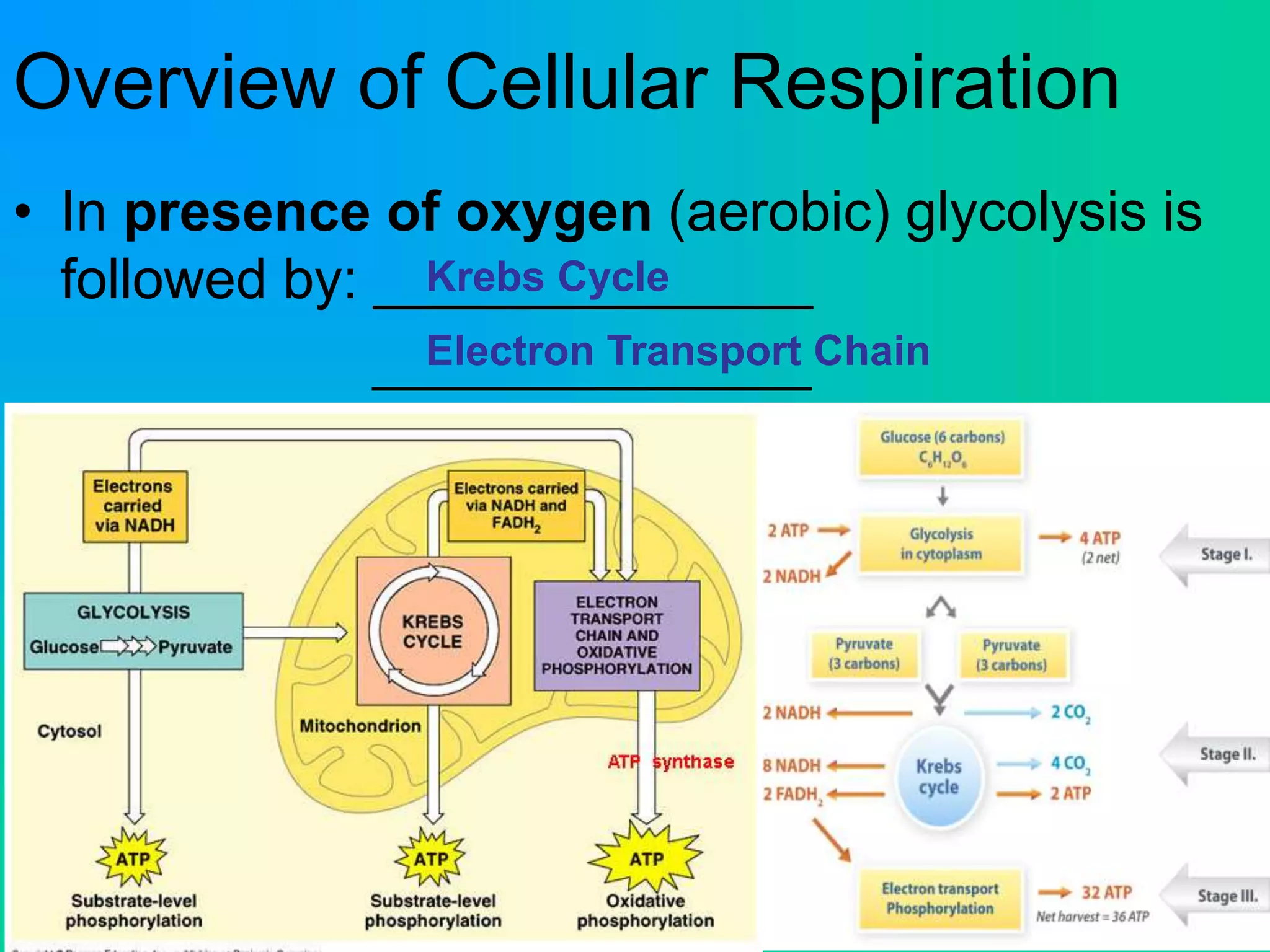
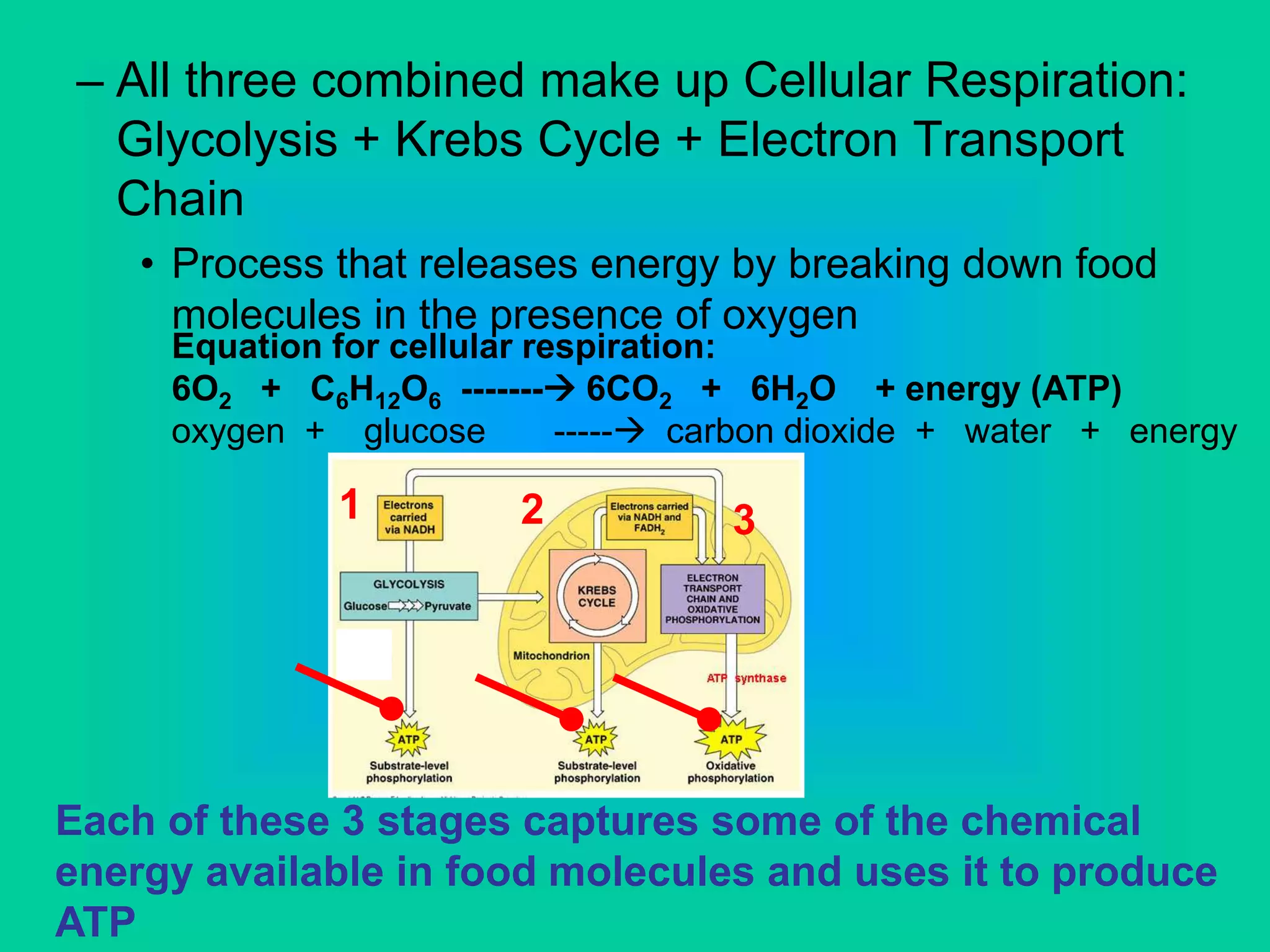
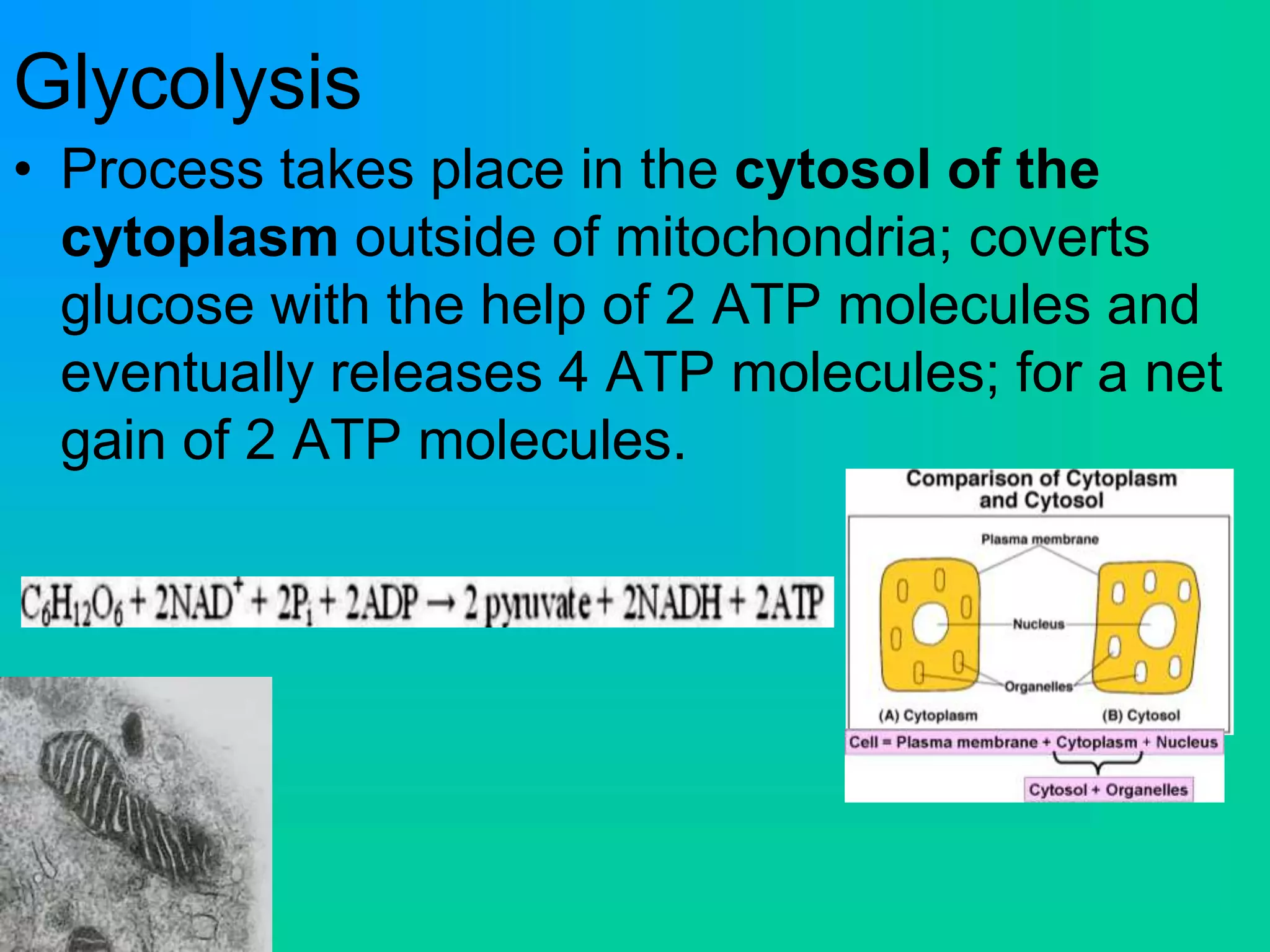
