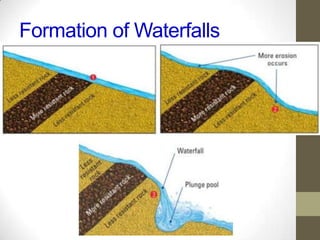
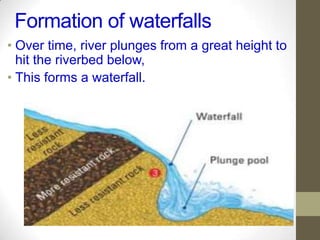
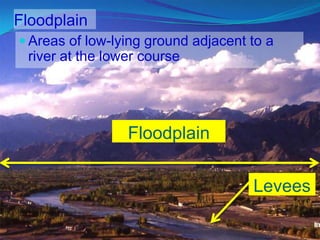
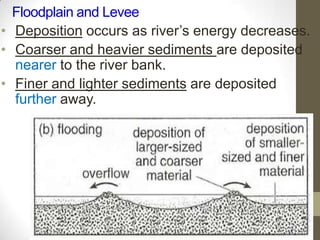
Rivers are formed through the hydrological cycle as precipitation falls and flows over land towards the sea. A river's features include its source, mouth, drainage basin, and tributaries. Waterfalls form through erosion of rocks of varying resistance. Meanders form as rivers curve to avoid obstacles, eroding cliffs on outer banks and depositing slip-off slopes on inner banks. Floodplains and levees develop from sediment deposition during floods, with coarser sediments forming raised levees and finer sediments creating flat floodplains. Deltas form at river mouths as sediments accumulate and cause the river to split into distributaries. While rivers provide water and transportation, overflowing can damage property and contaminated water risks disease.