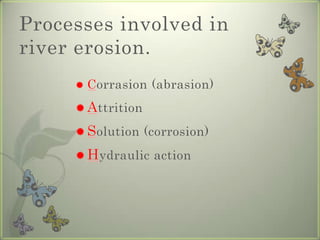
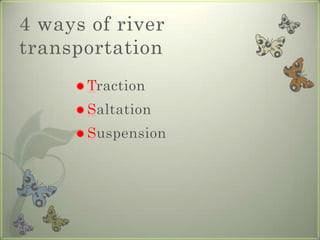
River erosion occurs through processes like abrasion and hydraulic action that wear away rock in the river bed and banks. This shapes the landscape, creating narrow V-shaped valleys through vertical erosion and lengthening rivers upstream through headward erosion. Lateral erosion widens the river channel and forms U-shaped valleys. River transportation involves moving eroded material downstream via traction, saltation, suspension, or solution based on the size and weight of the load.