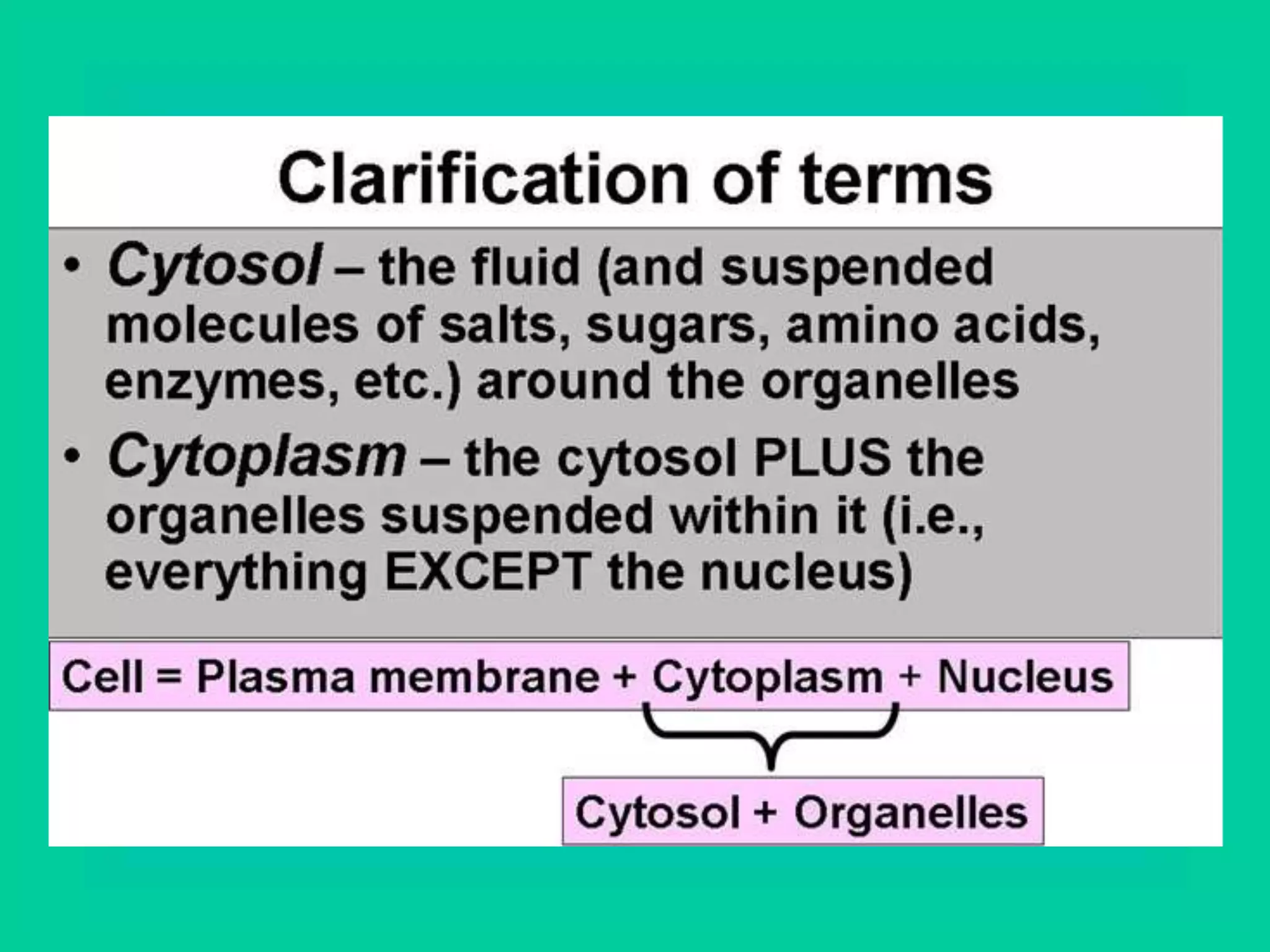
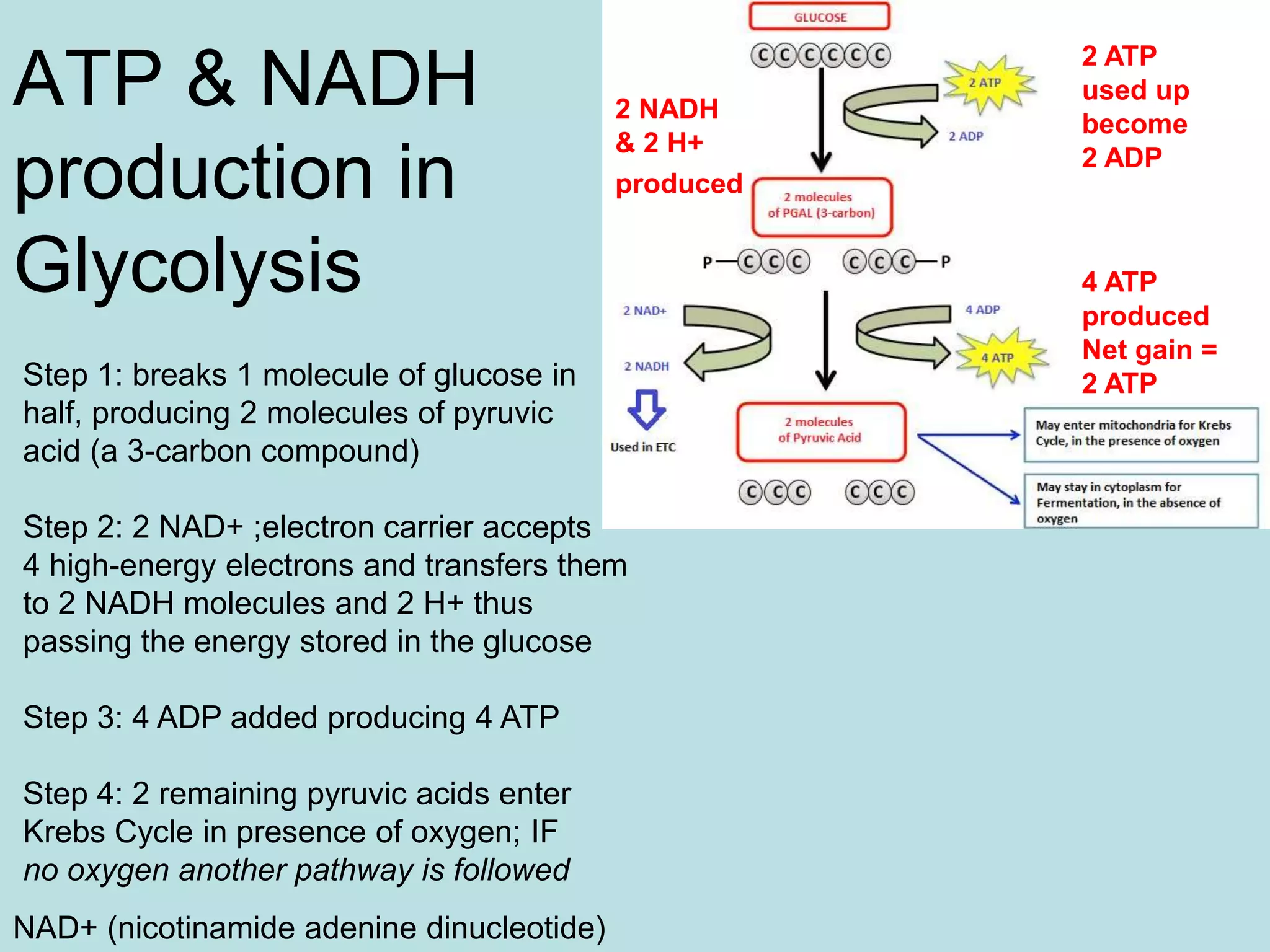
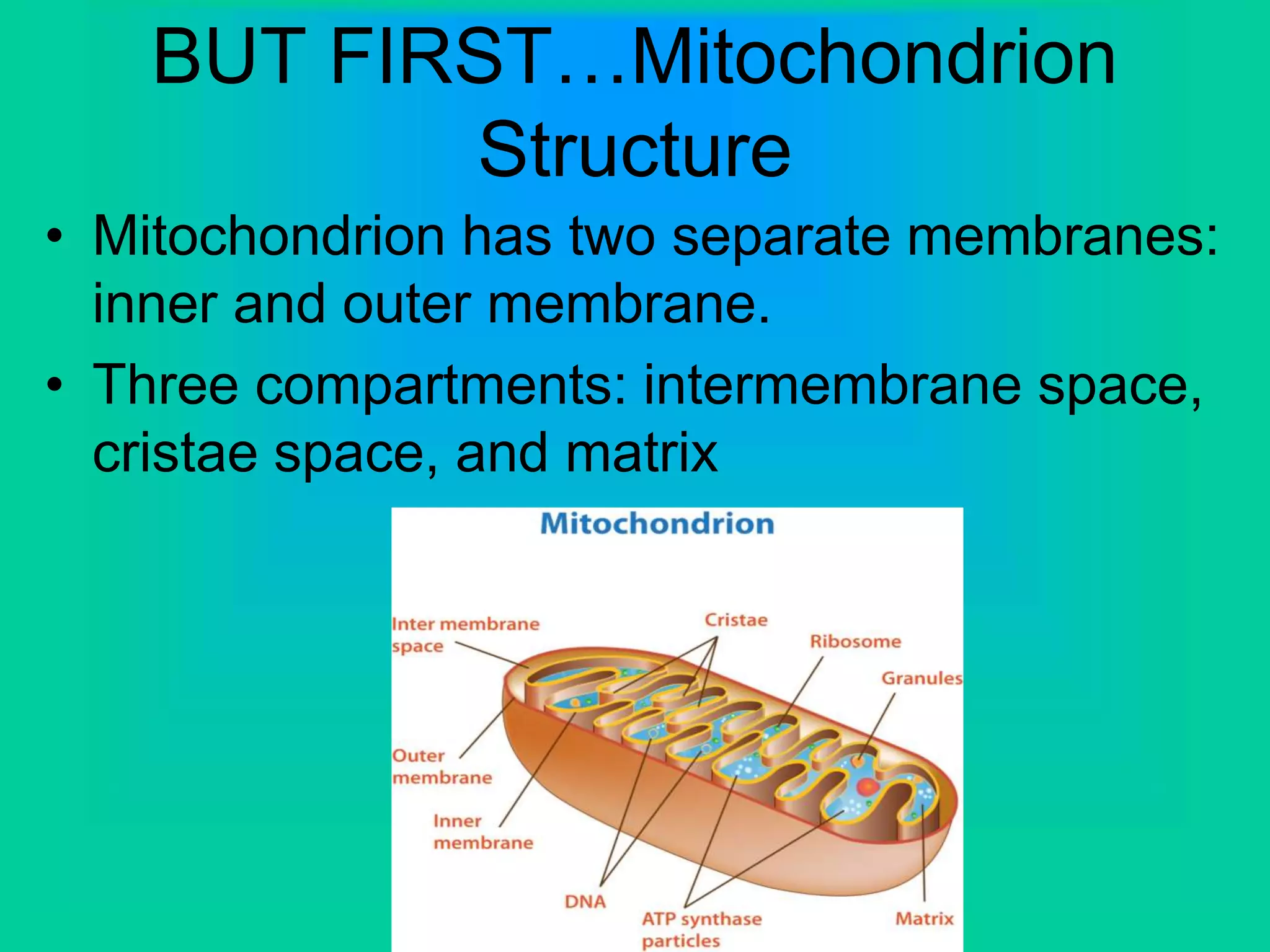
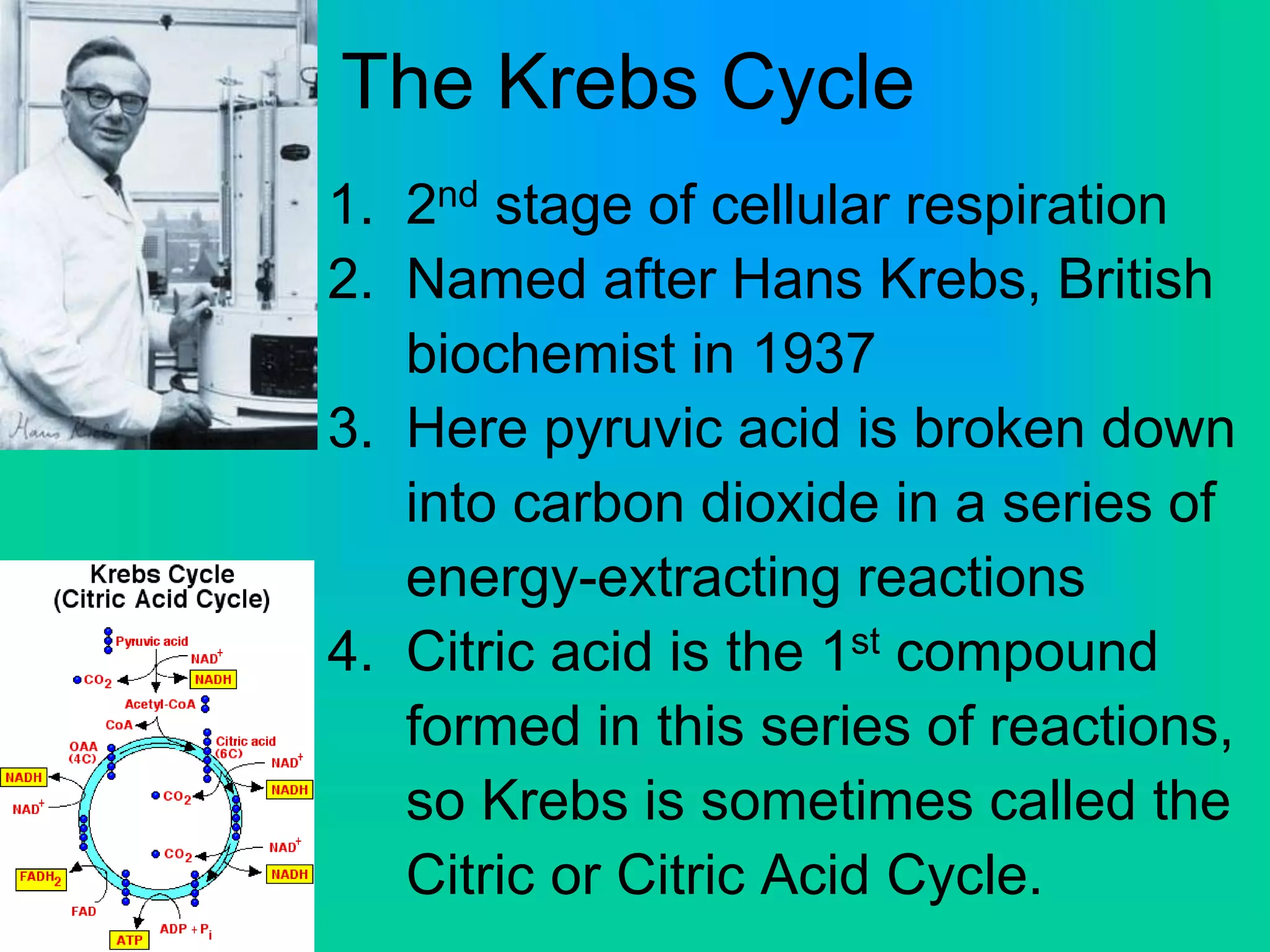
