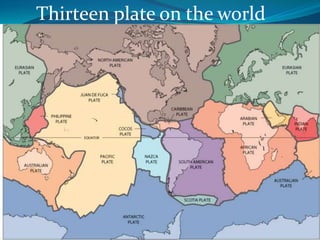
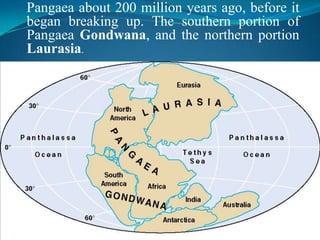
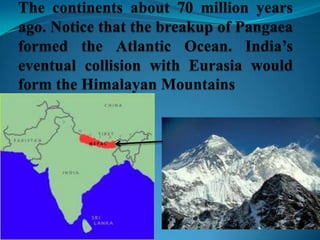
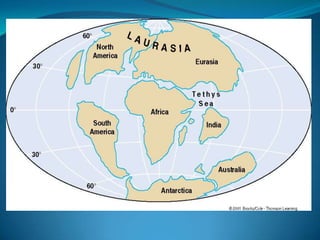
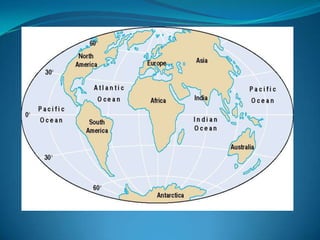
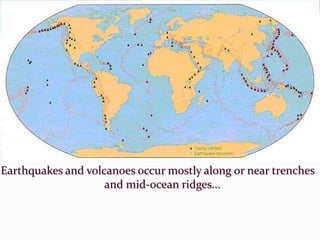
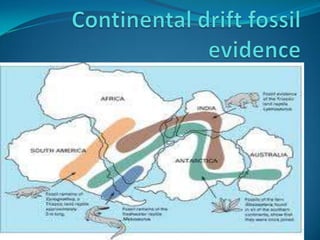
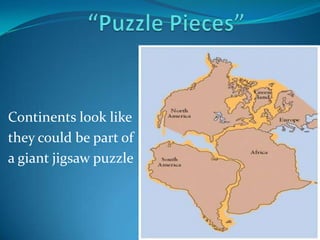
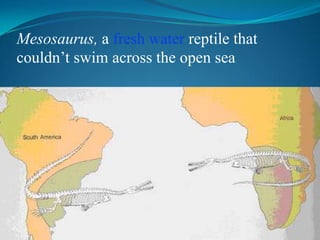
According to the continental drift hypothesis, the continents have slowly moved over time to their current positions. Alfred Wegener first proposed this theory in 1912. Seafloor spreading provided insight into the mechanism of plate tectonics, with magma pushing the plates apart at mid-ocean ridges and subduction zones pulling them under. About 225 million years ago, nearly all land was part of the supercontinent Pangaea, which has since broken apart, forming the continents in their current positions.