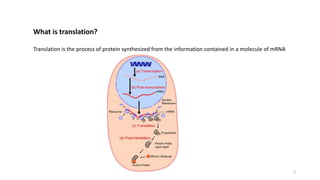
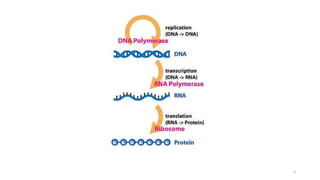
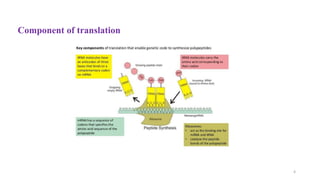
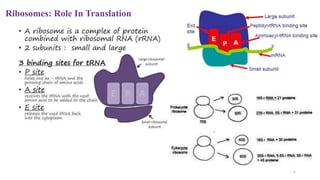
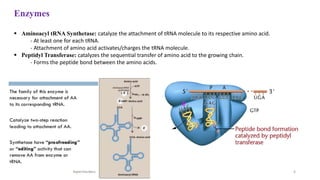
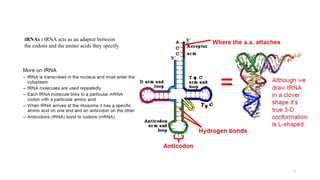
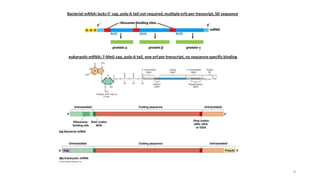
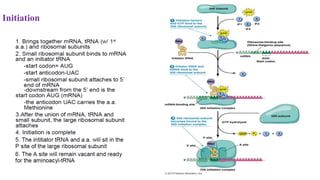
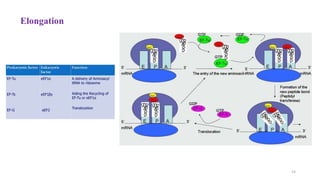
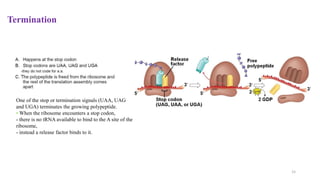
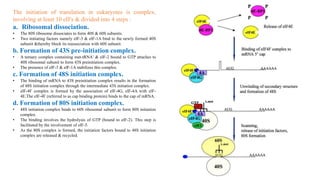
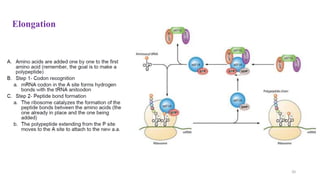
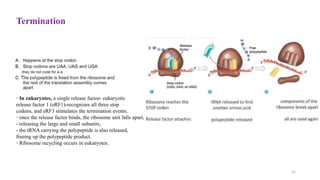
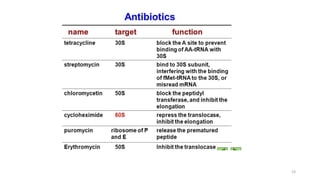
This document summarizes translation mechanisms in prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. It discusses that translation is the process of protein synthesis from mRNA, involving ribosomes, tRNAs, and enzymes. The three main steps of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination - are described for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Key differences between the two systems are the use of Shine-Dalgarno sequences and initiation factors in prokaryotes versus Kozak sequences and more complex initiation factor involvement in eukaryotes. Termination and ribosome recycling mechanisms are also compared between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.