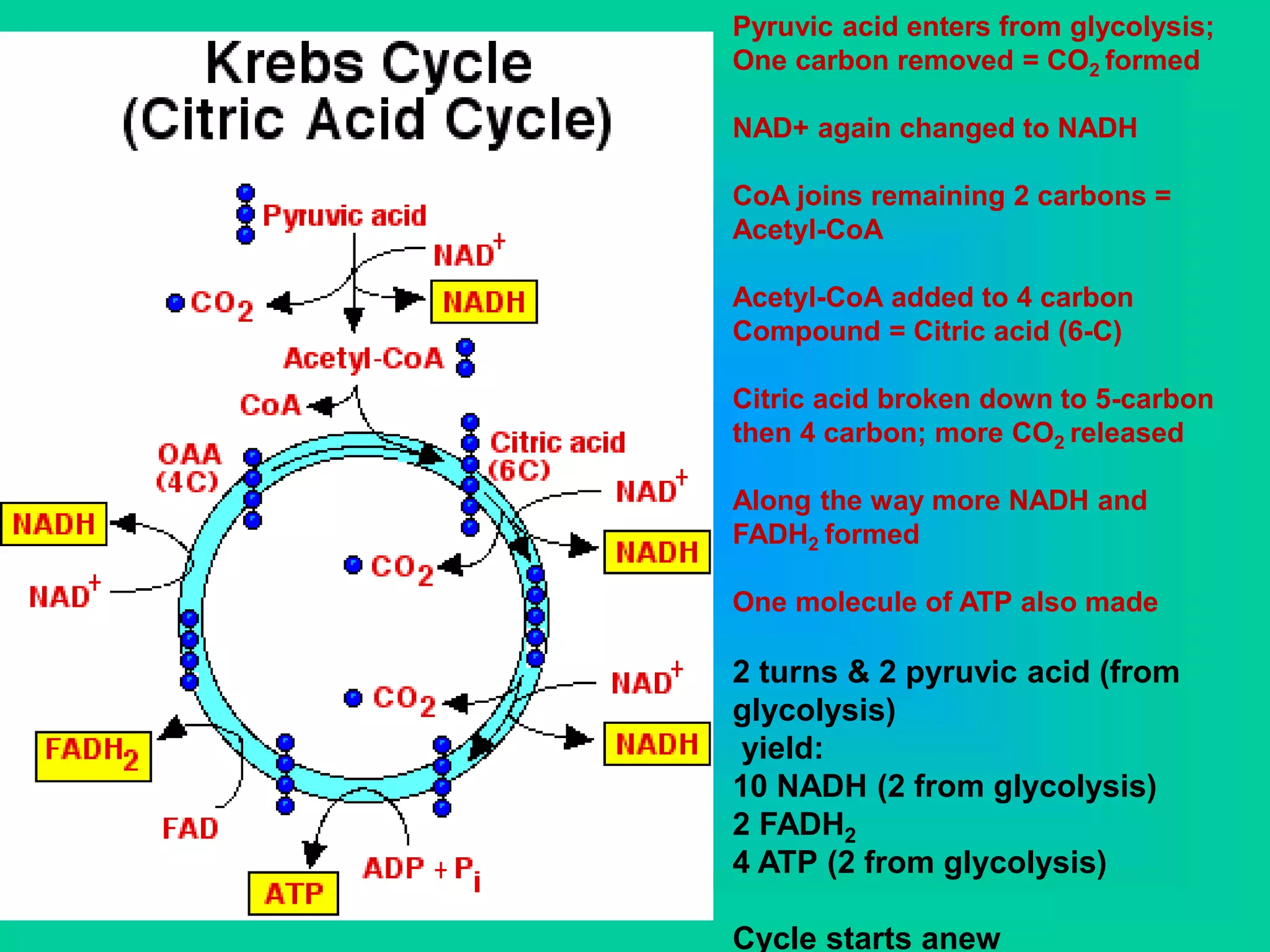
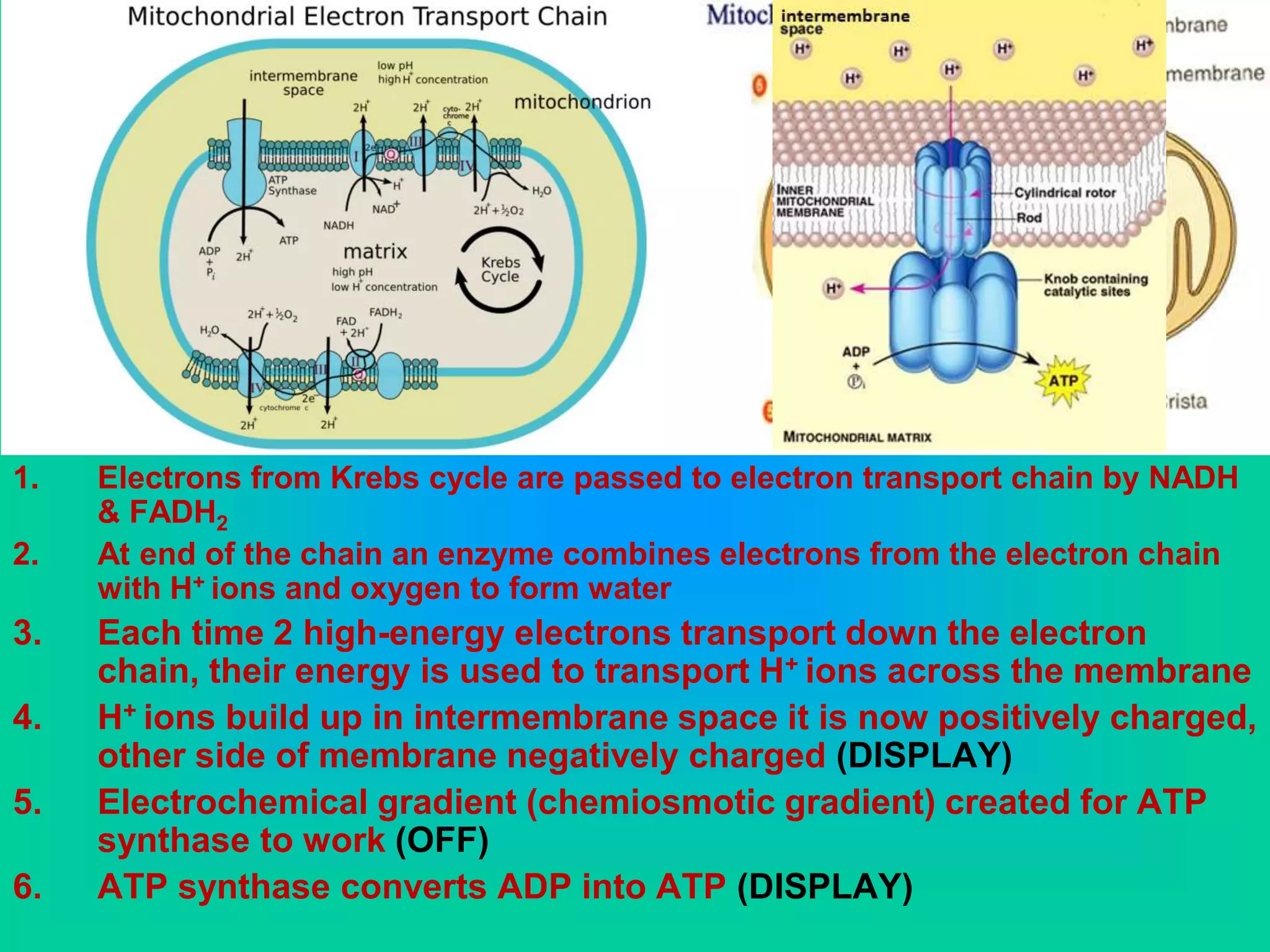
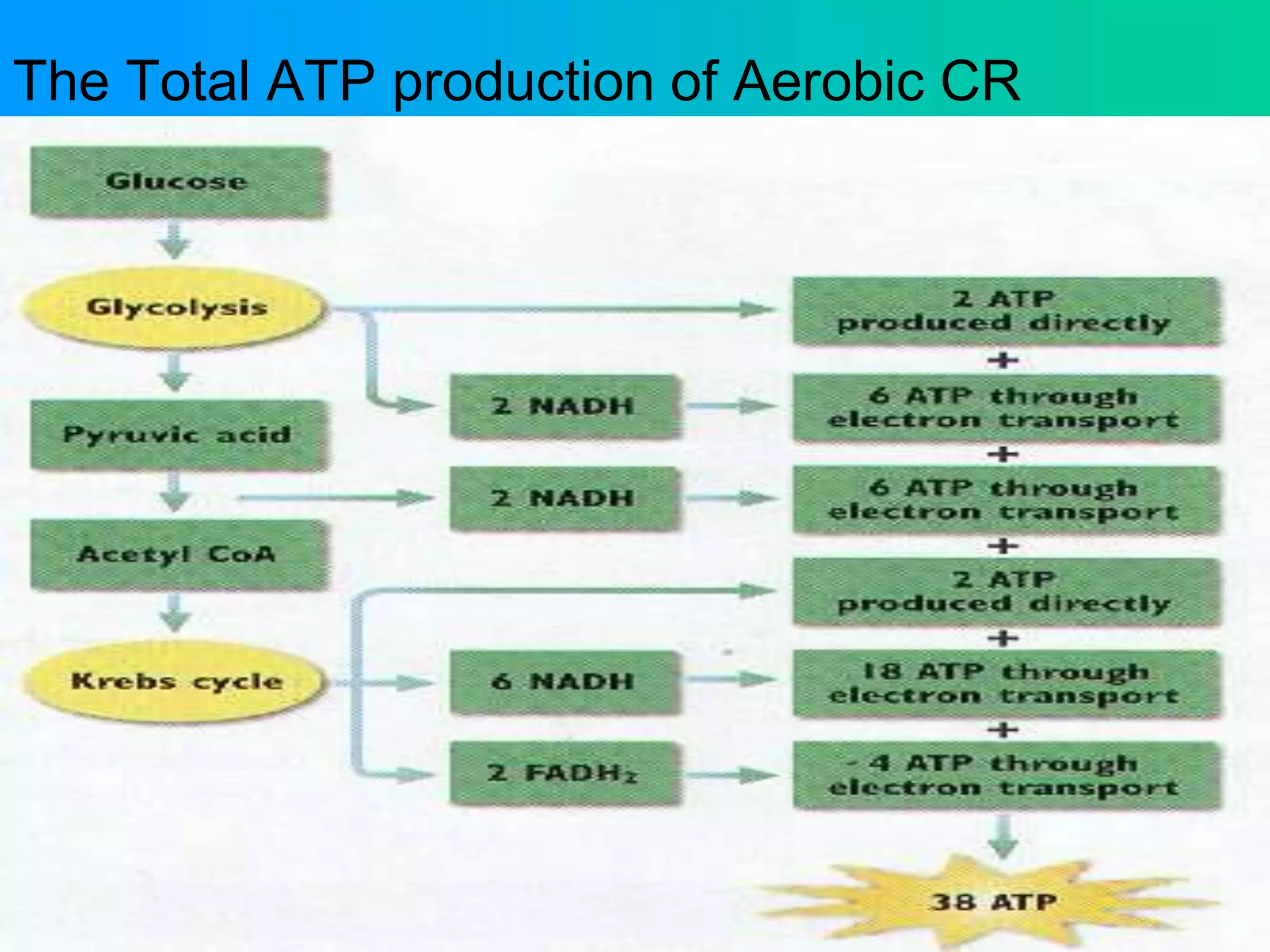
