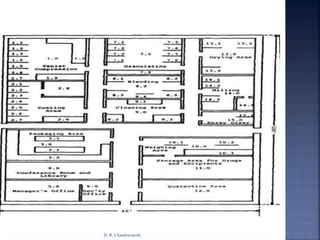
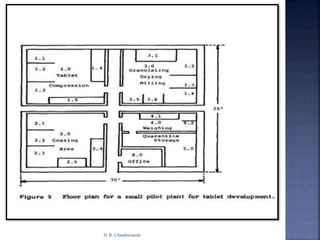
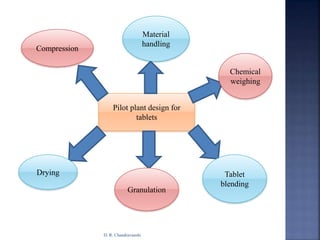
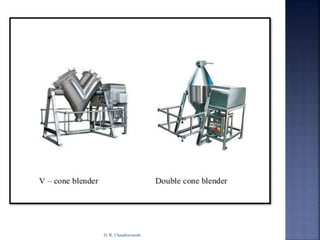
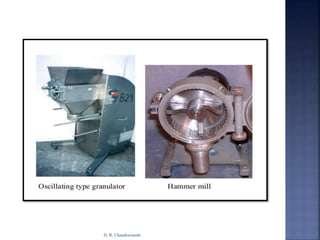
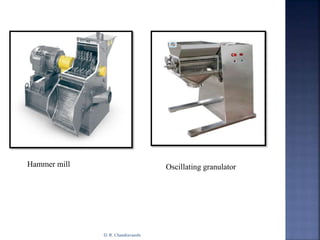
The document discusses pilot plant scale-up considerations for solid dosage forms in the pharmaceutical industry, detailing processes like blending, granulation, and drying. It emphasizes the importance of designing pilot plants to ensure consistent, economical, and reproducible large-scale production while minimizing cross-contamination. Additionally, it highlights the evaluation of laboratory studies and the necessity for thorough procedures in manufacturing chemistry to achieve product uniformity.