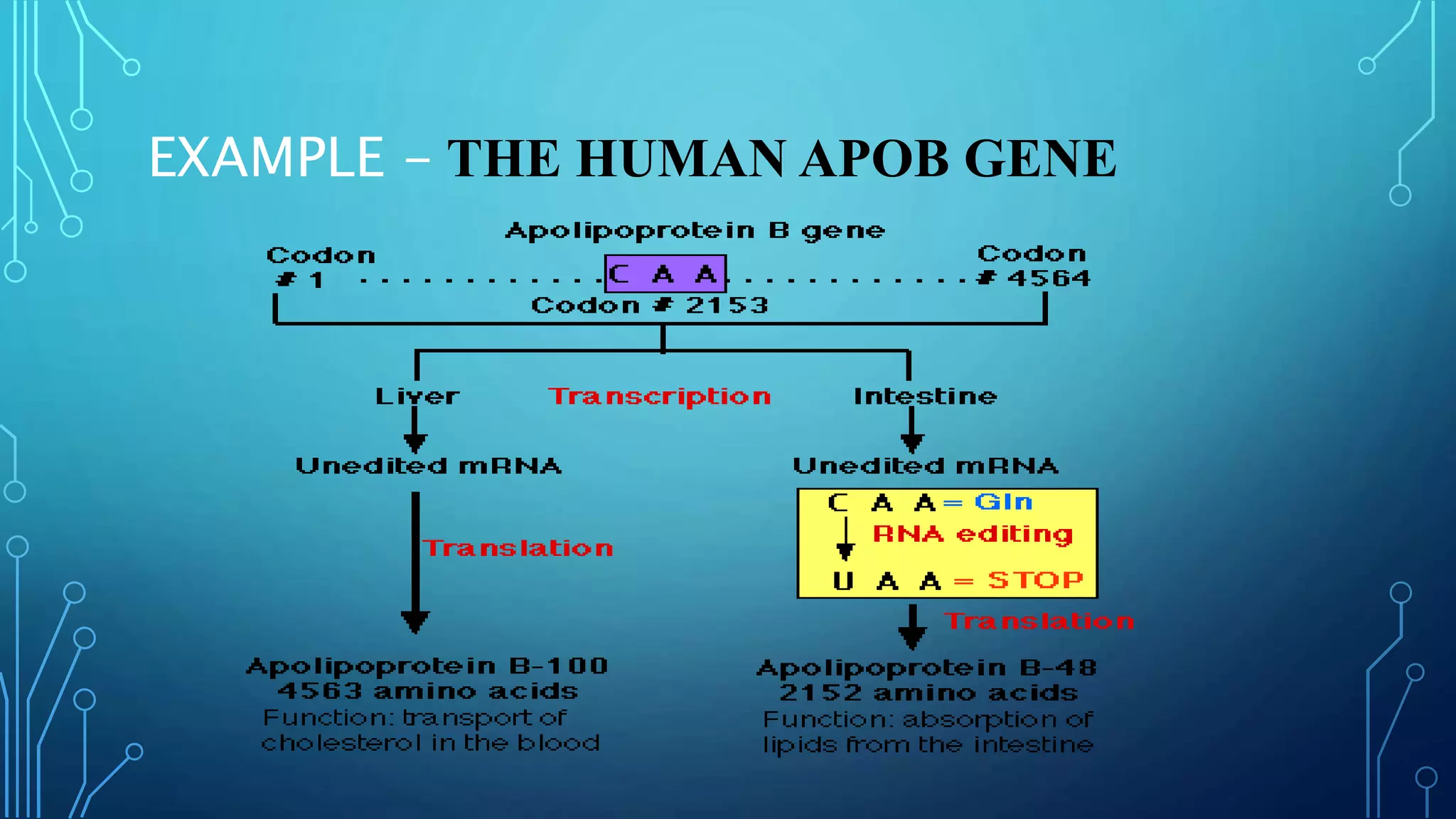
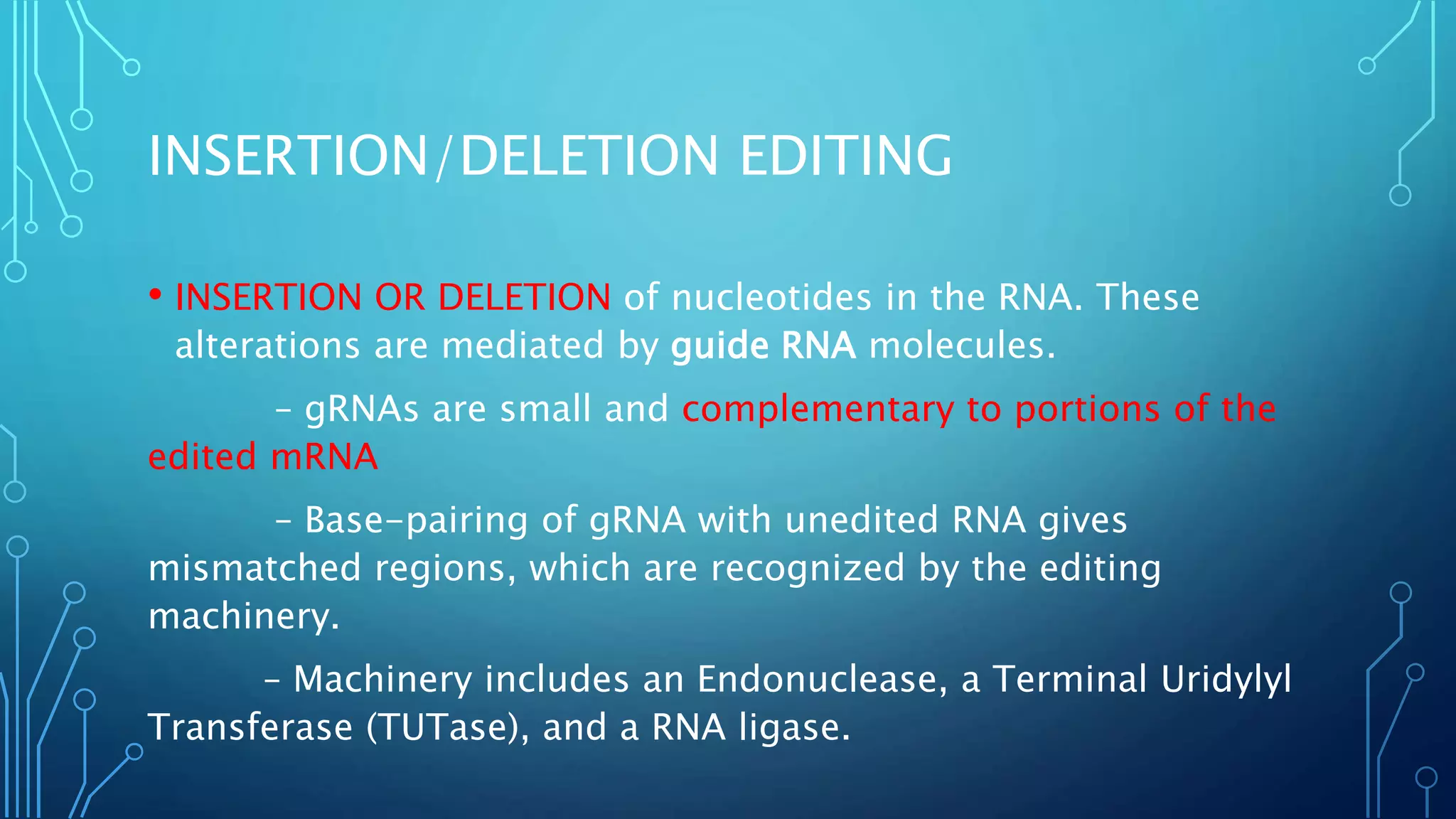
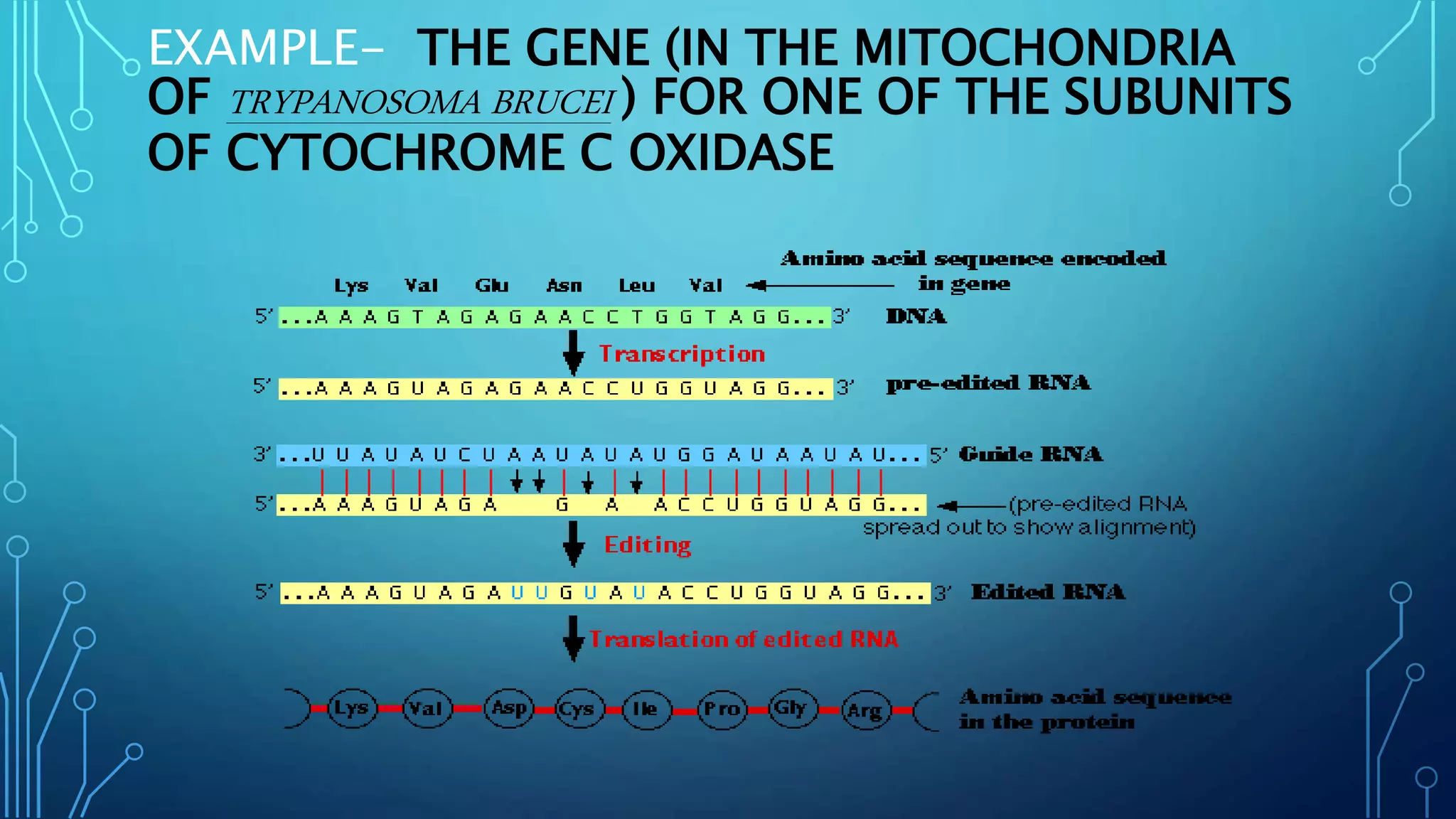
This document discusses RNA editing. It defines RNA editing as molecular processes that alter the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule after transcription from DNA. There are two main types of RNA editing: substitution editing, where individual nucleotides are chemically altered, and insertion/deletion editing, which adds or removes nucleotides. An example of substitution editing is provided in the human APOB gene, where an enzyme changes a codon resulting in alternative protein isoforms. Guide RNAs are also discussed as facilitating insertion/deletion editing through base-pairing with pre-mRNAs. RNA editing increases proteomic diversity and regulates gene expression.