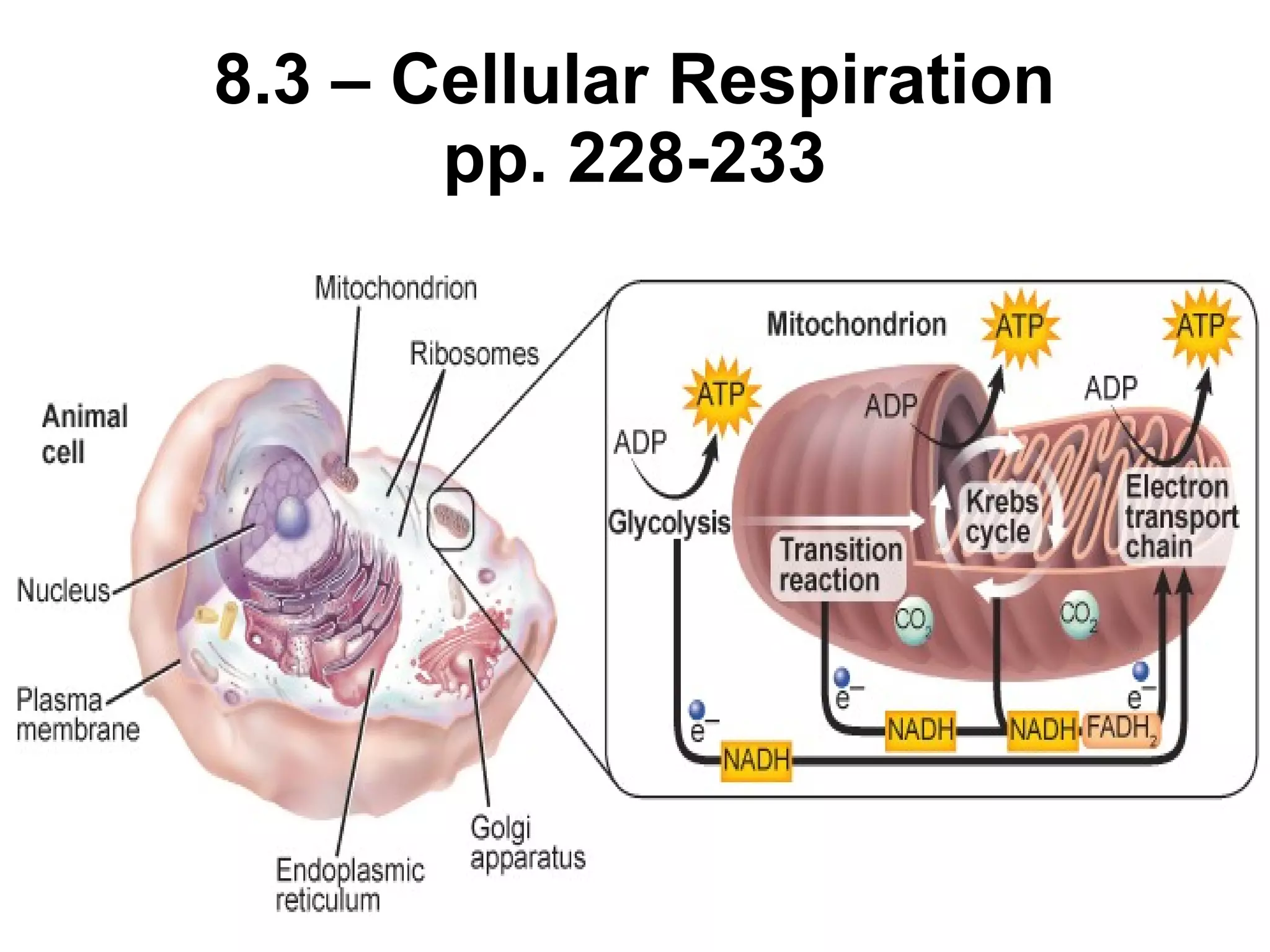
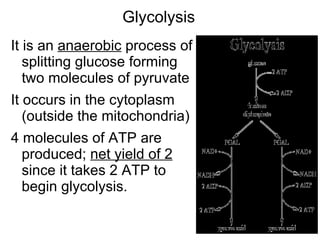
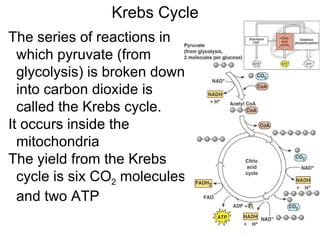
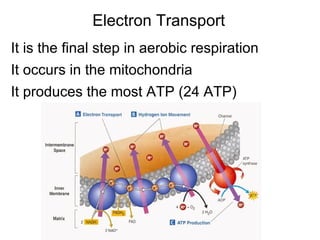
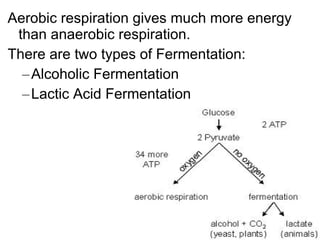
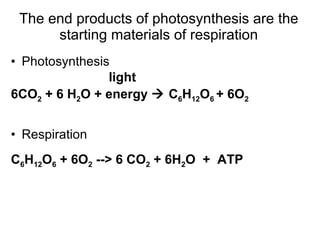
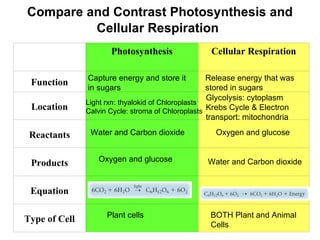
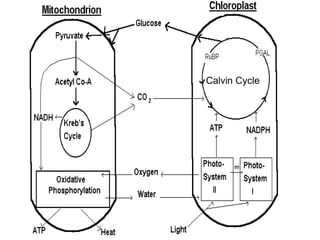
This document summarizes cellular respiration. It describes that cellular respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis and occurs in both plant and animal cells using mitochondria. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen and has three stages - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen through fermentation. Aerobic respiration produces more ATP than anaerobic respiration. The overall equation shows that glucose breakdown produces ATP through the process of cellular respiration.