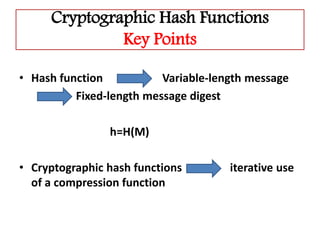
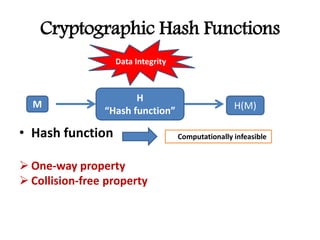
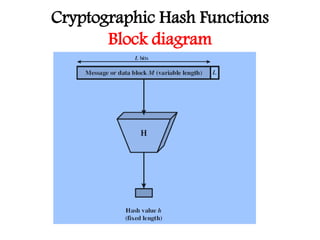
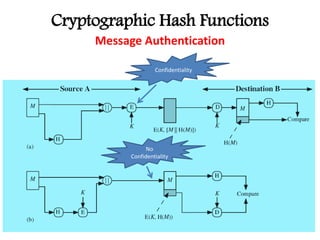
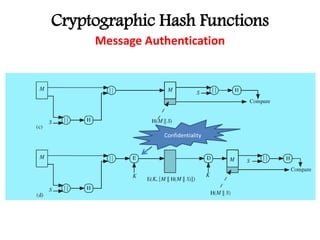
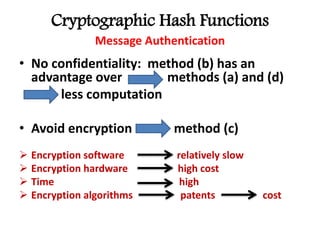
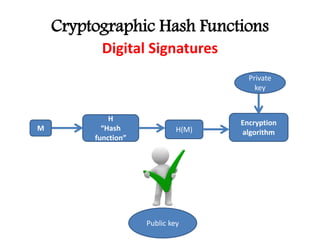
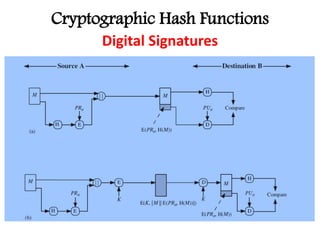
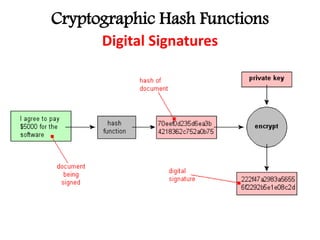
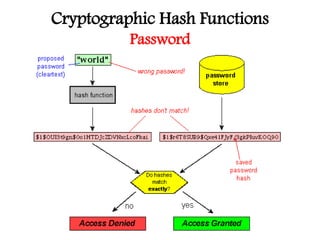
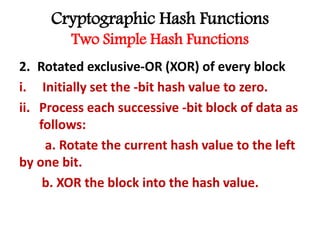
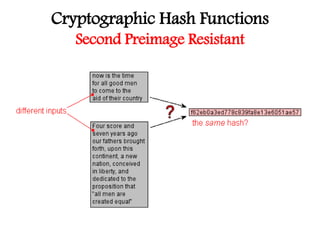
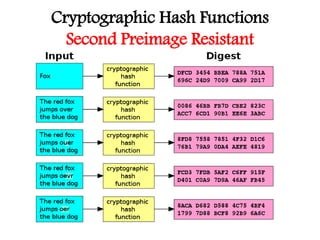
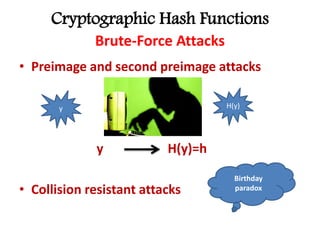
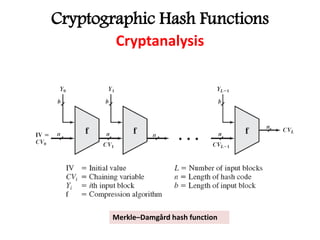
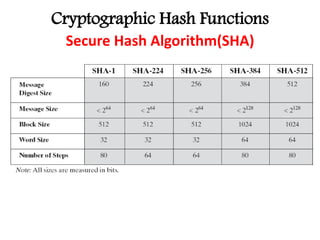
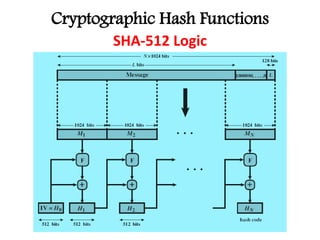
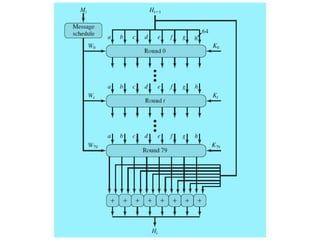
This document discusses cryptographic hash functions including their applications in message authentication and digital signatures. It describes the requirements for hash functions to be secure including resistance to brute force attacks and cryptanalysis. The document outlines some simple hash functions and provides details on the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) family of cryptographic hash functions used in standards like SHA-512 which operates on 1024-bit blocks through 80 rounds. It also mentions NIST's selection of the Keccak algorithm as the new SHA-3 standard.