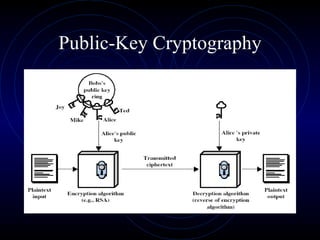
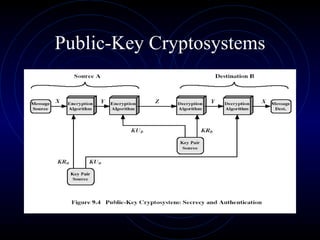
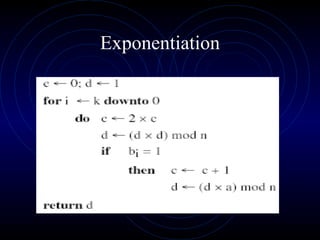
Public Key Cryptography uses two keys - a public key that can encrypt messages and verify signatures, and a private key that can decrypt messages and create signatures. The RSA algorithm, the most widely used public key algorithm, is based on the mathematical difficulty of factoring large prime numbers. It works by having users generate a public/private key pair using two large prime numbers and performing modular exponentiation. The security of RSA relies on the fact that it is computationally infeasible to derive the private key from the public key and modulus.