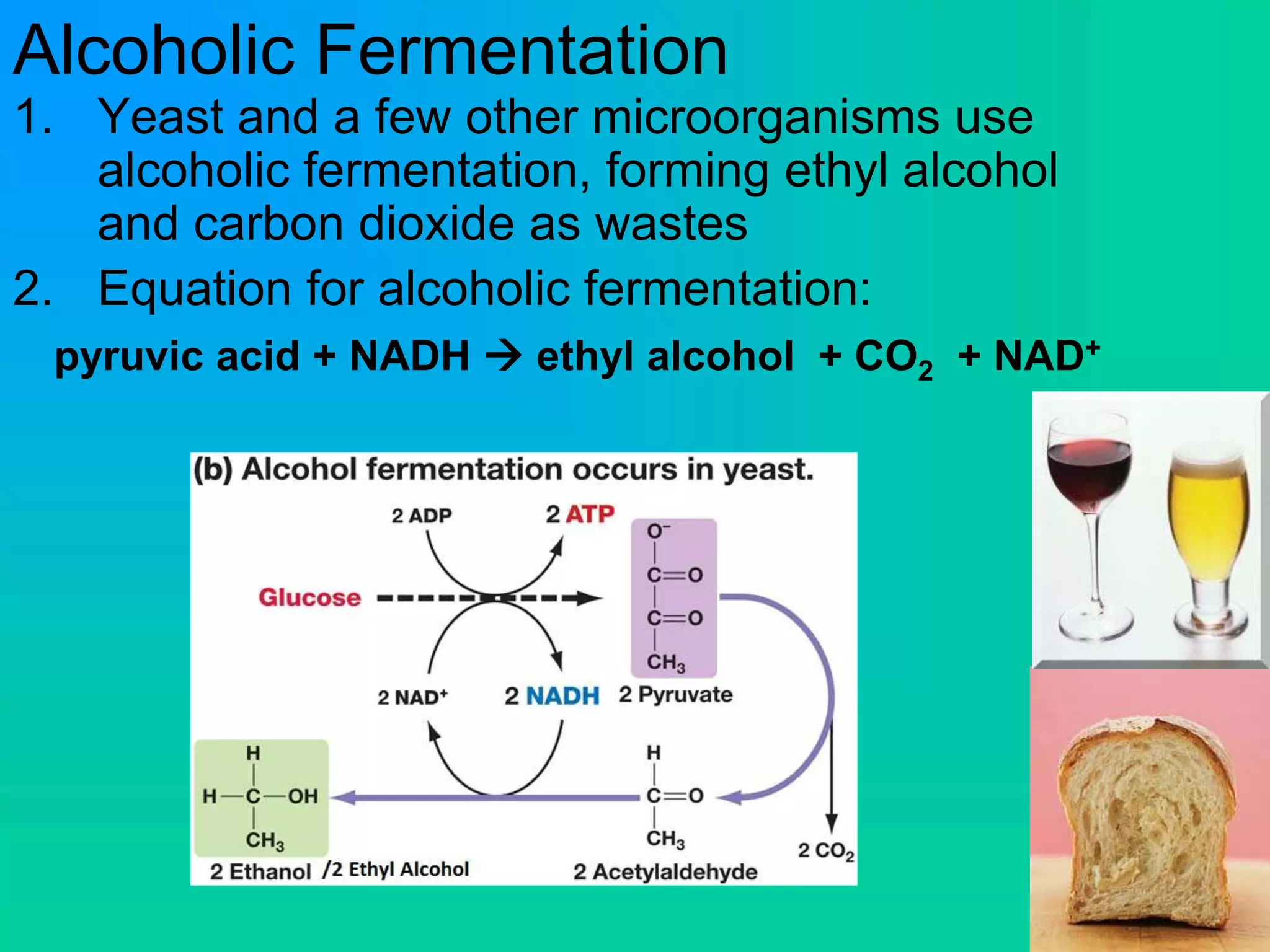
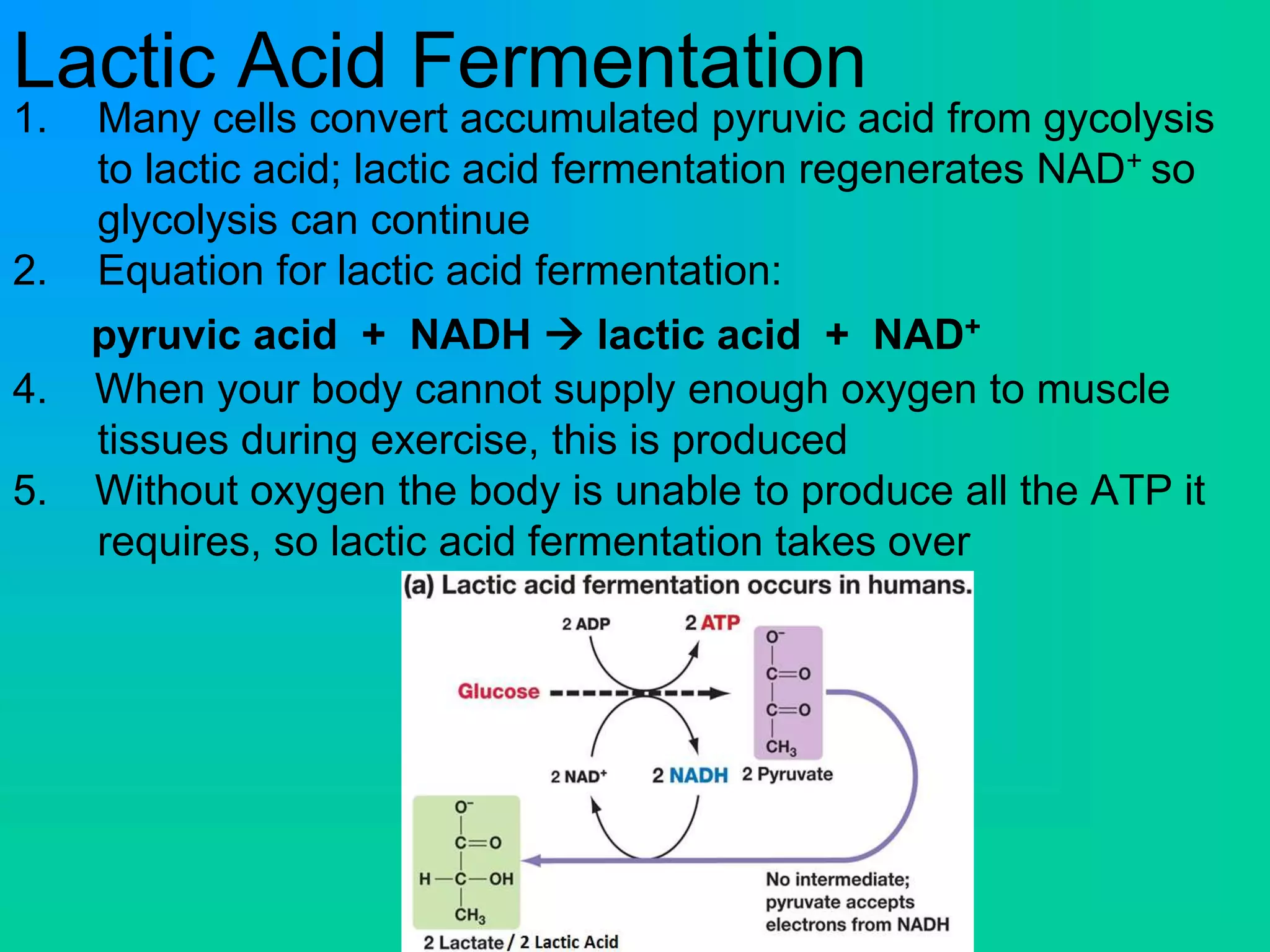
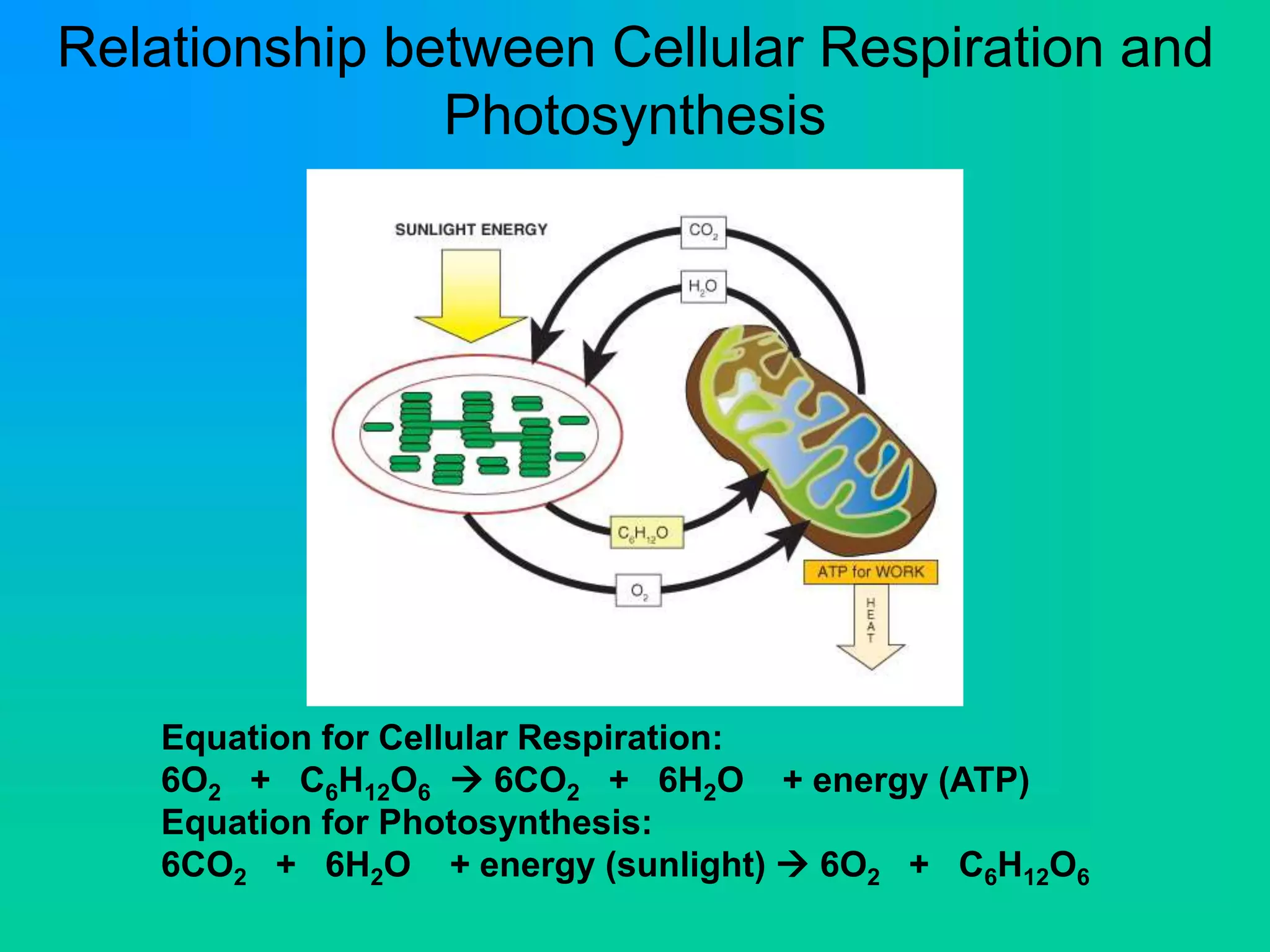
