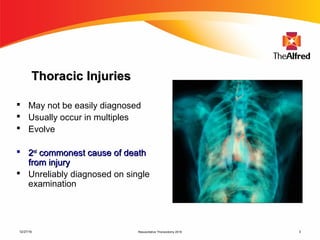
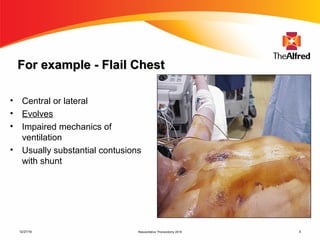
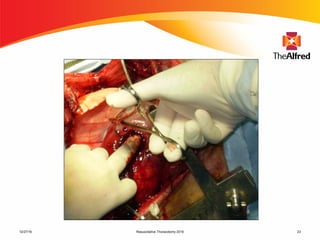
1) Thoracic trauma is responsible for 20-25% of all trauma deaths and contributes to an additional 25% of trauma fatalities. Many thoracic injuries are not immediately apparent and may evolve over time, potentially leading to cardiac tamponade, massive hemorrhage, or other lethal complications.
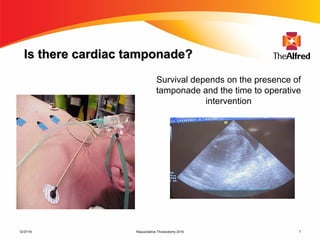
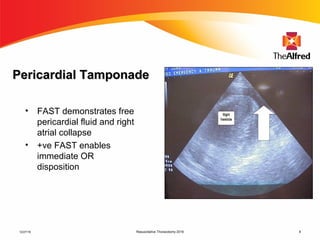
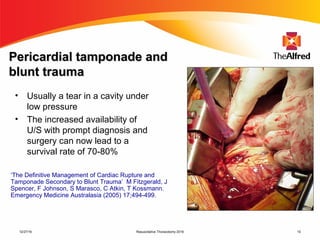
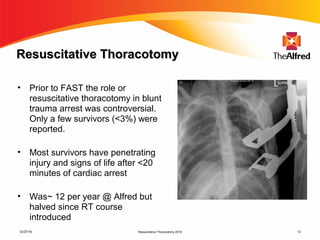
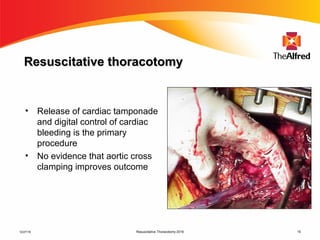
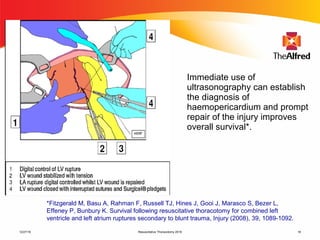
2) Resuscitative thoracotomy performed within 20 minutes of cardiac arrest may improve survival chances for trauma patients experiencing blunt chest or abdominal trauma with subsequent cardiac arrest and hemorrhagic shock. Immediate use of ultrasound to diagnose cardiac injuries like hemopericardium also allows for prompter surgical repair.
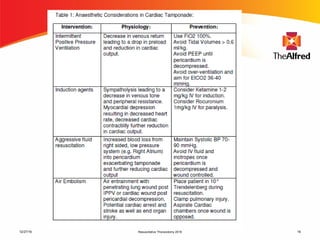
3) Credentialing in resuscitative thoracotomy involves training in