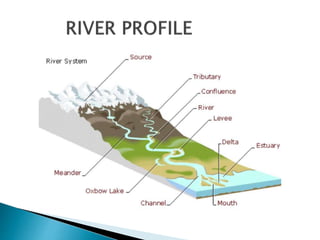
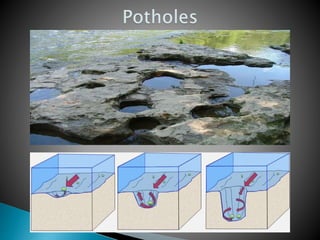
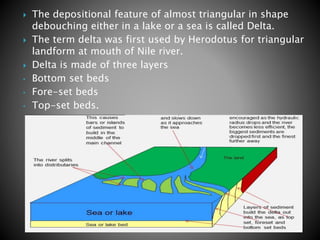
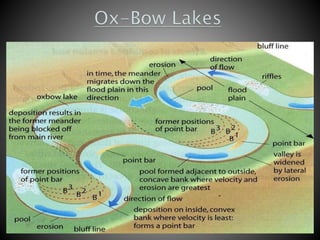
The document details the characteristics and processes of rivers, including their longitudinal profiles, methods of erosion like hydraulic action, attrition, and corrosion. It explains the formation of various landforms, such as valleys, gorges, canyons, and waterfalls, resulting from water flow and geological factors. Additionally, it discusses sediment transport and depositional features like alluvial fans, cones, and deltas.