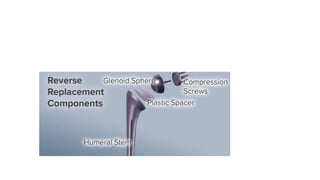
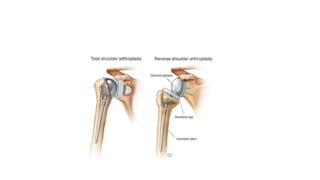
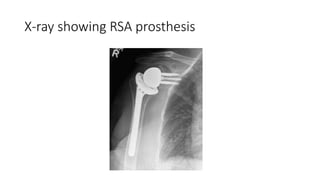
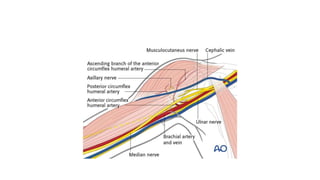
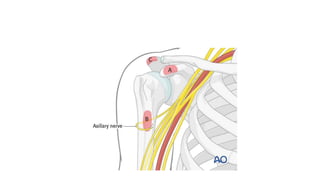
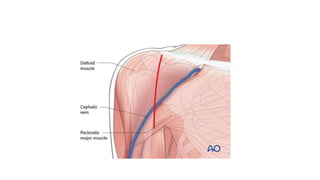
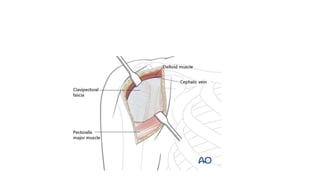
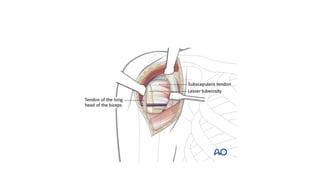
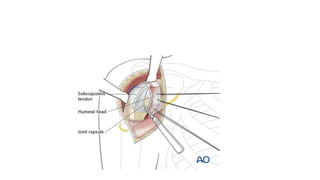
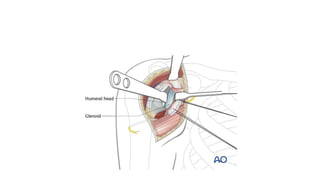
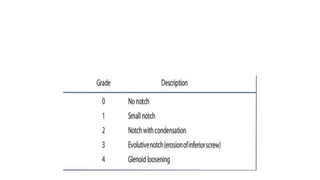
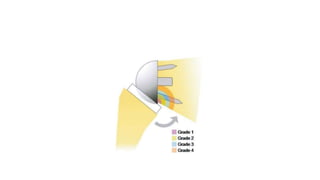
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty involves replacing the humeral head and glenoid fossa with prosthetics to alter the center of rotation and increase deltoid tension and function. It is indicated for rotator cuff tear arthropathy, proximal humeral fractures in the elderly, failed shoulder replacements, and other conditions. The procedure involves an deltopectoral approach to expose the joint, removal of the humeral head and shaping of the glenoid, then implantation of the glenosphere and humeral cup components. Outcomes are best for osteoarthritis and worse for trauma or revision cases. Complications can include infection, nerve injury, implant loosening or breakage.