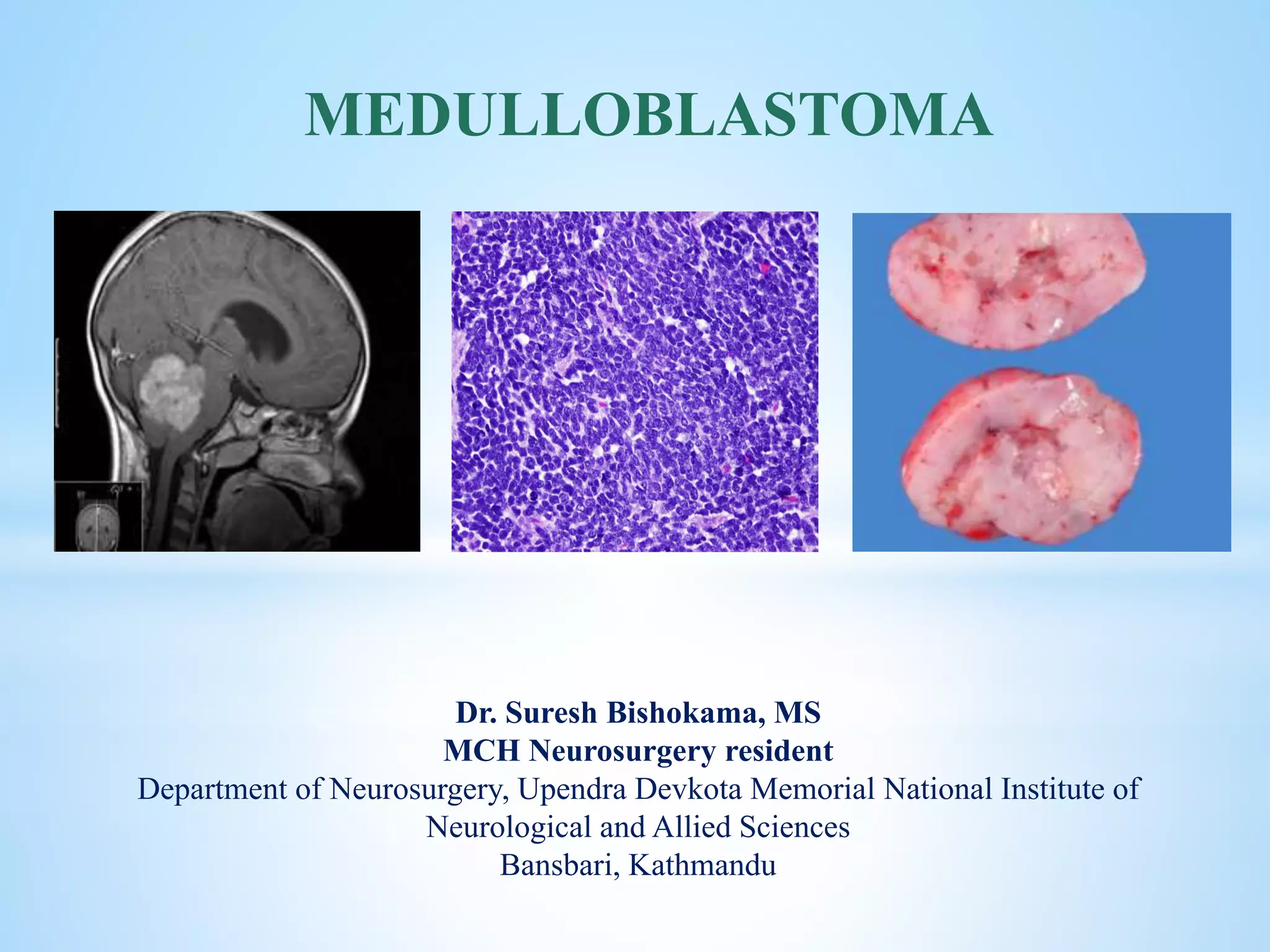
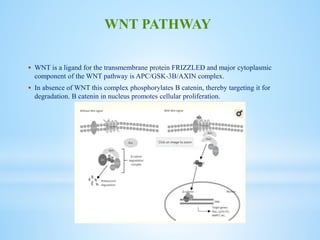
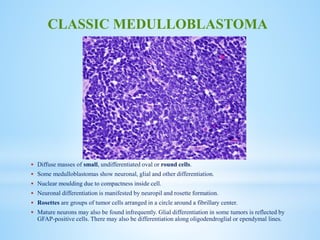
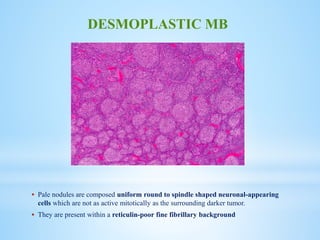
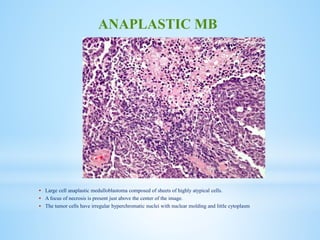
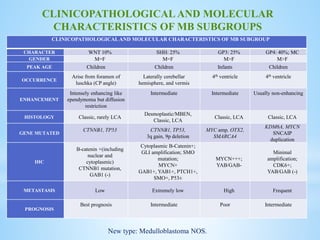
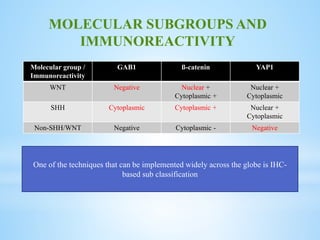
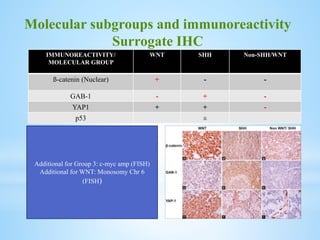
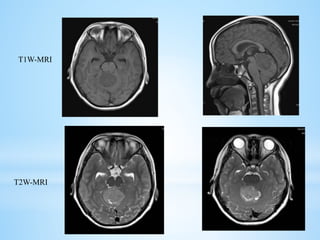
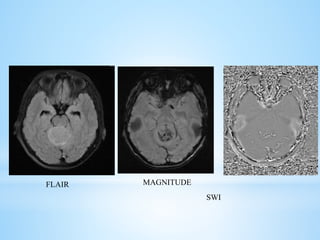
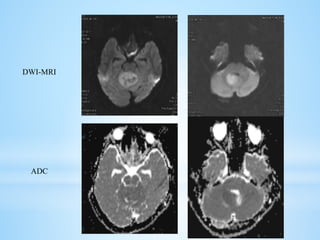
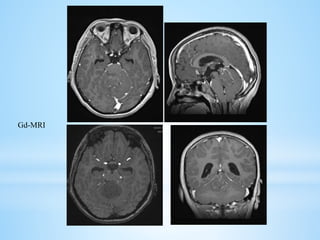
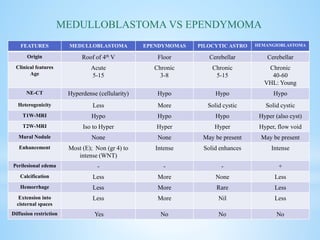
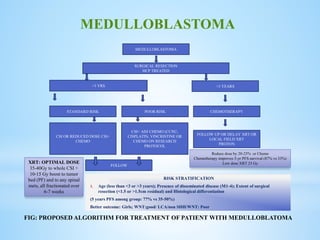
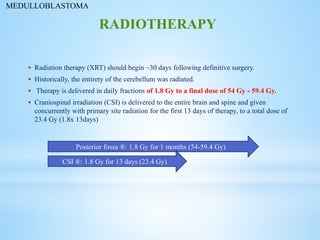
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children, accounting for a significant percentage of pediatric CNS tumors, and has varying presentation based on age and location. The document discusses its epidemiology, pathogenesis, histological subtypes, clinical presentation, treatment strategies, and prognostic factors, highlighting the importance of molecular subgroups in determining treatment and outcomes. Recent advances in imaging and targeted therapies are noted, with ongoing research into optimizing surgical and radiotherapy approaches for improved patient survival and quality of life.