Waterfalls form where a band of hard rock lies next to soft rock in the upper course of a river. As the river passes over the hard rock, the soft rock below erodes more quickly, undercutting the hard rock. Eventually the hard rock collapses, enlarging the plunge pool beneath through abrasion. As the waterfall retreats upstream through erosion, it forms a steep-walled gorge.
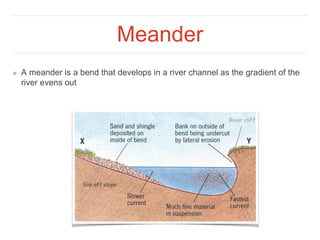
Meanders form as the river's gradient evens out. On the outer bend of a meander, faster flow causes greater erosion and deepening of the channel. On the inner bend, deposition occurs, building up a shallow area called a slip-off slope.
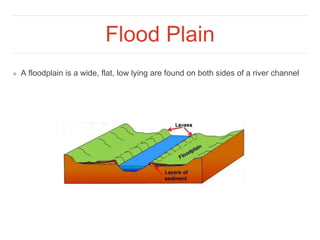
When a river floods and over