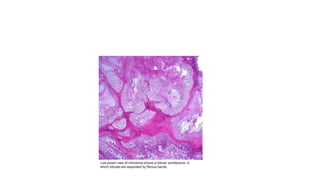
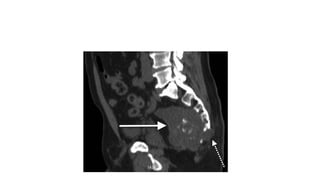
Sacral chordoma is a rare, slowly growing malignant tumor that arises from remnants of the notochord, usually occurring in the sacrum. It accounts for 1-4% of all malignancies and is the most common primary malignancy of the sacrum. Patients typically experience lower back pain worsening with sitting in their 5th-7th decade. Imaging shows a destructive lytic lesion in the sacrum. Complete surgical resection is the primary treatment, but recurrence is common due to the locally aggressive nature, leading to poor long-term survival rates.