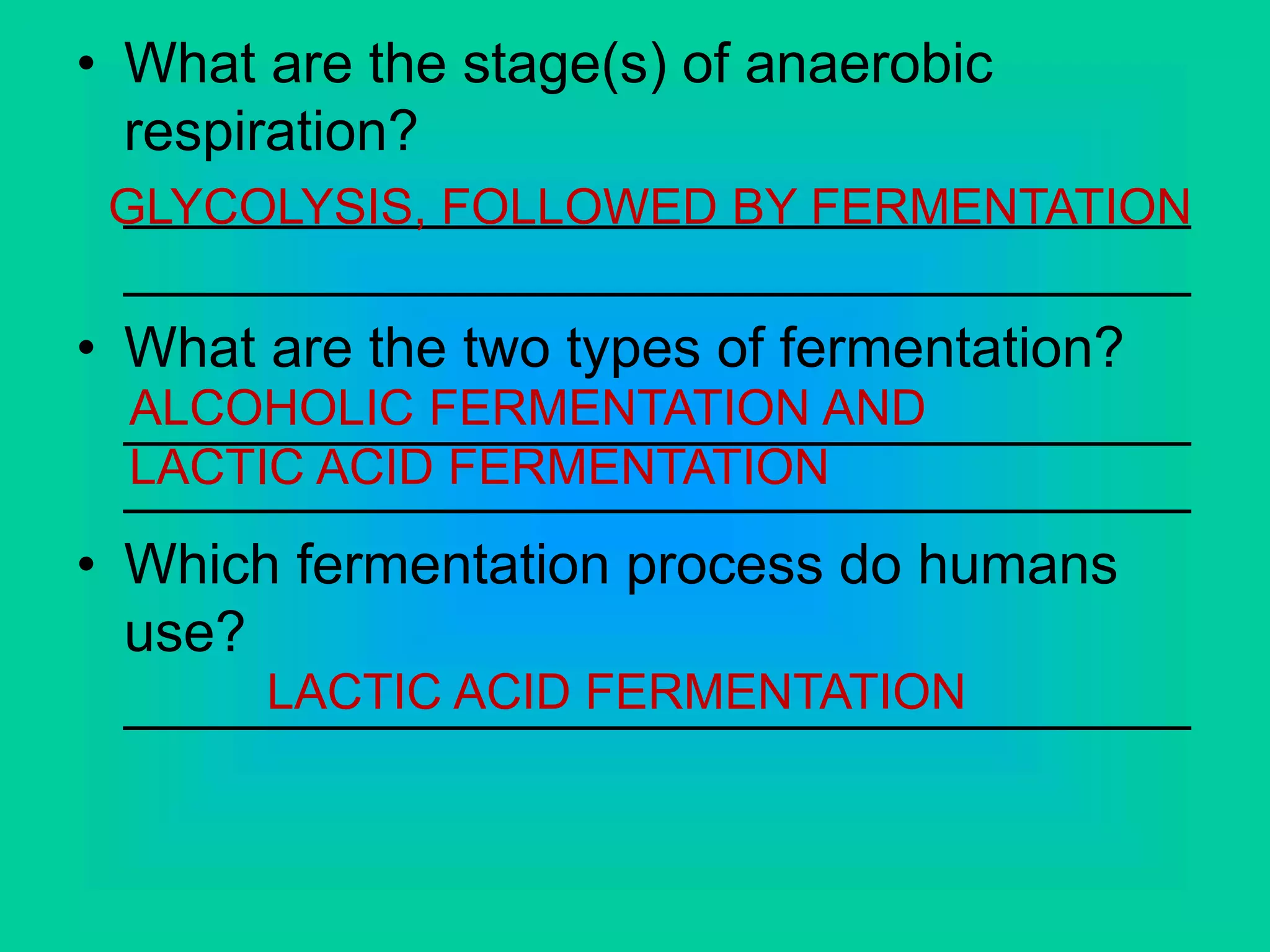
Cellular respiration has three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose for energy. In the presence of oxygen, the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain take place in the mitochondria to further extract energy from glucose through oxidative phosphorylation, producing up to 38 ATP molecules. Without oxygen, fermentation pathways like lactic acid fermentation take over after glycolysis to regenerate NAD+ and allow glycolysis to continue at a lower energy yield of 2 ATP.